91
Explanation
LvTcpΔuv
The following factors can be acquired as measurement value with L
v
T
cp
Δuv as color space of this
instrument.
L
v
: Luminance
T
cp
: Correlated color temperature
Δuv : Color difference from black body locus
In L
v
T
cp
Δuv, while L
v
stands for luminance, T
cp
and Δuv stand for color.
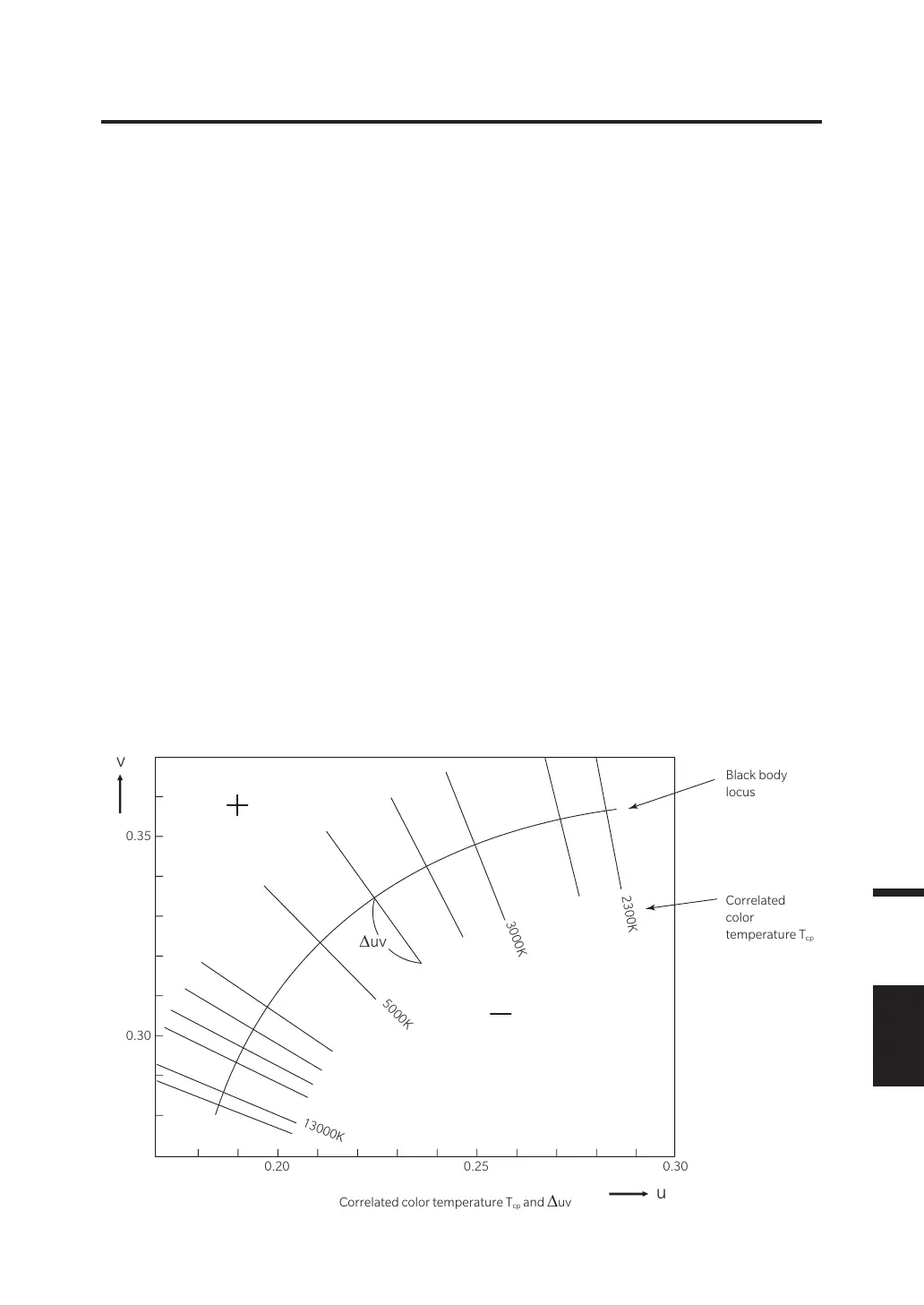
<Relation between correlated color temperature T
cp
and color difference from black body
locus Δuv>
Color temperature refers to the temperature of black body (perfect radiator) which has equal
chromaticity coordinates to certain light. However, color temperature only represents colors on black
body locus.
A slightly wider interpretation of color temperature, correlated color temperature covers those which
are slightly outside the range of that of black body locus.
If a certain color positions on the isotemperature line, the intersection point of isotemperature line and
black body locus is indicated as correlated color temperature for the color. Isotemperature line means a line
on chromaticity coordinates which is a set of colors visually close to color temperature on black body locus.
However, since all colors on a color-matching temperature line are represented with equal correlated color
temperature, it is not possible to describe color only with correlated color temperature. To solve this problem,
∆uv, deviation of correlated color temperature T from black body locus, is to apply for that purpose.
If ∆uv exists above the black body locus, it is represented by “+,” and by “-” when below.
v
u
Correlated
color
temperature T
cp
Correlated color temperature T
cp
and ∆uv
13000K
5000K
3000K
2300K
∆uv
0.35
0.30
0.20
0.25
0.30
Black body
locus

 Loading...
Loading...