Page 16-40
The simplification of the right-hand side of c(n), above, is easier done on paper
(i.e., by hand). Then, retype the expression for c(n) as shown in the figure to the
left above, to define function c(n). The Fourier series is calculated with
F(X,k,c0), as in examples 1 and 2 above, with c0 = 0.5. For example, for k =
5, i.e., with 11 components, the approximation is shown below:
A better approximation is obtained by using k = 10, i.e.,
For k = 20, the fitting is even better, but it takes longer to produce the graph:
Fourier series applications in differential equations
Suppose we want to use the periodic square wave defined in the previous
example as the excitation of an undamped spring-mass system whose
homogeneous equation is: d
2
y/dX
2
+ 0.25y = 0.
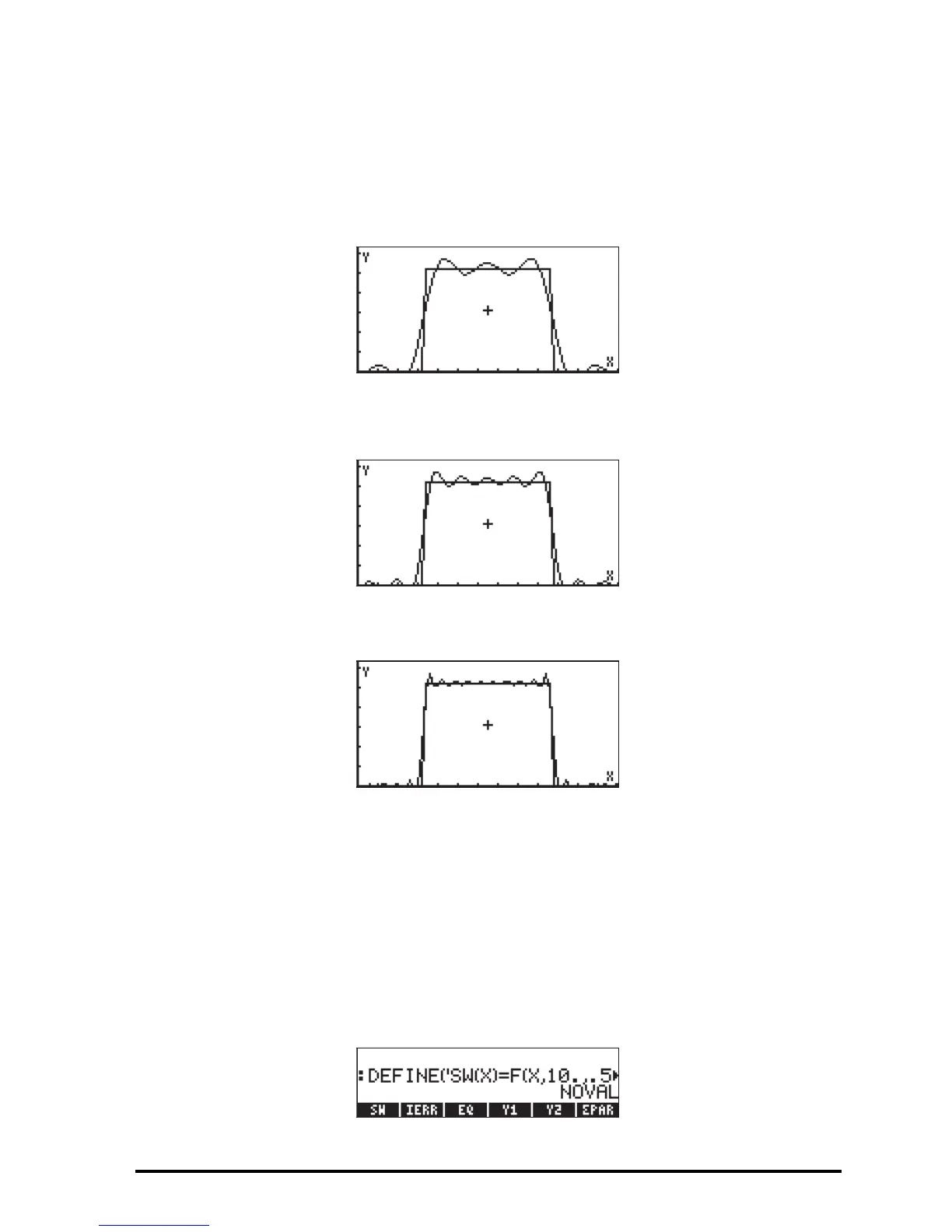
We can generate the excitation force by obtaining an approximation with k
=10 out of the Fourier series by using SW(X) = F(X,10,0.5):

 Loading...
Loading...




