DGS-3100 Series Gigabit Stackable Managed Switch User Manual
82
Defining Trunking
The Trunking Configuration Page contains information for assigning ports to LAGs and defining LAG parameters.
Load Balancing
Traffic forwarded to the trunk interface (LAG) is load-balanced across the physical links, thus achieving an effective
bandwidth close to the aggregate bandwidth of each of the port members of the trunk group (LAG).
Traffic load balancing over trunk groups is managed by a hash-based distribution function that distributes Unicast traffic
based on Layer 2 or Layer 3 packet header information. Multicast traffic always uses a single, unique LAG member.
The information used for the trunk is as follows:
Layer 2 — MAC source and destination addresses
Layer 3 — IP source and destination addresses
Layer 2 and layer 3 can be used either separately or together, as needed.
A hash function based on the above criteria is calculated and saved in the packet descriptor. The egress process uses this
hash function to select the specific trunk group member as the egress destination link. The hash algorithm ensures that the
order of packets within a specific flow is preserved
To assign ports to LAGs:
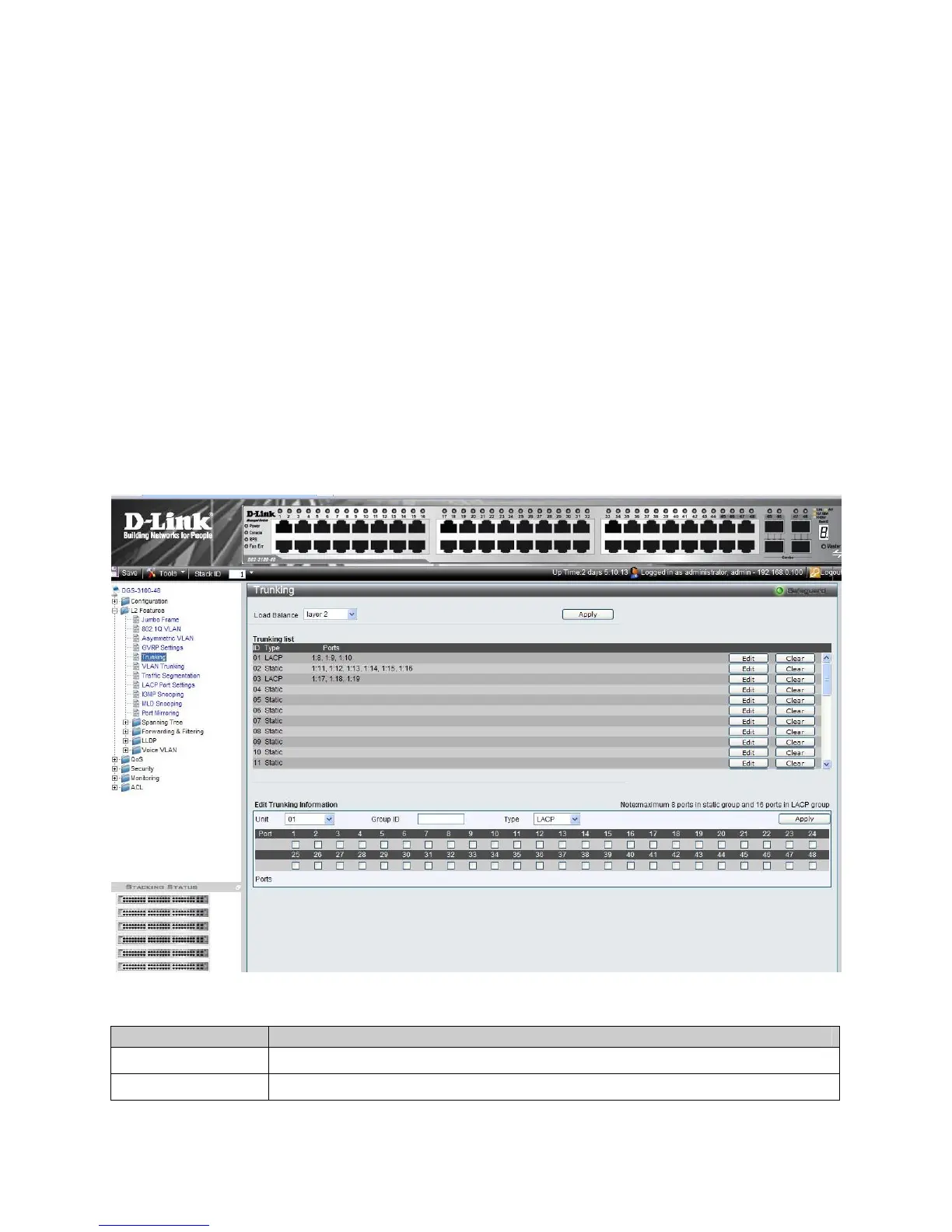
1. Click L2 Features > Trunking. The Trunking Configuration Page opens:
Figure 0–10 Trunking Configuration Page
The Trunking Configuration Page contains the following fields:
Field Description
Unit
Defines the stacking member’s Unit ID for which LAG parameters are displayed.
Load Balance
Defines the method used for load balancing over physical links. This allows for effective port
 Loading...
Loading...











