Issue 10/06 3 Functions
MICROMASTER 440 Operating Instructions
6SE6400-5AW00-0BP0
181
3.12 Setpoint channel
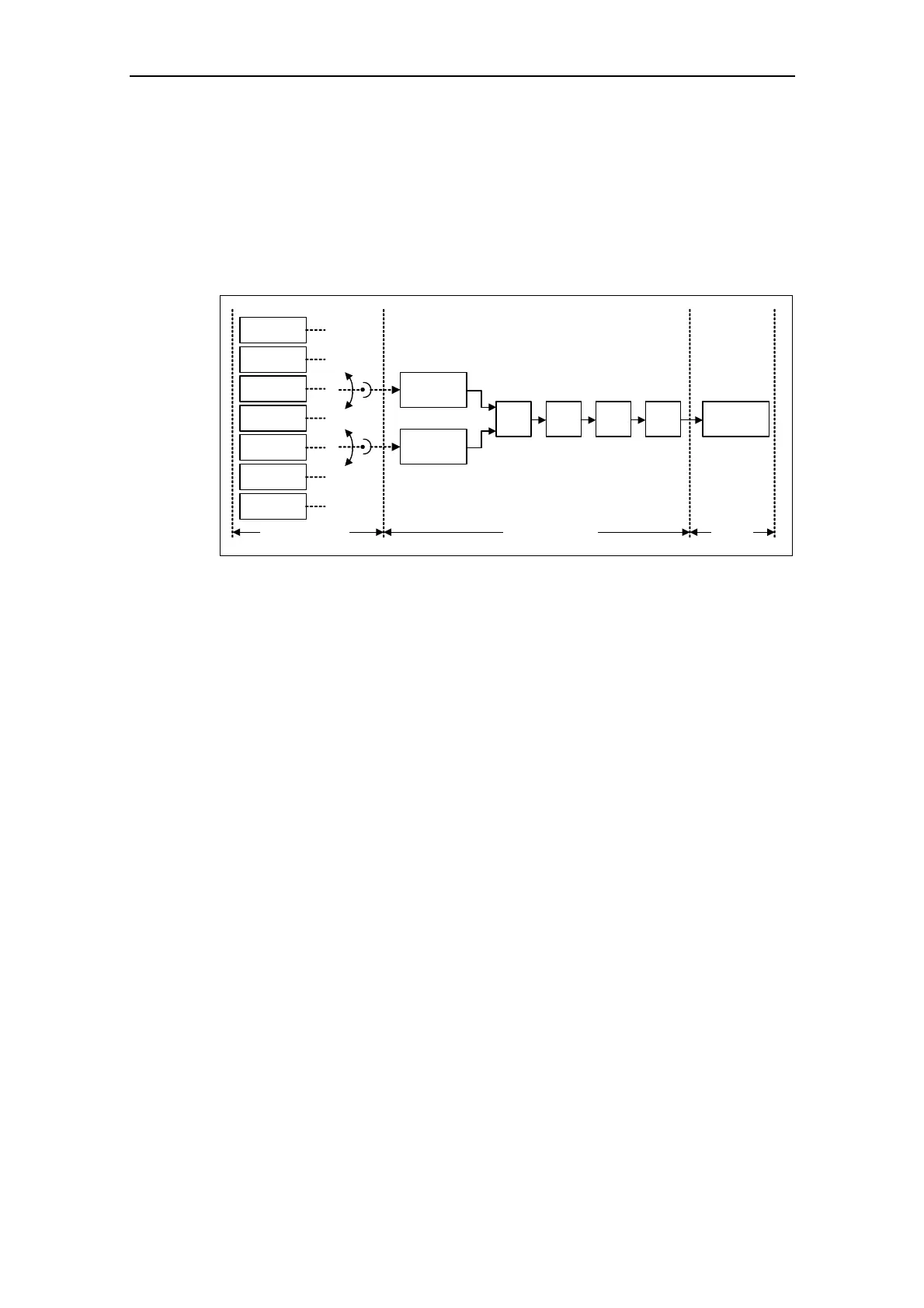
The setpoint channel (refer to Fig. 3-59) forms the coupling element between the
setpoint source and the closed-loop motor control. MICROMASTER has a special
characteristic which allows the setpoint to be entered simultaneously from two
setpoint sources. The generation and subsequent modification (influencing the
direction, suppression frequency, up/down ramp) of the complete setpoint is
carried-out in the setpoint channel.
MOP
ADC
FF
USS
BOP link
USS
COM link
CB
COM link
ADC2
Setpoint source
Main
setpoint
Additonal
setpoint
SUM AFM Limit RFG
Setpoint channel
Motor
control
Motor
control
Fig. 3-59 Setpoint channel
3.12.1 Summation and modification of the frequency setpoint (AFM)
Parameter range: P1070 – r1114
Warnings -
Fault -
Function chart number: FP5000, FP5200
For applications where the control quantities are generated from central control
systems, fine tuning is often required locally on-site (correction quantity). For
MICROMASTER, this can be very elegantly realized using the summation point
where the main and supplementary (additional) setpoint are added in the setpoint
channel. In this case, both quantities are simultaneously read-in via two separate
or one setpoint source and summed in the setpoint channel. Depending on
external circumstances, the supplementary setpoint can be dynamically
disconnected or switched-in to the summation point (refer to Fig. 3-60). This
functionality can be used to advantage, especially for discontinuous processes.

 Loading...
Loading...














