111
ACCELERATION CONTROL: ACC(888) Section 5-8
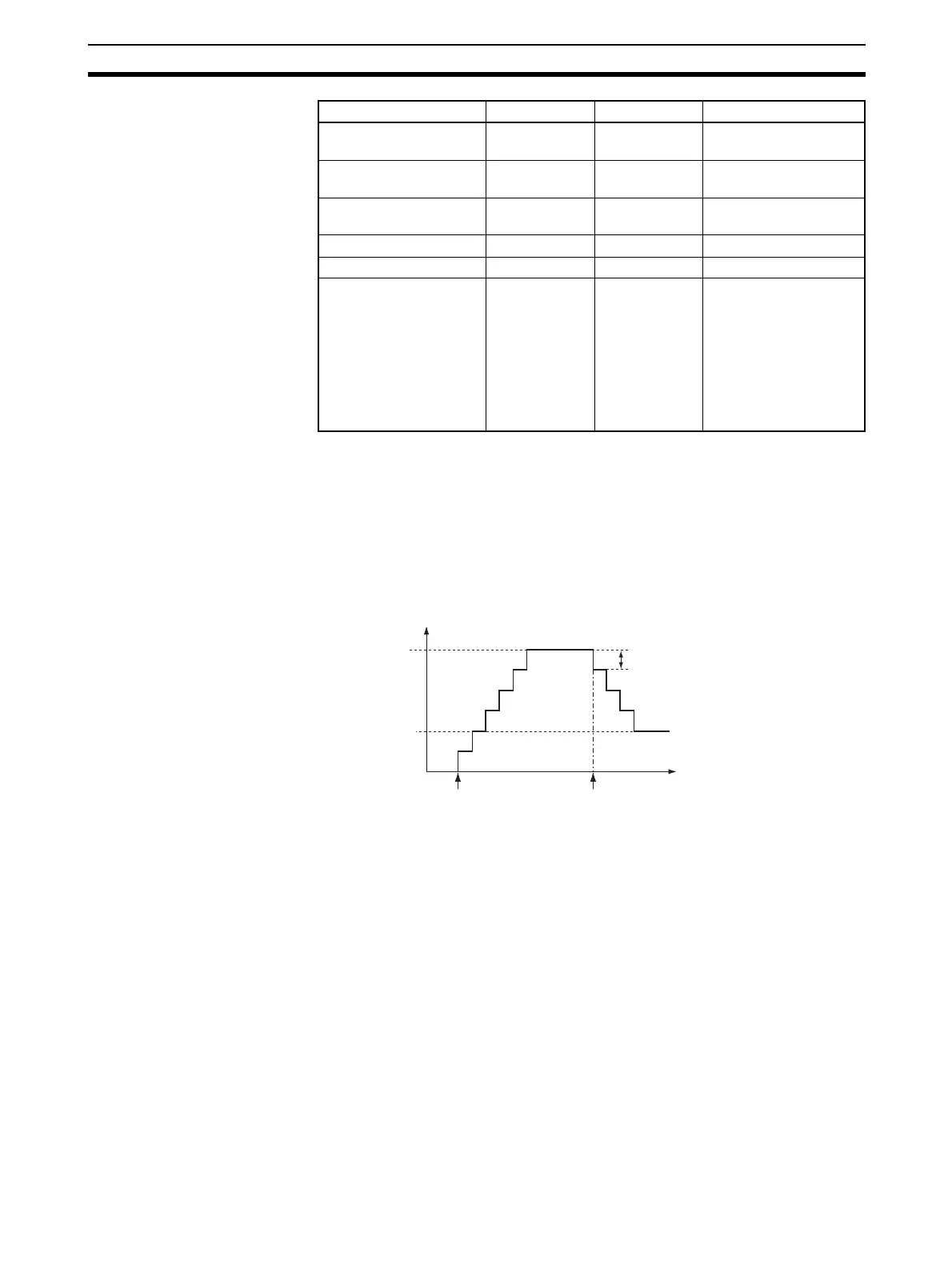
Description ACC(888) starts pulse output on the port specified in P using the mode speci-
fied in M using the target frequency and acceleration/deceleration rate speci-
fied in S. The frequency is increased every pulse control period (4 ms) at the
acceleration rate specified in S until the target frequency specified in S is
reached.
Pulse output is started each time ACC(888) is executed. It is thus normally
sufficient to use the differentiated version (@ACC(888)) of the instruction or
an execution condition that is turned ON only for one scan.
In independent mode, pulse output stops automatically when the specified
number of pulses has been output. In continuous mode, pulse output contin-
ues until it is stopped from the program.
An error will occur if an attempt is made to switch between independent and
continuous mode during pulse output.
With the CJ1M CPU Units, PLS2(887) can be executed during pulse output
for ACC(888) in either independent or continuous mode, and during accelera-
tion, constant speed, or deceleration. (See note.) ACC(888) can also be exe-
cuted during pulse output for PLS2(887) during acceleration, constant speed,
or deceleration.
Note Executing PLS2(887) during speed control with ACC(888) (continuous mode)
with the same target frequency as ACC(888) can be used to achieved inter-
rupt feeding of a fixed distance. Acceleration will not be performed by
PLS2(887) for this application, but if the acceleration rate is set to 0, the Error
Flag will turn ON and PLS2(887) will not be executed. Always set the acceler-
ation rate to a value other than 0.
Indirect DM/EM
addresses in binary
--- --- @ D00000 to @
D32767
Indirect DM/EM
addresses in BCD
--- --- *D00000 to *D32767
Constants See description
of operand.
See description
of operand.
---
Data Registers --- --- ---
Index Registers --- --- ---
Indirect addressing
using Index Registers
--- --- ,IR0 to ,IR15
–2048 to +2047 ,IR0 to
–2048 to +2047 ,IR15
DR0 to DR15, IR0 to
IR15
,IR0+(++) to ,IR15+(++)
,–(– –)IR0 to, –(– –
)IR15
Area P M S
Target frequency
Time
Acceleration/deceleration rate
ACC
888
executed.
Pulse frequency
ACC(888) executed.

 Loading...
Loading...











