227
Appendix C
Interrupt Response Times
Note The actual performance depends on a variety of factors that affect CPU Unit operation such as the func-
tion's operating conditions, user program complexity, and cycle time. Use the performance specifica-
tions as guidelines, not absolute values.
Built-in Interrupt Input Response Time
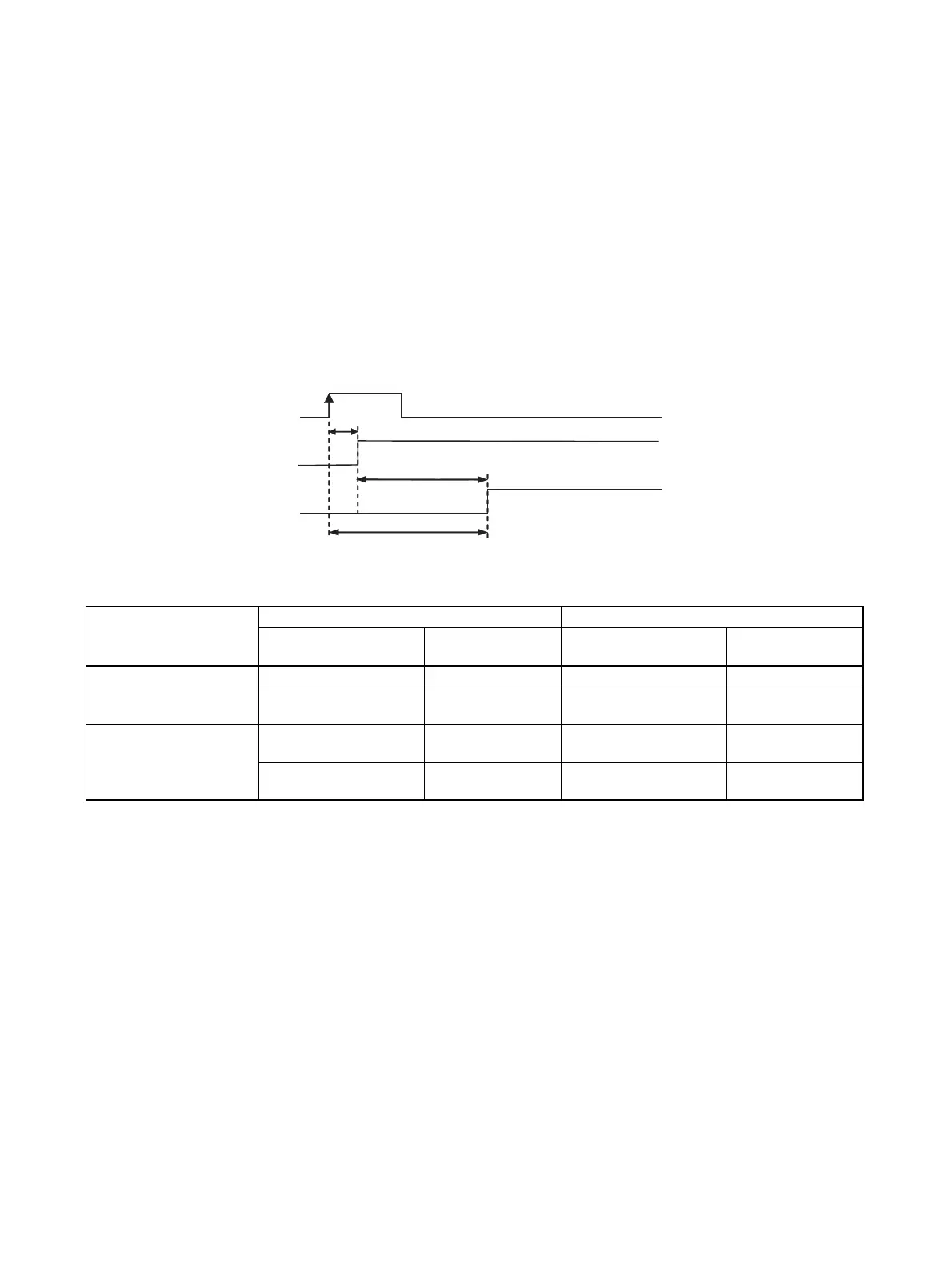
The interrupt response time is the time it takes between an OFF-to-ON signal (or ON-to-OFF signal for down-
differentiation) at the built-in interrupt input terminal until the corresponding I/O interrupt task is actually exe-
cuted. The total response time is the sum of the hardware response time and software response time.
Note The term a is the delay caused when there is a conflict with another interrupt process. In general, this
delay may be anywhere between 6 µs and 150 µs long.
Item CJ1M-CPU22/23 CJ1M-CPU21
Interrupt response
time
Counter interrupts Interrupt response
time
Counter interrupts
Hardware interrupt
response time
Up-differentiation 30 µs --- Up-differentiation 30 µs ---
Down-differentiation
150 µs
--- Down-differentiation
150 µs
---
Software interrupt
response time
Minimum: 93 µs Maximum: 203 µs +
α
Minimum: 159 µs 187 µs
Maximum: 209 µs + α
(See note.)
Minimum: 103 µs Maximum: 289 µs + α
(See note.)
287 µs
Input
Signal read at the
built-in input terminal
Interrupt task execution
Hardware response time
Software response time
Built-in interrupt input
response time
Built-in interrupt input response time = Hardware interrupt response time + Software interrupt response time

 Loading...
Loading...











