15-12
Catalyst 6500 Series Switch and Cisco 7600 Series Router Firewall Services Module Configuration Guide
OL-6392-01
Chapter 15 Using Failover
Understanding Failover
Disabling Configuration Synchronization
Management applications may lose connectivity when upgrading the FWSM with complex
configurations. This can result in incomplete configuration files being applied to the standby FWSM.
You can disable the automatic configuration synchronization in order to avoid incomplete configurations
being applied to the standby FWSM. You need to disable configuration synchronization when upgrading
a software image or changing the configuration on the active FWSM to verify that the configuration files
are complete before the configuration is synchronized with the standby FWSM configuration. After you
verify that the configuration is complete, reenable configuration synchronization
To disable configuration synchronization, enter this command:
fwsm(config)# failover suspend-config-sync
To reenable configuration synchronization, use the no form of the this command.
Failover Triggers
The module can fail if one of the following events occurs:
• The module has a hardware failure or a power failure.
• The module has a software failure.
• Too many monitored interfaces fail.
Because the FWSM can have a large number of interfaces, it cannot monitor every interface. Rather,
you configure the FWSM to monitor a subset of interfaces. The FWSM fails over when a certain
number of monitored interfaces fails; you configure the failure threshold to be an absolute value or
a percentage of the total number of monitored interfaces.
See the “Failover Monitoring” section on page 15-13 for more information about when a module or
interface is considered to be failed.
Failover Actions
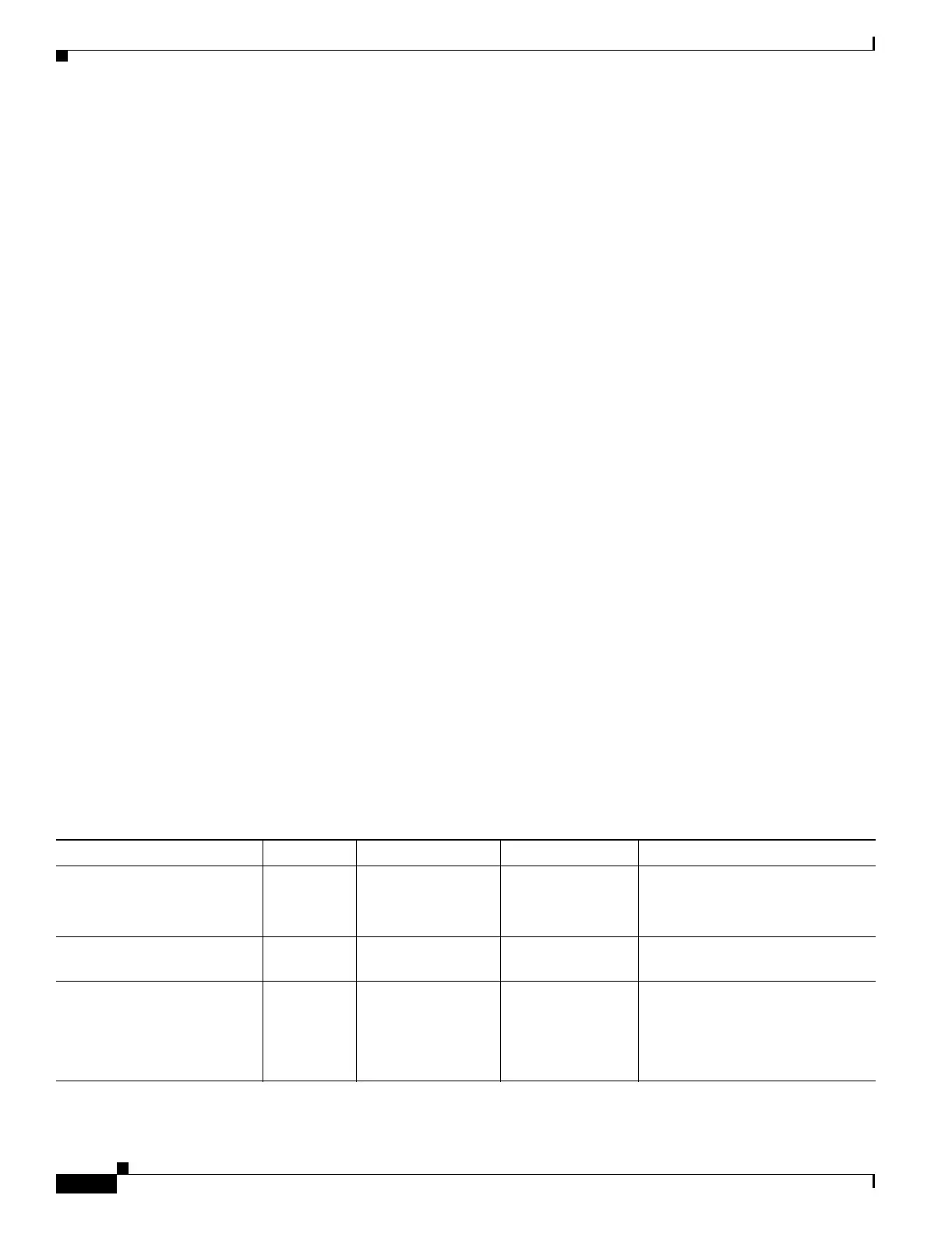
Table 15-1 shows the failover action for each failure event.
Table 15-1 Failover Behavior
Failure Event Policy Active Action Standby Action Notes
Active module failed (power
or hardware)
Failover n/a Become active
Mark active as
failed
No hello messages are received on
any monitored interface or the
failover link.
Formerly active module
recovers
No failover Become standby No action None.
Standby module failed (power
or hardware)
No failover Mark standby as
failed
n/a When the standby module is
marked as failed, then the active
module will not attempt to fail
over, even if the interface failure
threshold is surpassed.

 Loading...
Loading...

















