IEEE-488 Reference
3-34
3.11.11 *SRE <NRf> — service request enable Program Service Request Enable Register
SRE? — service request enable query Read Service Request Enable Register
<NRf> = 0 Clears enable register
1 Set MSB bit (Bit 0)
4 Set EAV bit (Bit 2)
8 Set QSB bit (Bit 3)
16 Set MAV bit (Bit 4)
32 Set ESB bit (Bit 5)
128 Set OSB bit (Bit 7)
255 Sets all bits
The *SRE command is used to program the Service Request Enable Register. This command is
sent with the decimal equivalent of the binary value that determines the desired state (0 or 1) of
each bit in the register. This register is cleared on power-up.
This enable register is used along with the Status Byte Register to generate service requests
(SRQ). With a bit in the Service Request Enable Register set, an SRQ occurs when the corre-
sponding bit in the Status Byte Register is set by an appropriate event. For details on register
structure, refer to paragraph 3.8.
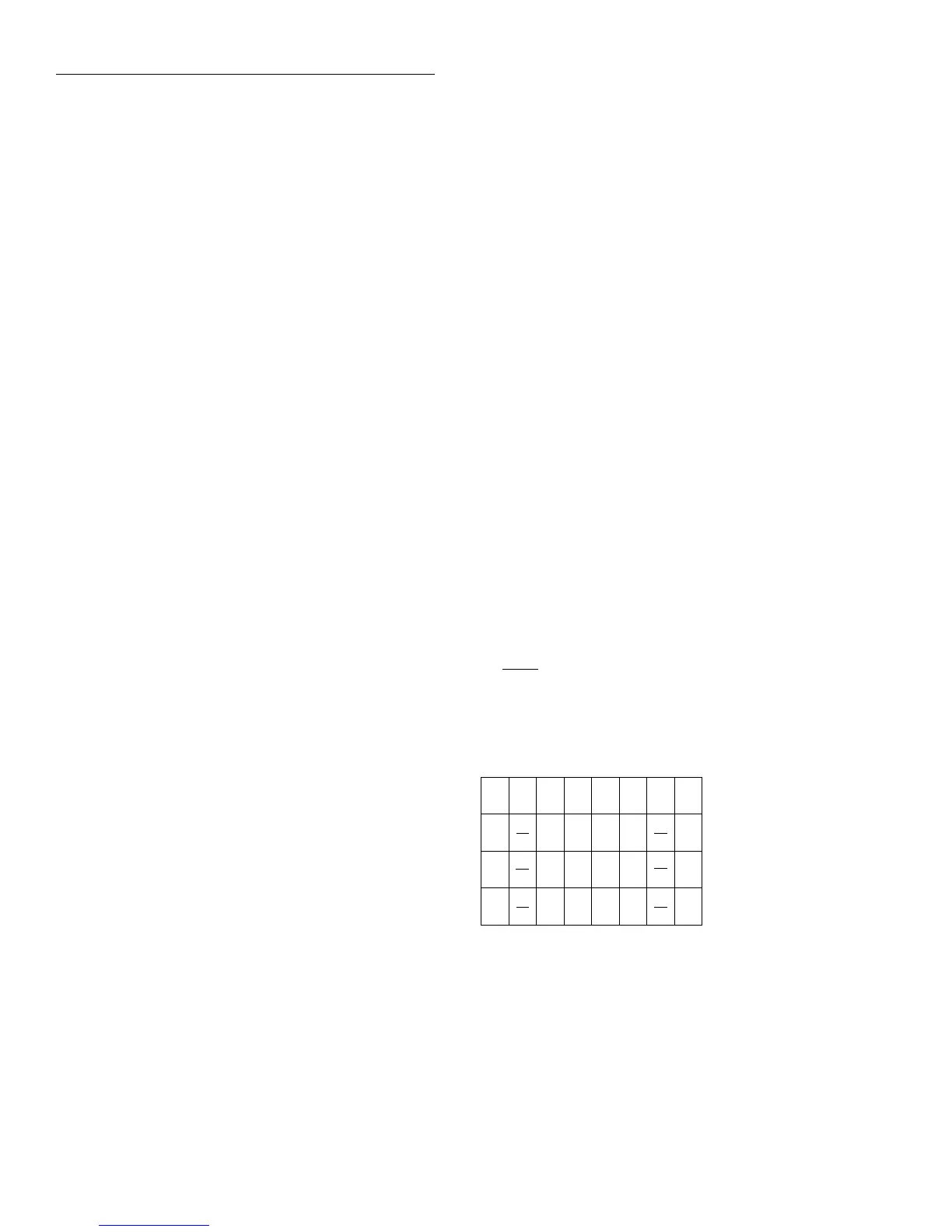
The Service Request Enable Register is shown in Figure 3-17. Notice that the decimal weight
of each bit is included in the illustration. The sum of the decimal weights of the bits that you
wish to set is the value that is sent with the *SRE command. For example, to set the ESB and
MAV bits of the Service Request Enable Register, send the following command:
*SSE 34
where; ESB (bit B5) = Decimal 32
MAV (bit B4) = Decimal 16
<NRf> = 48
The contents of the Service Request Enable Register can be read using the *SRE? query com-
mand.
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
(2 )
7
(2 )
5
(2 )
4
(2 )
3
(2 )
2
(2 )
0
32
0/1
Bit Position
Event
Decimal Weighting
Value
Value : 1 = Enable Service Request
Event
0 = Disable (Mask) Service
Request Event
Events : OSB = Operation Summary Bit
ESB = Event Summary Bit
MAV = Message Available
QSB = Questionable Summary Bit
EAV = Error Available
MSB = Measurement Summary Bit
OSB ESB MAV QSB EAV
0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1
128 16 8 4
MSB
1
0/1
Figure 3-17
Service Request Enable Register

 Loading...
Loading...