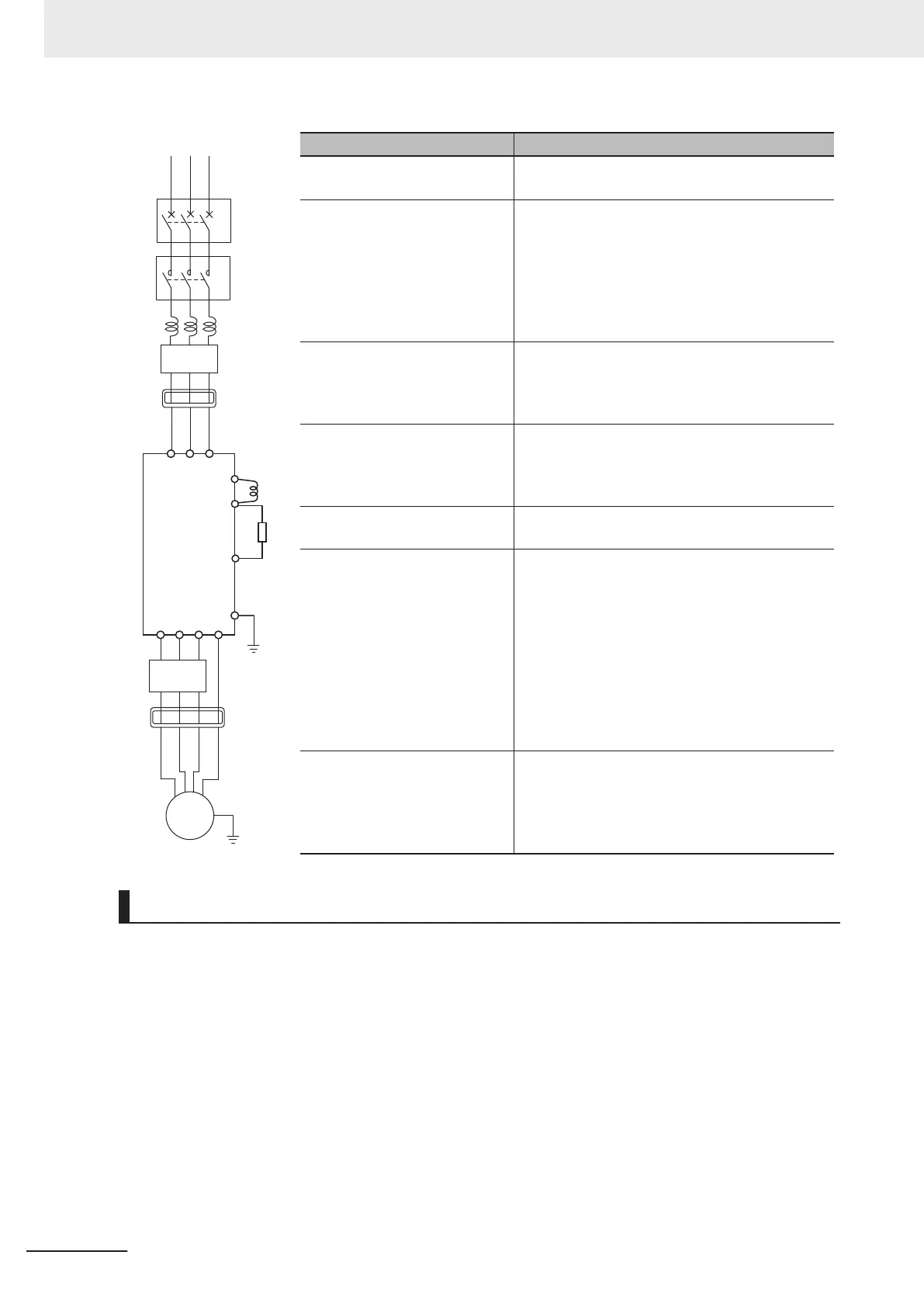
Name Function
(a) (b) (c) Refer to Recommended Cable Size, Wiring De-
vice, and Crimp Terminal on page
2-18.
(d) AC reactor This is used as a harmonic suppression meas-
ure. It also helps improve the power factor. The
AC reactor is used when the power supply volt-
age unbalance factor is 3% or more, the inverter
capacity is 500 kVA or more, or rapid change in
the power supply voltage occurs to reduce its ef-
fect.
(e) Input noise filter This filter reduces the conductive noise generat-
ed in the inverter and transmitted via wires. Con-
nect it to the primary side (input side) of the inver-
ter.
(f) Radio noise filter The inverter in operation may cause noise
through the power supply wiring etc., which could
affect radio receivers or other equipment nearby.
This filter reduces such noise (radiated noise).
(g) DC reactor This reactor helps suppress harmonics generated
by the inverter.
(h) Braking resistor These increase the amount of regenerative ener-
gy absorption when the inverter applies motor
braking and are used to decrease the speed of
an elevator or load with a large moment of inertia.
All models of the 3G3M1 Series Inverter have
built-in regenerative braking processing circuit.
The regenerative braking unit is necessary only if
a large braking torque is required and the built-in
regenerative braking processing circuit cannot al-
low it.
(j) Output noise filter This filter is installed between the inverter and the
motor to reduce the radiated noise emitted from
cables. It is used to reduce radio and television
interference and prevent meter and sensor mal-
function.
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g)
(h)
R S
T
+1
P/+2
RB
U V W G
(i)
(f)
M
MC
MCCB
(a)
(b)
Inverter
Power supply
Arrangement of Main Circuit Terminals
The arrangement of terminals on the inverter main circuit terminal block is shown below.
2 Design
2-16
M1 Series Standard Type User's Manual (I669)
 Loading...
Loading...