76
4-2-6
4-2-6
4-2-6
4-2-6
.
.
.
.
Protective
Protective
Protective
Protective function
function
function
function parameters
parameters
parameters
parameters ( Group
Group
Group
Group P5
P5
P5
P5 )
This parameter defines the protection mode when overload or overheat occurs.
0
0
0
0 :
Inverter
Inverter
Inverter
Inverter
locking
locking
locking
locking output
output
output
output
.
When
overload or
overheat occur s
,
inverter will
lock output
and
the
motor
will
coast-to-stop.
1
1
1
1 : Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
.
.
.
.
M
otor will
be without
overload
protection
and
inverter
will
do
the overload
protection
for the motor.(Cautions
to
using)
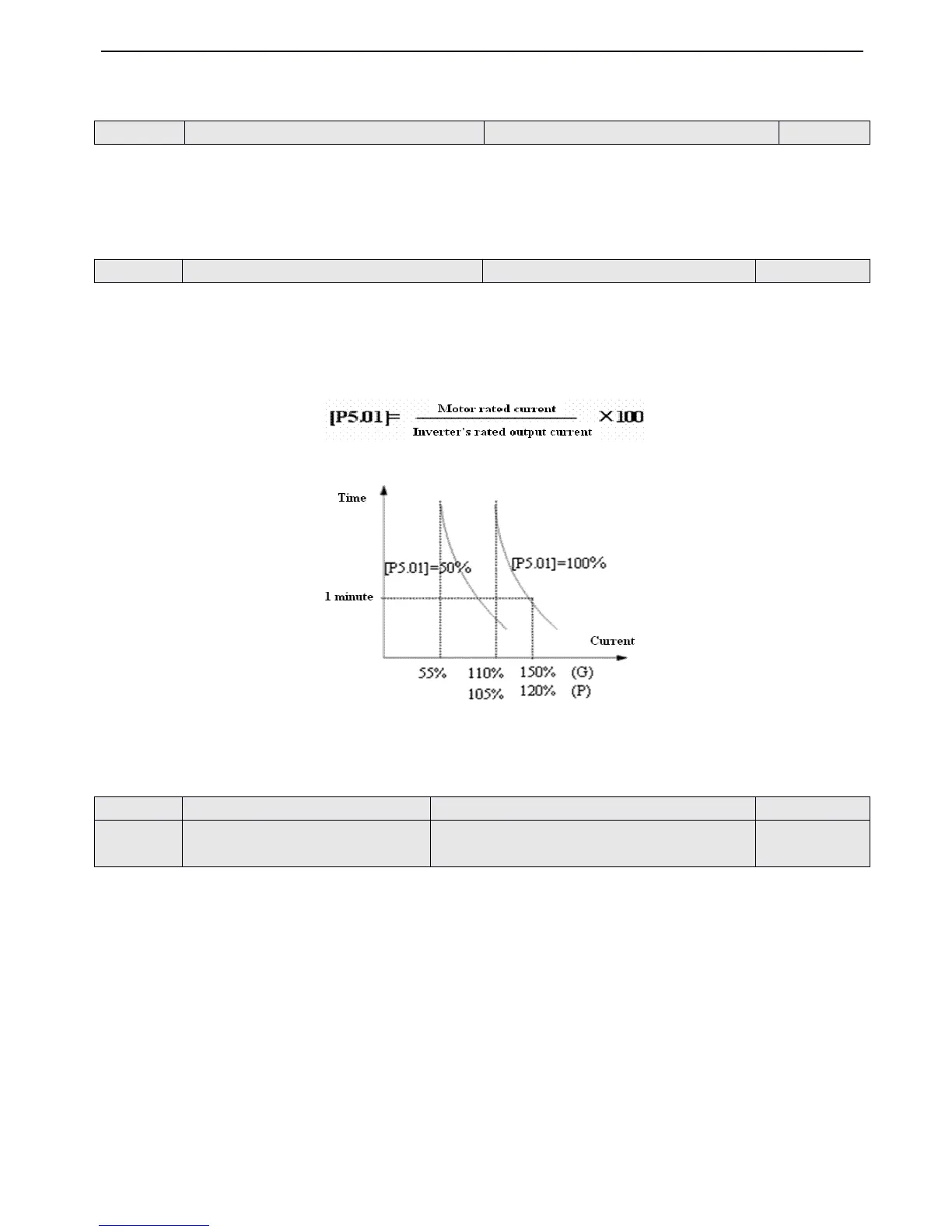
This parmeter is used to set sensitivity of thermal rel
ay
protection from inverter to overload. When the output current value
of load motor can not match the rated current of the inverter, correct thermal protection can be realized
by
setting this
parameter, as shown in Fig.4-30 .
Use the following coefficient to ca l culate .
Fig.
Fig.
Fig.
Fig. 4-30
4-30
4-30
4-30 Thermal
Thermal
Thermal
Thermal relay
relay
relay
relay protection
protection
protection
protection
Note
Note
Note
Note
: When one inverter run with multi-motors, inverter
’
s
thermal
relay
protection
will
be
disabled. Therefore,
please
install
thermal
relay
in
the wire
end
of each motor
to
protect
motor more e
fficient
ly .
0
0
0
0 : Prohitit
Prohitit
Prohitit
Prohitit
1
1
1
1 : Permit
Permit
Permit
Permit
During deceleration, the motor
’
s decelerate rate may be lower than that of inverter
’
s output frequency due to the load inertia.
At this time, the motor will feed back the energ
y
to the drive, resulting in the voltage rise on the inverter 's DC bus. If no
measures taken, the inverter will trip due to over voltage.
During the deceleration, the inverter detects the bus voltage and compares it with the over voltage point at stall defined
by
P5.03
.
If the bus voltage exceeds the stall overvoltage point, the inverter will stop reducing its output frequency. When the
bus voltage become s lower than the point, the deceleration continues, as shown in Fig.4-31.
 Loading...
Loading...