15-10
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch and Cisco 7600 Series Router Firewall Services Module Configuration Guide
OL-6392-01
Chapter 15 Using Failover
Understanding Failover
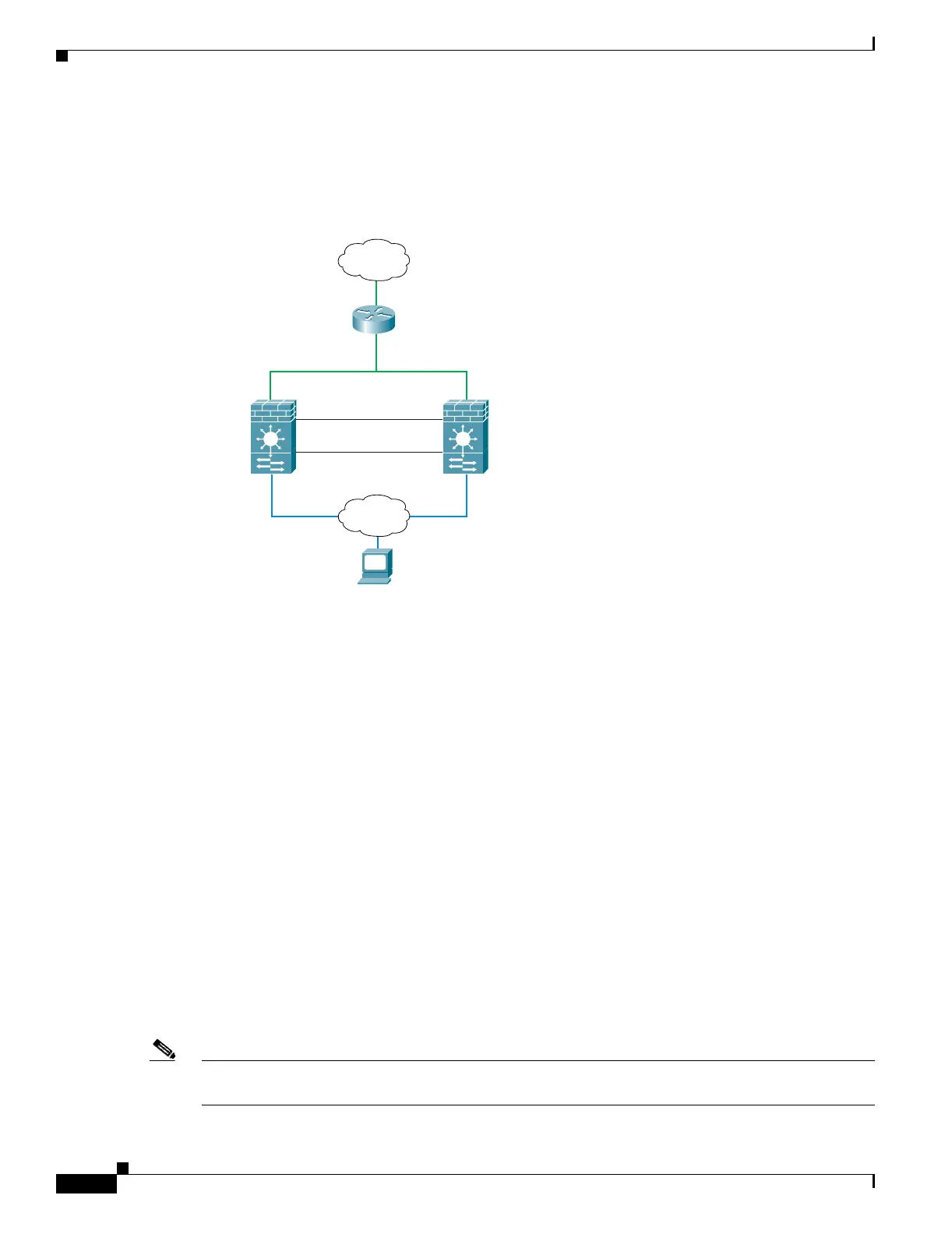
when inside packets destined for the outside get endlessly replicated by both FWSMs (see Figure 15-7).
The spanning tree protocol can break such loops if there is a timely exchange of BPDUs. To break the
loop, BPDUs sent between VLAN 200 and VLAN 201 need to be bridged.
Figure 15-7 Potential Loops in Transparent Mode
Primary/Secondary Status and Active/Standby Status
The main differences between the two modules in a failover pair are related to which module is active
and which module is standby, namely which IP addresses to use and which module actively passes
traffic.
However, a few differences exist between the modules based on which module is primary (as specified
in the configuration) and which module is secondary:
• The primary module always becomes the active module if both modules start up at the same time
(and are of equal operational health).
• The primary modulemodule MAC address is always coupled with the active IP addresses. The
exception to this rule occurs when the secondary module is active, and cannot obtain the primary
MAC address over the failover link. In this case, the secondary MAC address is used.
Configuration Replication
The two FWSM modules share almost the identical configuration. The configuration can be the same
because it includes both the active IP addresses and the standby IP addresses. When a module is active,
it uses the active IP addresses; when a module is standby, it uses the standby IP addresses.
Note Because the configuration is the same on both modules, the host names, usernames, and passwords are
also the same.
Active
FWSM
VLAN 200
MSFC
VLAN 201
Active
FWSM
Internet
State VLAN 11
Failover VLAN 10
Inside
104894
 Loading...
Loading...

















