Rockwell Automation Publication MOTION-UM003K-EN-P - January 2019 239
Commission an Axis Chapter 11
Load
The Load dialog box contains the characteristics of the motor load. You can
also use the values that are provided by autotune. The Autotune automatically
sets most of these values:
• If you use the Catalog Number as the Data Source, the Motor Inertia,
Total Inertia, and System Inertia are pre-populated with the correct
values.
• If you know what the Load Ratio values are, you can enter that
information on the Load dialog box or you can use the values that are
provided by Autotune.
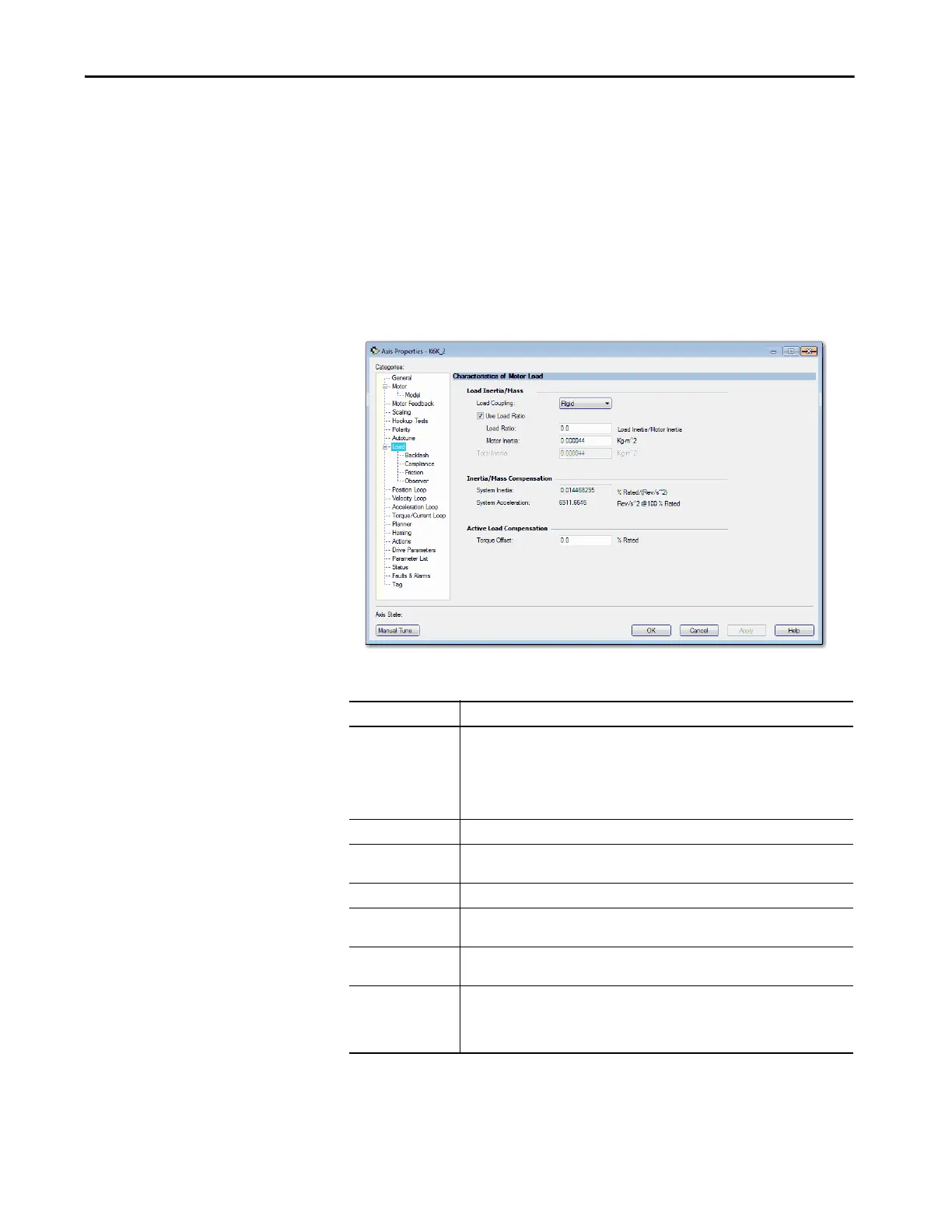
Figure 103 - Kinetix 6500 Load Dialog Box
Table 48 - Load Inertia/Mass Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
Load Coupling Lets you control how tightly the system is physically coupled. Your choices are the
following:
• Rigid (default)
•Compliant
Load Coupling appears dimmed when the axis is Servo On.
Inertia Compensation Inertia compensation controls relate to rotary motors.
Load Ratio The value of the Load Ratio attribute represents the ratio of the load inertia or mass to the
motor inertia, or mass.
Motor Inertia The Motor Inertia attribute is a float that specifies the unloaded inertia of a rotary motor.
Total Inertia Total Inertia represents the combined inertia of the rotary motor and load in engineering
units.
Inertia/Mass
Compensation
Inertia compensation controls relate to rotary motors. Mass compensation controls relate
to linear motors.
System Acceleration System Inertia is recalculated anytime the System Acceleration changes:
• System Inertia = 0, if System Acceleration = 0
• System Inertia = 1/System Acceleration
• Units are Rev/s^2 @100% Rated

 Loading...
Loading...