104
6 Programming: Programming Contours
CC
Z
Y
X
X
CC
Y
CC
Example NC blocks
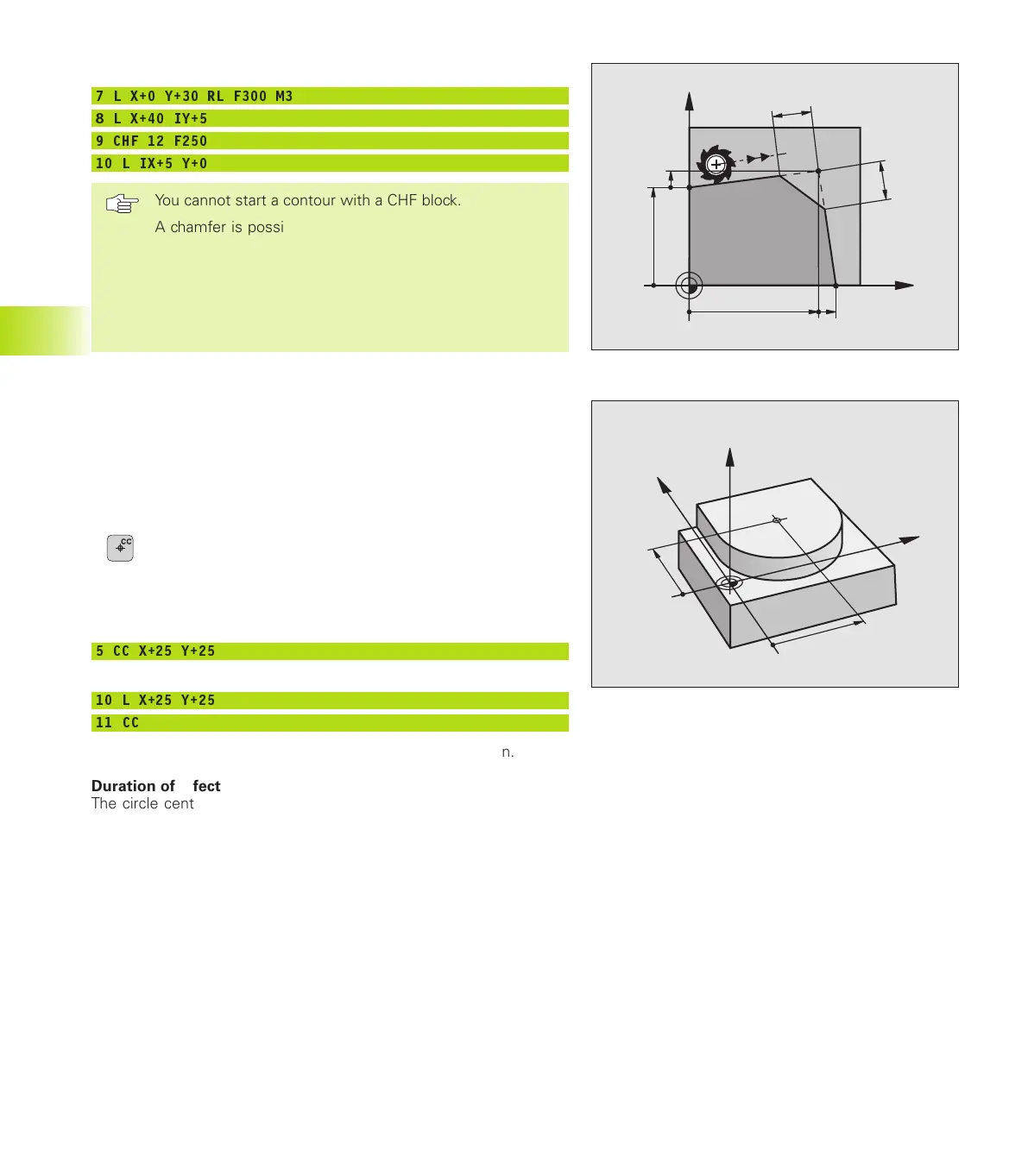
7 L X+0 Y+30 RL F300 M3
8 L X+40 IY+5
9 CHF 12 F250
10 L IX+5 Y+0
You cannot start a contour with a CHF block.
A chamfer is possible only in the working plane.
A feed rate programmed in the CHF block is effective
only in that block. After the CHF block, the previous feed
rate becomes effective again.
The corner point is cut off by the chamfer and is not part
of the contour.
Circle center CC
You can define a circle center CC for circles that are programmed
with the C key (circular path C). This is done in the following ways:
■
Entering the Cartesian coordinates of the circle center
■
Using the circle center defined in an earlier block
■
Capturing the coordinates with the actual-position-capture key
ú
Coordinates CC: Enter the circle center coordinates
If you want to use the last programmed position, do
not enter any coordinates.
Example NC blocks
5 CC X+25 Y+25
or
10 L X+25 Y+25
11 CC
The program blocks 10 and 11 do not refer to the illustration.
Duration of effect
The circle center definition remains in effect until a new circle
center is programmed. You can also define a circle center for the
secondary axes U, V and W.
Entering the circle center CC incrementally
If you enter the circle center with incremental coordinates, you
have programmed it relative to the last programmed position of the
tool.
X
Y
40
12
30
5
12
5
6.4 Path Contours — Cartesian Coordinates
Gkap6.pm6 30.06.2006, 07:04104
www.EngineeringBooksPdf.com

 Loading...
Loading...











