105HEIDENHAIN TNC 426 B, TNC 430
The only effect of CC is to define a position as circle
center: The tool does not move to this position.
The circle center is also the pole for polar coordinates.
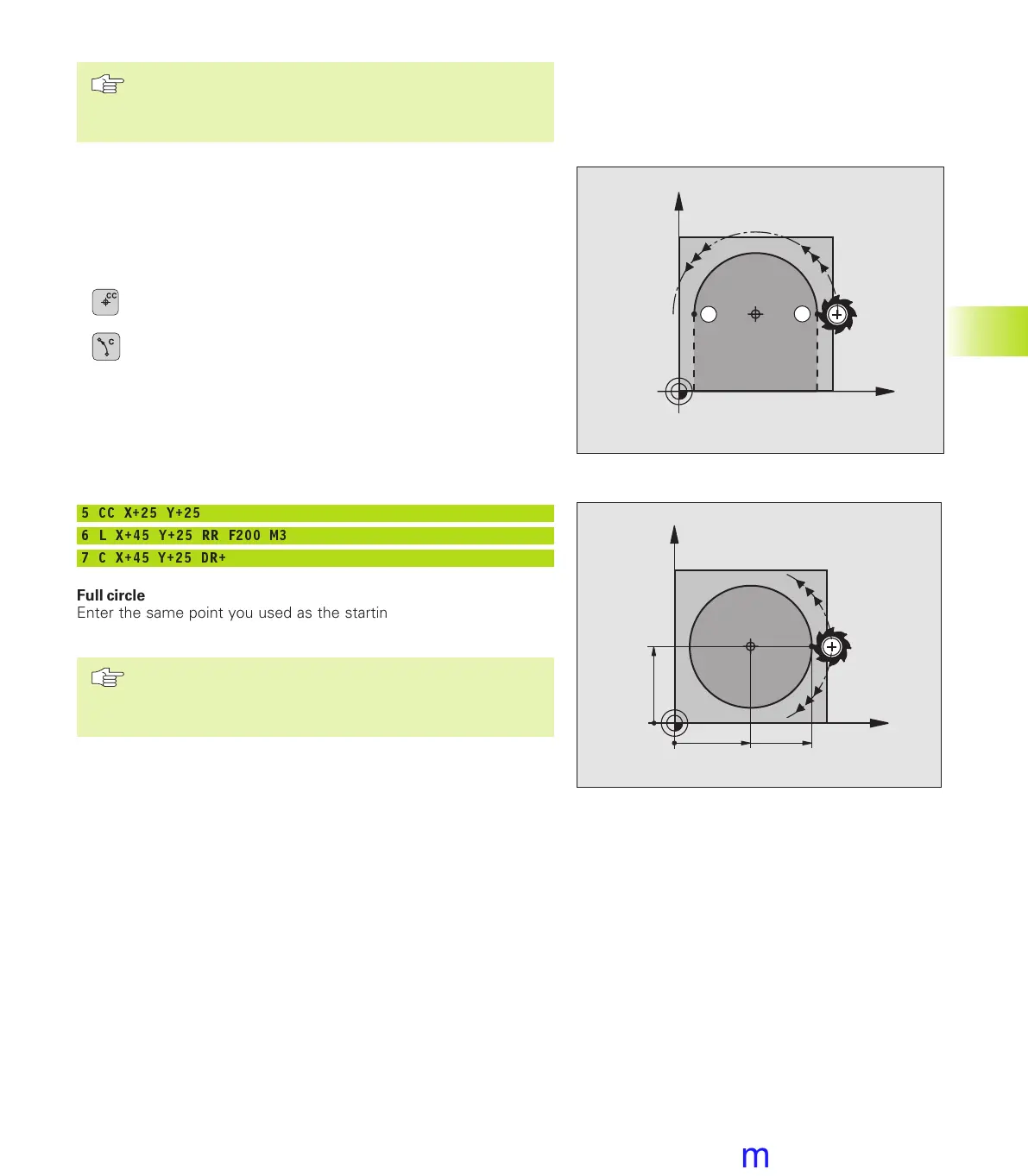
Circular path C around circle center CC
Before programming a circular path C, you must first enter the
circle center CC. The last programmed tool position before the C
block is used as the circle starting point.
ú
Move the tool to the circle starting point.
ú
Enter the coordinates of the circle center.
ú
Enter the coordinates of the arc end point
ú
Direction of rotation DR
Further entries, if necessary:
ú
Feed rate F
ú
Miscellaneous function M
Example NC blocks
5 CC X+25 Y+25
6 L X+45 Y+25 RR F200 M3
7 C X+45 Y+25 DR+
Full circle
Enter the same point you used as the starting point for the end
point in a C block.
The starting and end points of the arc must lie on the
circle.
Input tolerance: up to 0.016 mm (selected with MP7431).
X
Y
25
45
25
CC
DR+
DR–
S
E
X
Y
CC
6.4 Path Contours — Cartesian Coordinates
Gkap6.pm6 30.06.2006, 07:04105
www.EngineeringBooksPdf.com

 Loading...
Loading...