92
FTP server configuration example
Network requirements
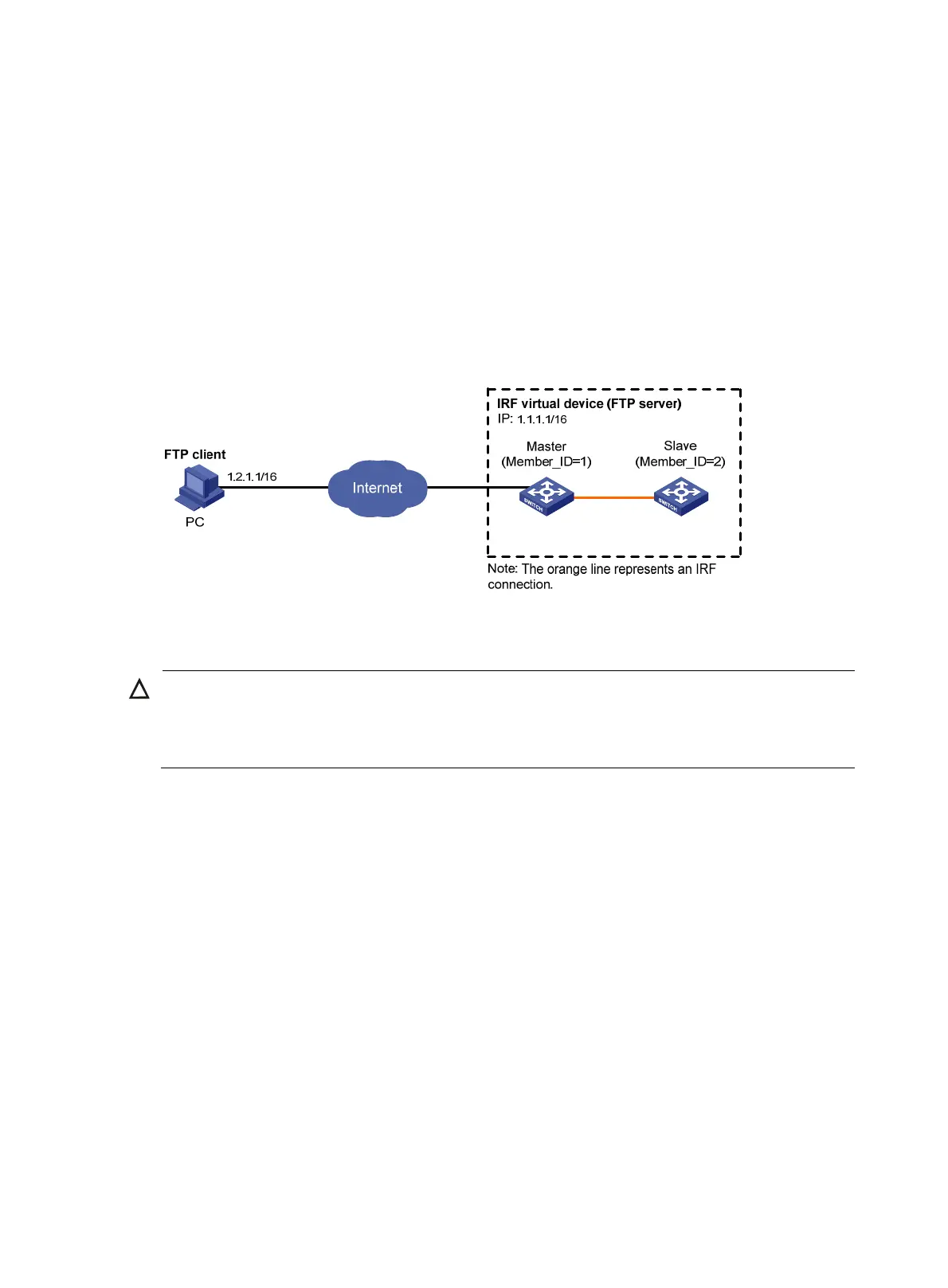
• As shown in Figure 28, an IRF virtual device comprises a master and a slave FTP server. The member
ID of the master is 1 and that of the slave switch is 2.
• The IRF virtual device serves as an FTP server, and the PC serves as an FTP client. The IRF virtual
device and the PC are reachable to each other.
• The PC keeps the updated boot file of the IRF virtual device. Use FTP to upgrade the IRF virtual
device and back up the configuration file.
• Set the username to ftp and the password to pwd for the FTP client to log in to the FTP server.
Figure 28 Upgrading using the FTP server
Configuration procedure
CAUTION:
If the available memory space of the master and slave switches is insufficient, use the fixdisk command to
clear the memory or use the delete /unreserved
file
-
url
command to delete the files not in use and then
perform the following operations.
1. Configure the IRF virtual device (FTP Server)
# Create an FTP user account ftp, set its password to pwd and the user privilege level to level 3 (the
manage level). Allow user ftp to access the root directory of the flash on the master, and specify ftp to use
FTP.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] local-user ftp
[Sysname-luser-ftp] password simple pwd
[Sysname-luser-ftp] authorization-attribute level 3
[Sysname-luser-ftp] authorization-attribute work-directory flash:/
# To access the root directory of the storage medium of a slave switch (with the member ID 2), replace
flash:/ with slot2#flash:/ in authorization-attribute work-directory flash:/.
[Sysname-luser-ftp] service-type ftp
[Sysname-luser-ftp] quit
# Enable FTP server.
[Sysname] ftp server enable
[Sysname] quit
2. Configure the PC (FTP Client)
 Loading...
Loading...











