3-39
erative energy absorption capacity. (The capacity varies depending on the model. For details, refer to
3-3-2 Servo Driver Regenerative Energy Absorption Capacity.)
• For Servo Driver models with internal regeneration resistance for absorbing regenerative energy (i.e.,
models of 500 W or more), the average amount of regeneration P
r
(unit: W) must be calculated, and
this value must be lower than the Servo Driver’s regenerative energy absorption capacity. (The capac-
ity varies depending on the model. For details, refer to 3-3-2 Servo Driver Regenerative Energy Ab-
sorption Capacity.)
The average amount of regeneration (P
r
) is the power consumed by regeneration resistance in one
cycle of operation.
P
r
= (E
g1
+ E
g2
)/T [W]
T: Operation cycle [s]
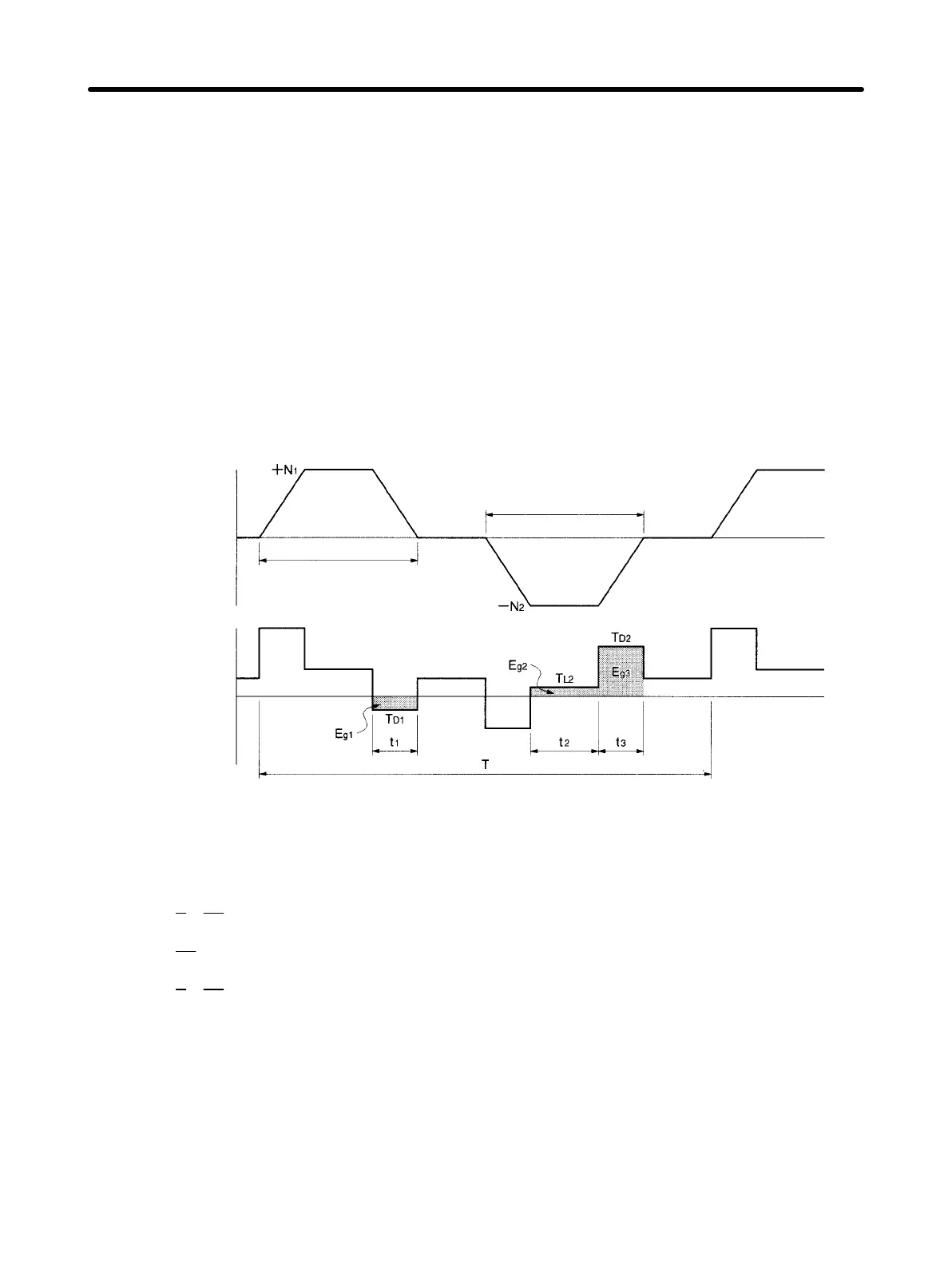
H Vertical Axis
Fall
Rise
Servomotor
operation
Servomotor
output torque
Note In the output torque graph, acceleration in the positive direction (rise) is shown as positive, and
acceleration in the negative direction (fall) is shown as negative.
• The regenerative energy values for E
g1
, E
g2
, and E
g3
are derived from the following equations.
E
g1
1
2
2p
60
N
1
T
D1
t
1
[J]
E
g2
2p
60
N
2
T
L2
t
2
[J]
N
1
, N
2
: Rotation speed at beginning of deceleration [r/min]
T
D1
, T
D2
: Deceleration torque [NSm]
T
L2
: Torque when falling [NSm]
t
1
, t
3
: Deceleration time [s]
t
2
: Constant-velocity travel time when falling [s]
E
g3
1
2
2p
60
N
2
T
D2
t
3
[J]
Note There is some loss due to winding resistance, so the actual regenerative energy will be approxi-
mately 90% of the values derived from these equations.
System Design and Installation
Chapter 3

 Loading...
Loading...











