Safety and operating instructions
© Anbaufräsen PC GmbH | 3390 5221 01 | 2020-09-07
Original Instructions
37
5.6.7 Selecting the correct drilling auger
The selection of the appropriate drilling auger depends on various factors. Prior to attaching the drilling auger, contact
the authorized Customer Center / Dealer in your area in order to guarantee optimum working efficiency. The authorized
Customer Center / Dealer will advise on the use of suitable tools and the requisite drilling capacity.
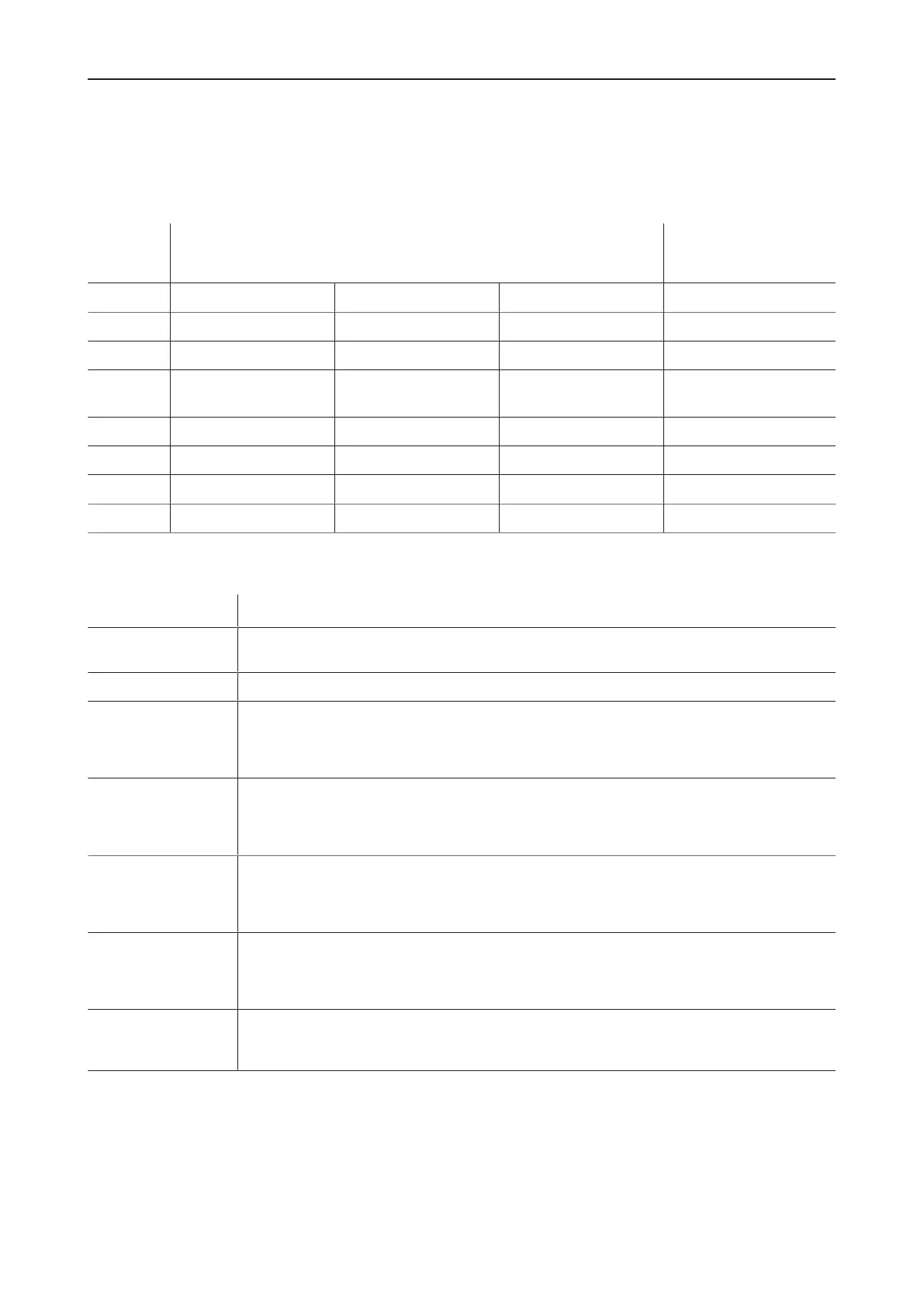
Type Maximum recommended drilling diameter
Soil classification
Maximum recom-
mended drilling depth
1 - 3* 4 - 5* 6 - 7*
ADU 100 400 mm (15.75 in.) 300 mm (11.81 in.) - 3500 mm (137.80 in.)
ADU 250 500 mm (19.69 in.) 400 mm (15.75 in.) 300 mm (11.81 in.) 5000 mm (196.85 in.)
ADU 450
ADU 600
900 mm (35.43 in.) 700 mm (27.56 in.) 500 mm (19.69 in.) 6000 mm (236.22 in.)
ERL 700 1000 mm (39.37 in.) 900 mm (35.43 in.) 600 mm (23.62 in.) 6000 mm (236.22 in.)
ERL 1100 1500 mm (59.10 in.) 1200 mm (47.24 in.) 900 mm (35.43 in.) 7000 mm (375.59 in.)
ADU 1500 1500 mm (59.10 in.) 1200 mm (47.24 in.) 900 mm (35.43 in.) 7000 mm (375.59 in.)
ADU 2000 1600 mm (62.99 in.) 1500 mm (59.10 in.) 1100 mm (43.31 in.) 8000 mm (314.96 in.)
5.6.8 Specification of soil classes for earth & rock drilling
Class (DIN18300) This class comprises
Class1: Topsoil Top layer of soil containing humus & soil organisms, as well as inorganic material such as
gravel, sand, silt and clay mixtures
Class2: Liquid soil Fluid or pasty soil that tends to retain water
Class3: Soil easy to
excavate
Noncohesive or slightly cohesive sand, gravel and grit, with up to 15% of silt & clay (with a par-
ticle size smaller than 0.06mm (0.002in.)) containing at most 30% of boulders larger than
63mm (2.5in.) each having a maximum volume of 0.01m³* (0.0006in³*); organic soil with lit-
tle water (e.g. strong peat)
Class4: Soil medium
hard to excavate
Mixtures of sand, gravel, silt & clay with more than 15% of their particles smaller than 0.06mm
(0.002in.); cohesive soil with low or medium plasticity, soft to semi-firm according to its water
content , and containing at most 30% of boulders larger than 63mm (2.5in.) each having a
maximum volume of 0.01m³* (0.0006in³*)
Class5: Soil hard to
excavate
Soil of classes 3 & 4, but with more than 30% of boulders larger than 63mm (2.5in.) each
having a maximum volume of 0.01m³* (0.0006in³*); noncohesive or cohesive soil with at most
30% of boulders each having a volume from 0.01to 0.1m³* (0.0006to 0.06in³*); distinctly
plastic clay, from soft to semi-firm, according to its water content
Class6: Rock easy
to excavate & similar
soil
Cemented rock with a mineral matrix but highly fissured, friable, crumbly, soft or weathered, as
well as comparable firm, cohesive or noncehesive soil which may have been strengthened by
drying out, freezing or chemical treatment; noncohesive and cohesive soils with more than
30% of boulders each having a volume from 0.01to 0.1m³* (0.0006to 0.06in³*)
Class7: Rock hard to
excavate
Rock with a strong mineral matrix which is slightly fissured or weathered; strongly bedded, un-
weathered shale, pudding stone, slag heaps from smelting plants, etc.; boulders each having a
volume of more than 0.1m³* (0.006in³*)
*0.01m³ (0.0006in³*) corresponds to a sphere with a diameter of about 0.3m (11.8in.) and 0.1m³ (0.06in³*) corre-
sponds to a sphere with a diameter of about 0.6m (23.6in.)
 Loading...
Loading...