5 Basic Operations and Trial Run
-
69
-
5
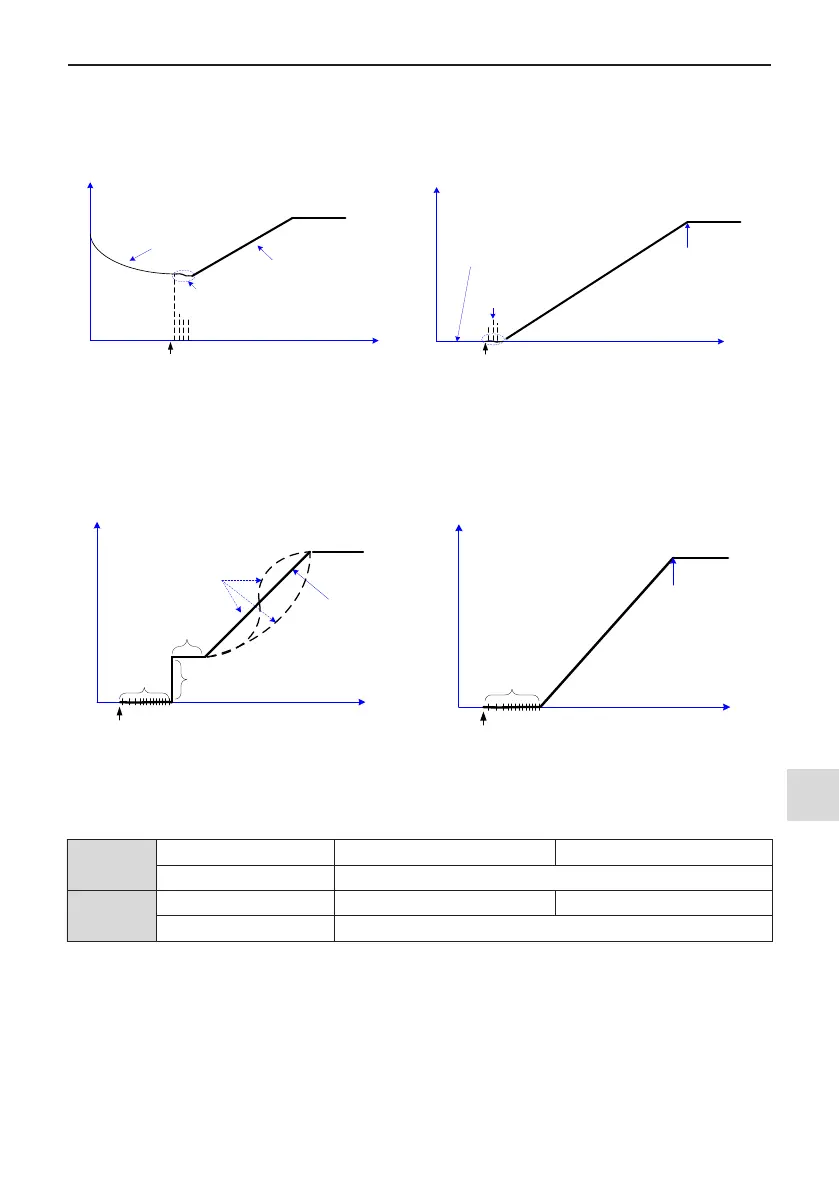
1: Catching a spinning motor
It is applicable to large-inertia loads, and the frequency curve is shown in the following gure. When the AC
drive starts, the load motor is still running because of the ywheel inertia. In this case, this function can be used
to avoid overcurrent during startup.
F
0-10
Max. frequency
F0-17
Acceleration time
f
t
Running command
Initial rotation speed
F6-00=1:
Catching a Spinning Motor
Automatic rotation speed
track and detection
F0-10
Max. frequency
F0-17
Acceleration time
f
t
Running command
Initial rotation speed=0
F6-00=1: Catching a Spinning Motor
Automatic rotation speed
track and detection
Figure 5-10 Catching a Spinning Motor
2: Pre-excited Start
It is valid only for asynchronous motors and used for building magnetic eld before motor running. It can im-
prove quick response of asynchronous motors and shorten acceleration time. The frequency curve is shown in
the following gure.
F
6-07
Acceleration/
deceleration mode
F0-10
Max.
frequency
F0-17
Acceleration time
f
t
Running command
F6-00=2: Pre
-excited Start
F6-04
Startup frequency
retention time
Pre-excitation
time
F6-06
F6-03
Startup frequency
F0-10
Max.
frequency
F0-17
Acceleration time
f
t
Running command
Default value:
F6-03=0.00Hz;
F6-04=0.0s;
F6-
07=0.
F6-00=2: Pre-excited Start
Pre-excitation
time
F6-06
Figure 5-11 Pre-excited start
5.8.2 Start Frequency
F6-03
Start frequency Default 0.00 Hz
Setting Range 0.00 Hz to 10.00 Hz
F6-04
Start frequency holding time Default 0.0s
Setting Range 0.0s to 100.0s
Set an appropriate start frequency to ensure the motor torque when the motor starts. The start frequency needs
to be retained for a period of time for full magnetic ux when the motor starts.
F6-03 has no lower frequency limit. If target frequency is smaller than start frequency, the motor does not start
and is idle.
Retention time of start frequency is not counted into acceleration time but into running time of simple PLC
func tion.

 Loading...
Loading...











