13-15
SYNCHRONOUS SERIAL I/O UNIT
If the receiver is disabled while a data value is being shifted into the shift register, it continues
running until the last bit is shifted in. Then the shift register is loaded into the buffer register, the
shift register stops and the clock pin (SRXCLK) is three-stated if in the master mode.
If the receiver is disabled then enabled before the current word has been shifted in, it continues
as if it were never disabled.
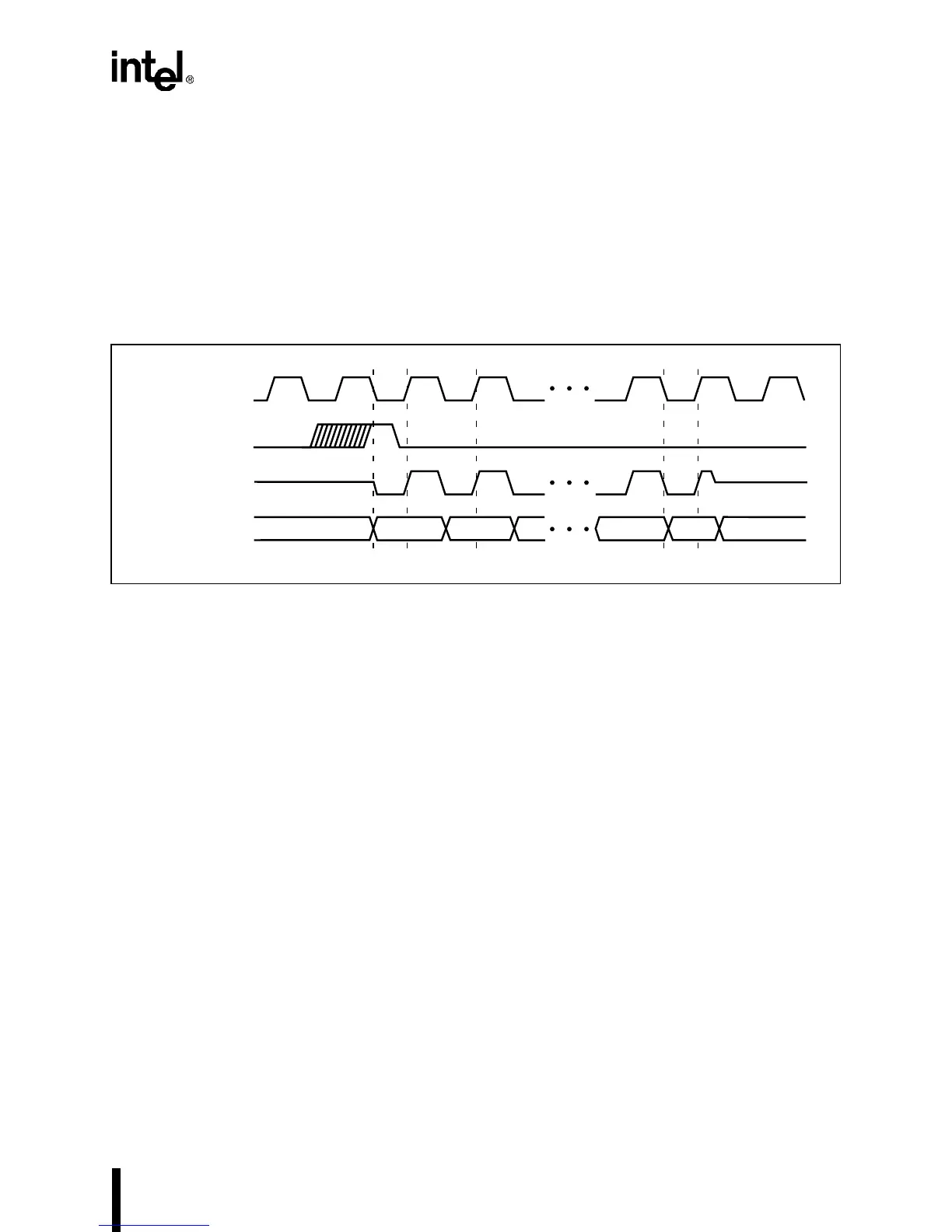
Figure 13-14 shows the serial receive data (SSIORX) pin values for a master mode, single word
transfer. For single word transfers, it is necessary to enable the receiver thus starting the shifting
process, then disable the receiver before 16 bits are shifted in.
Figure 13-14. Receiver Master Mode, Single Word Transfer
Operation in receiver slave mode is similar to master mode, except the receiver is clocked from
the SRXCLK pin. When the receiver is enabled any time during the SRXCLK clock cycle, data
on the SSIORX pin is latched into the shift register at the next rising edge of SRXCLK. The SRX-
CLK and SSIORX pins are three-stated.
Baud-rate
Generator Clock
SRXCLK
Receiver Enable
RB15 RB14
SSIORX
Float
Ignored
Float
A2446-01
Ignored
RB1 RB0

 Loading...
Loading...











