3 Functions Issue 10/06
MICROMASTER 440 Operating Instructions
148 6SE6400-5AW00-0BP0
3.7.1.1 Protocol specification and bus structure
The USS protocol has the following significant features:
¾ Supports
♦ a multi-point-capable link, e.g. EIA RS 485 hardware or
♦ a point-to-point link, e.g. EIA RS 232
¾ Master-slave access technique
¾ Single-master system
¾ Maximum 32 nodes (max. 31 slaves)
¾ Operation with variable or fixed telegram length
¾ Simple, reliable telegram frames
¾ The same bus mode of operation as with the PROFIBUS (DIN 19245 Part 1)
¾ Data interface to the basic unit according to PROFILE variable-speed drives.
This means that, when the USS is being used, information is transferred to the
drive in the same way as with the PROFIBUS-DP.
¾ Can be used for start-up, service and automation
¾ PC-based service tools (e.g. STARTER and DriveMonitor)
¾ Can be easily implemented in customized systems
Protocol specification
The USS protocol defines an access technique according to the master-slave
principle for communications via a serial bus. The point-to-point link is included as
a sub-quantity.
One master and a maximum of 31 slaves can be connected to the bus. The
individual slaves are selected by the master using an address character in the
telegram. A slave can never transmit without first being initiated by the master so
that direct information transfer between individual slaves is not possible. The
master function cannot be transferred (single-master system). The following
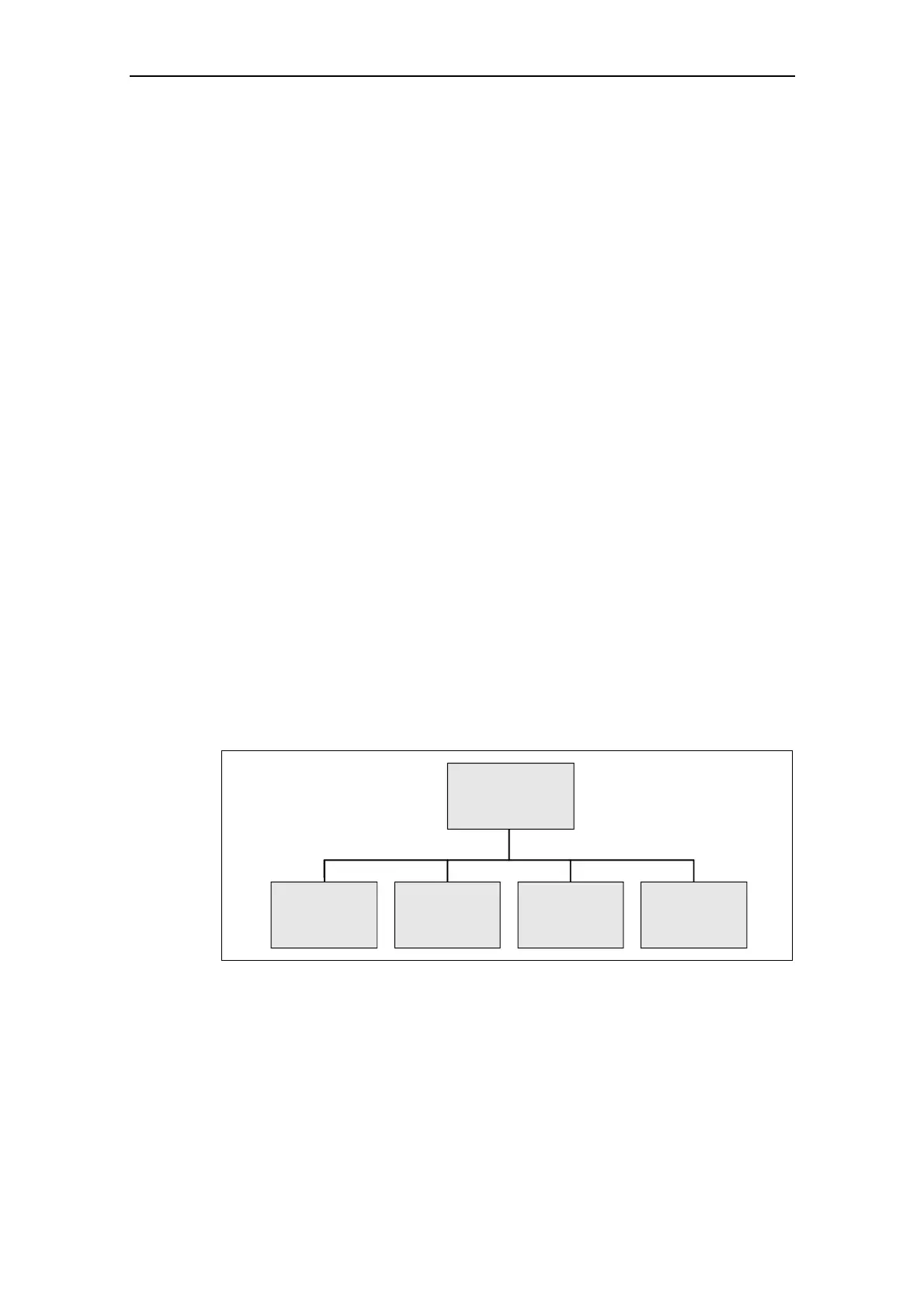
illustration shows a bus configuration using drive technology as an example.
MICROMASTER
Higher-level computer
"Master"
MICROMASTER MICROMASTER MICROMASTER
"Slave""Slave""Slave""Slave"
Fig. 3-38 Serial linking of MICROMASTER (slaves) with a higher-level computer
(master)

 Loading...
Loading...














