Page 15-7
produces the vector potential function Φ
2
= [0, ZYX-2YX, Y-(2ZX-X)], which is
different from Φ
1
. The last command in the screen shot shows that indeed F =
∇× Φ
2
. Thus, a vector potential function is not uniquely determined.
The components of the given vector field, F(x,y,z) = f(x,y,z)i+g(x,y,z)j
+h(x,y,z)k, and those of the vector potential function, Φ(x,y,z) =
φ(x,y,z)i+ψ(x,y,z)j+η(x,y,z)k, are related by f = ∂η/∂y - ∂ψ/∂x, g = ∂φ/∂z - ∂η/
∂x, and h = ∂ψ/∂x - ∂φ/∂y.
A condition for function Φ(x,y,z) to exists is that div F = ∇•F = 0, i.e., ∂f/∂x +
∂g/∂y + ∂f/∂z = 0. Thus, if this condition is not satisfied, the vector potential
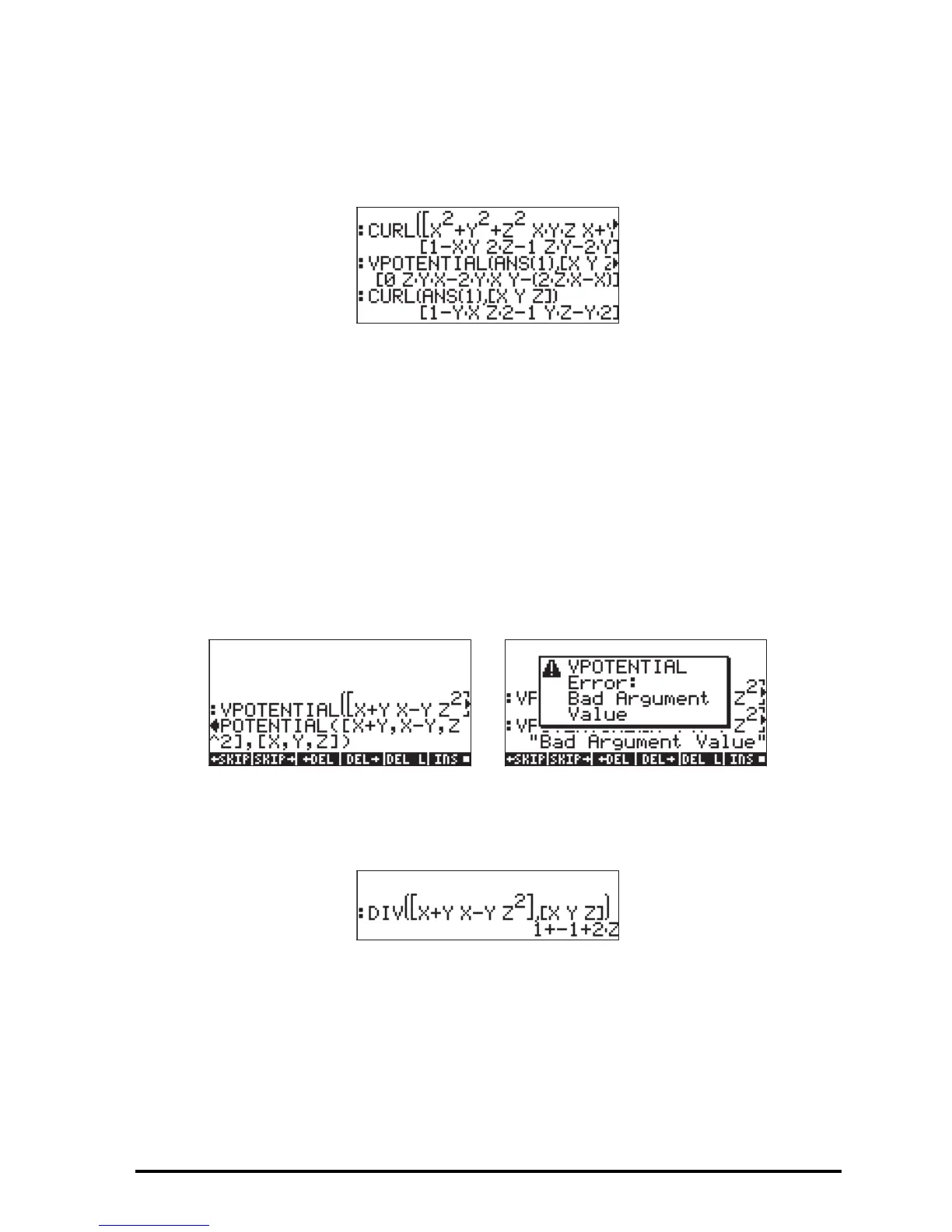
function Φ(x,y,z) does not exist. For example, given F = [X+Y,X-Y,Z^2], function
VPOTENTIAL returns an error message, since function F does not satisfy the
condition ∇•F = 0:
The condition ∇•F ≠ 0 is verified in the following screen shot:

 Loading...
Loading...




