ZXR10 GER (V2.6.03) General Excellent Router User Manual Volume-I
166 Confidential and Proprietary Information of ZTE CORPORATION
[<distance-metric>] [globle] [tag <tag>] command in
global configuration mode as shown in
Table 206.
TABLE 206 DEFAULT ROUTE COMMAND
Command Format
Command Mode
Command
Function
ip route <prefix>
<net-mask>
{[<interface-
number>]
[<forwarding-
address>]}
[<distance-metric>]
[globle] [tag
<tag>]
global config
This configures
default route
Result: This sets default route.
Tag is a route label. Two static routes (with different next
hop IP addresses) to same destination network cannot have
same tag value.
Example: An example is given in the following to describe
the functions and use of the default route.
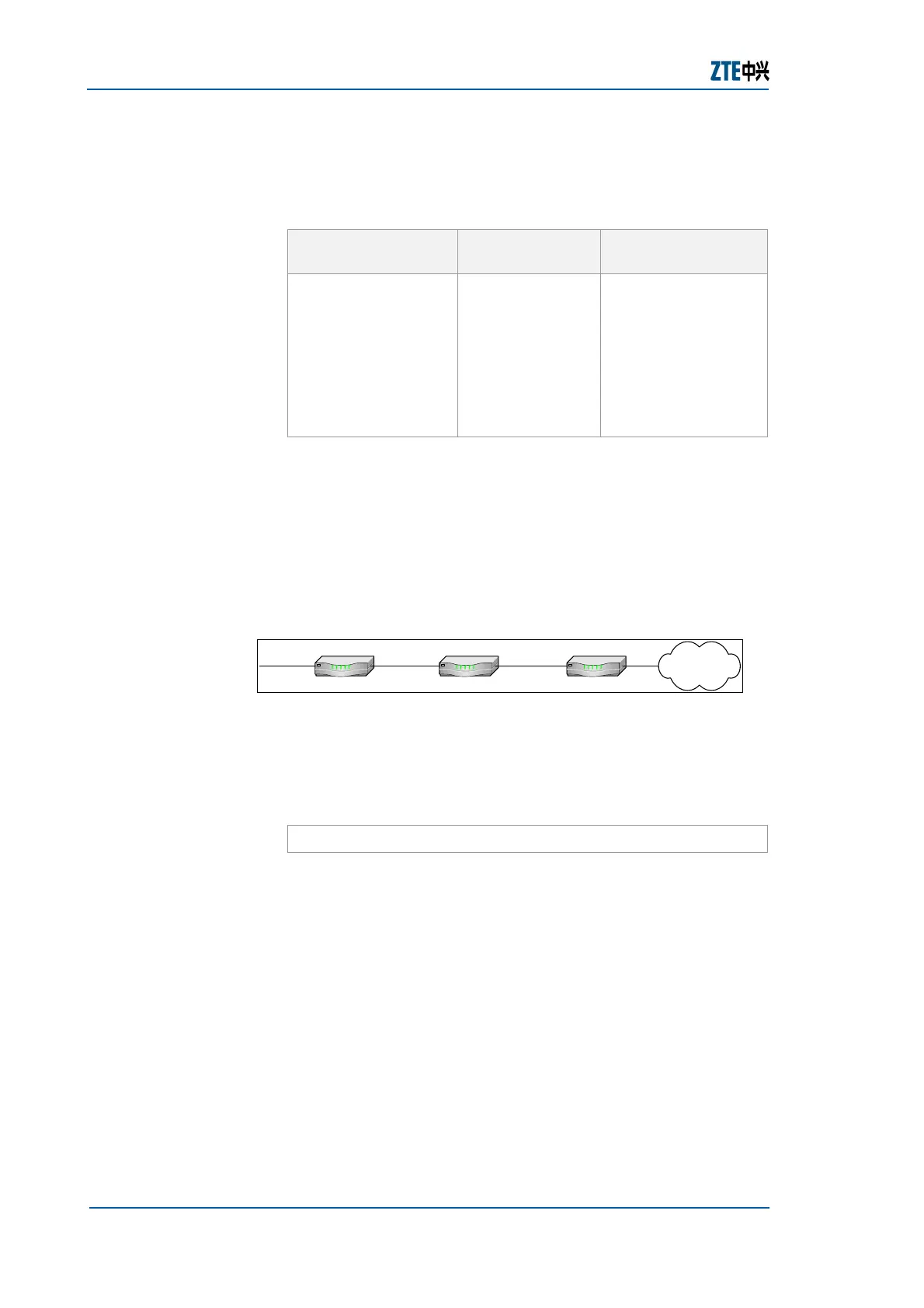
FIGURE 82 DEFAULT ROUTE COMMAND
R1 R2 R3
192.168.3.1/24
192.168.4.1/24
192.168.4.2/24
211.211.211.1/24
211.211.211.2/24
Internet
As shown in
Figure 82, R2 is connected to router R3 in
Internet. R2 does not record addresses of all networks on the
Internet, so it uses a default route to directly send unknown
packets to R3 for proper processing. The configuration of the
default route in R2 is as follows:
ZXR10_R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 211.211.211.2
When default route is used in routing protocol configuration,
default route varies with routing protocols.
If default route is configured for a router where an RIP runs, the
RIP will advertise default route 0.0.0.0/0 to its neighbor, and
even route redistribution is not needed in RIP domain.
For OSPF protocol, a router where the OSPF protocol runs will
not inject the default route into its neighbor automatically. For
OSPF to send the default route to OSPF domain, the command
notifies default route must be used. If this is necessary to
redistribute the default route in OSPF domain, such an
advertisement is normally implemented by an ASBR
(Autonomous System Border Router) in OSPF domain.
Default route configuration is completely the same as static
route configuration and only difference is that the network part
RIP Protocol
OSPF Protocol

 Loading...
Loading...