Acquiring Waveforms
3-60
CSA7000B Series & TDS7000B Series Instruments User Manual
Optical Bandwidth
CSA7000B Series: Traditionally bandwidth is defined as the frequency at which
the power out is one half the power out at a frequency near DC. In the voltage
domain the power dissipated into a resistive load (such as a 50 Ω termination of
an input) is the V
RMS
2
/R where V
RMS
is the RMS of the voltage swing seen at
the resistive load, and R is the resistance value. A logarithmic scale using
decibels is typically used to describe the frequency dependent response. A value
expressed in terms of a decibel relative to a reference is defined as:
dB = 10 log
Ꮛ
value
reference
Ꮠ
For electrical bandwidths the reference of a system is commonly the response of
the system to a sinusoidal frequency at or near DC. The point at which the
system response is one half would therefore be:
dB = 10 log
Ꮛ
0.5
response at DC
Ꮠ
=−3dB
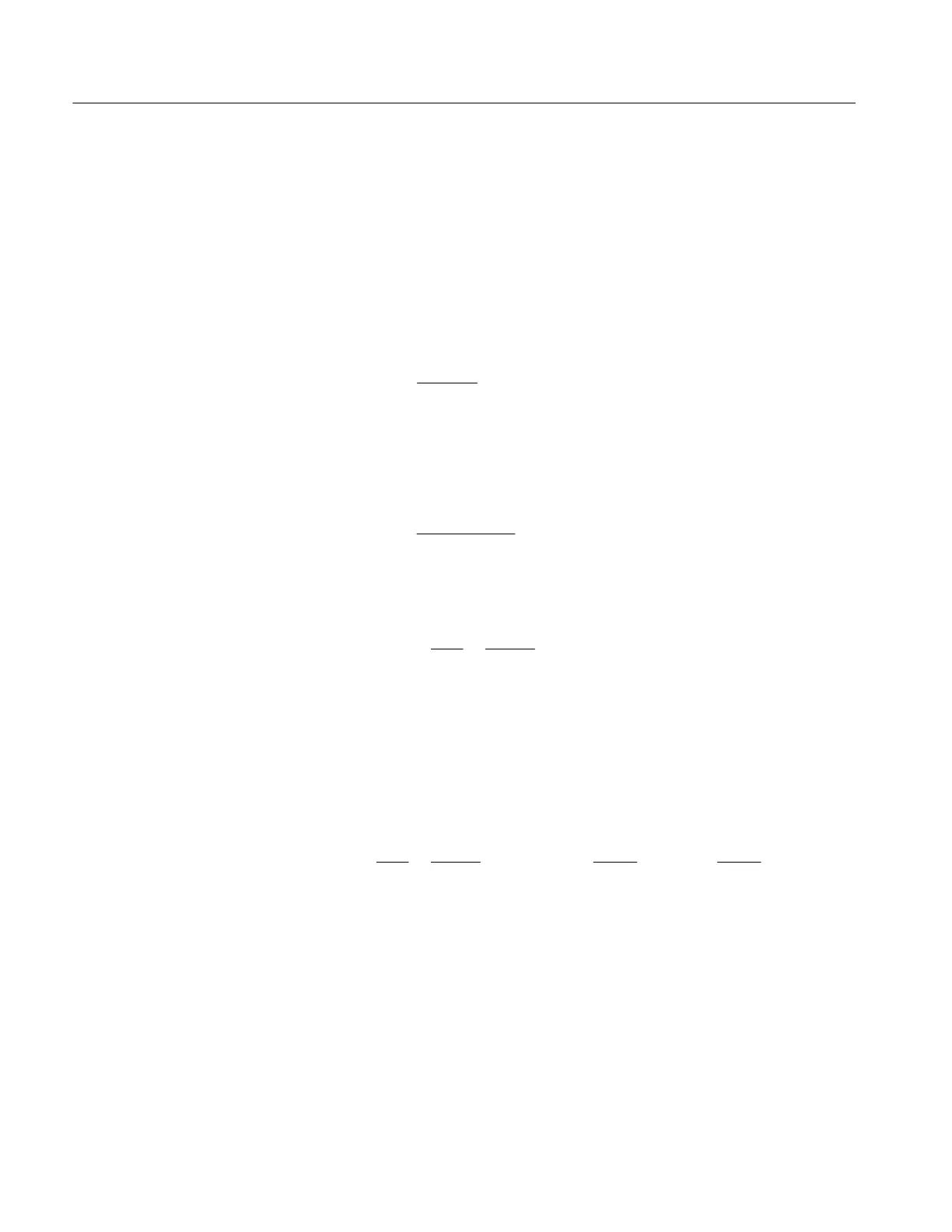
In terms of frequency, voltage, and resistance the bandwidth is expressed as:
–3dB = 10 log
Ꮛ
V
(
f
)
2
R
÷
V
(
DC
)
2
R
Ꮠ
where V(f) is the RMS of the voltage swing response at the bandwidth frequency
and V(
DC) is the RMS voltage swing response at a frequency approaching DC.
Further math yields V(
f) = 0.707¢V(DC).
The expression is simplified by cancelling the R and moving the squared term
inside the log expression to a multiple outside the log expression:
10 log
Ꮛ
V
(
f
)
2
R
÷
V
(
DC
)
2
R
Ꮠ
= 2 × 10 log
Ꮛ
V
(
f
)
V
(
DC
)
Ꮠ
= 20 log
Ꮛ
V
(
f
)
V
(
DC
)
Ꮠ

 Loading...
Loading...











