Page 10-23
matrix does not survive decomposition, i.e., it is no longer available in the
stack.
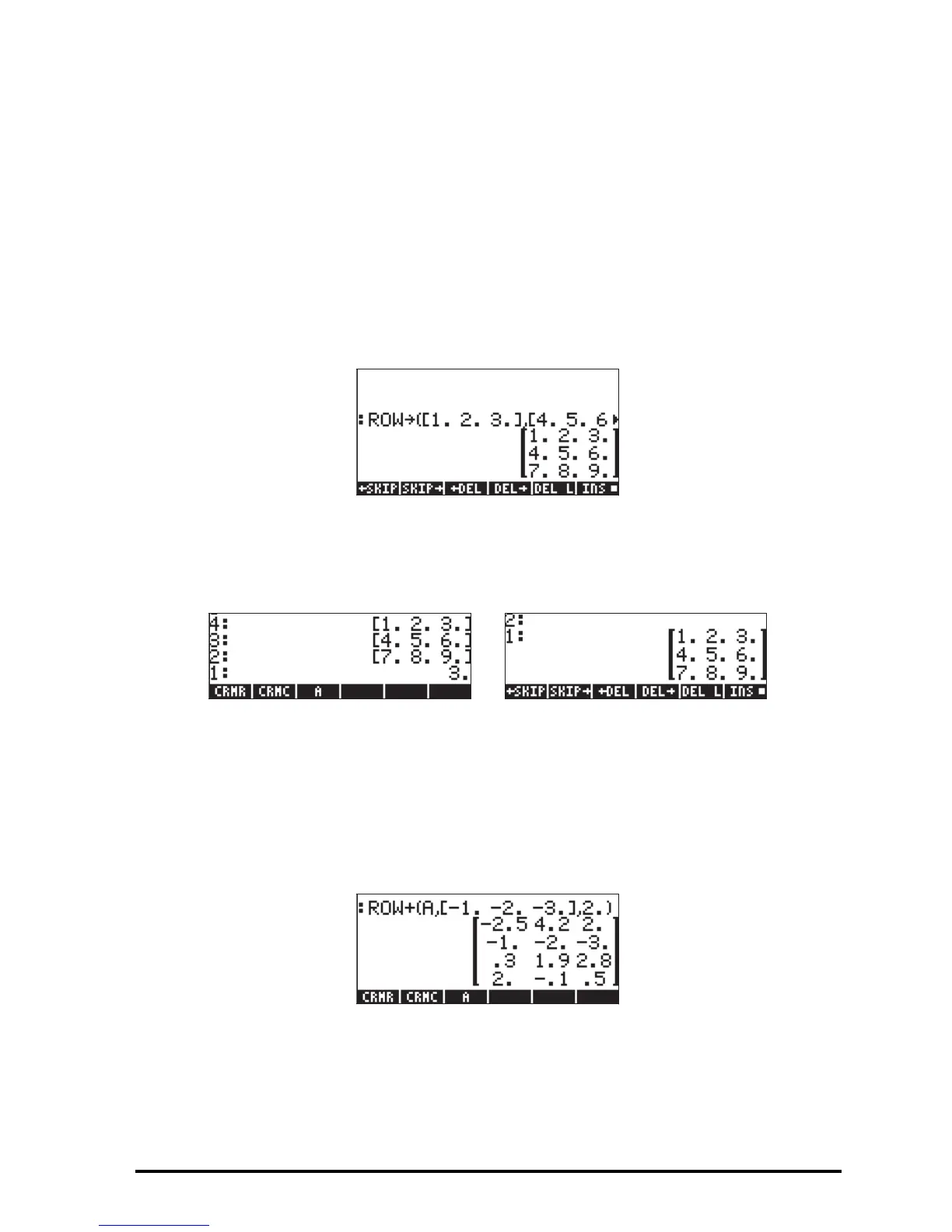
Function ROW→
Function ROW→ has the opposite effect of the function →ROW, i.e., given n
vectors of the same length, and the number n, function ROW builds a matrix
by placing the input vectors as rows of the resulting matrix. Here is an example
in ALG mode. The command used was:
ROW([1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9],3)
In RPN mode, place the n vectors in stack levels n+1, n, n-1,…,2, and the
number n in stack level 1. With this set up, function ROW places the vectors
as rows in the resulting matrix. The following figure shows the RPN stack before
and after using function ROW.
Function ROW+
Function ROW+ takes as argument a matrix, a vector with the same length as
the number of rows in the matrix, and an integer number n representing the
location of a row. Function ROW+ inserts the vector in row n of the matrix. For
example, in ALG mode, we’ll insert the second row in matrix A with the vector [-
1,-2,-3], i.e.,
In RPN mode, enter the matrix first, then the vector, and the row number, before
applying function ROW+. The figure below shows the RPN stack before and
after applying function ROW+.

 Loading...
Loading...




