06.2005 Engineering Information
Siemens AG 6SE7087-6QX70 (Version AE)
SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES Compendium Motion Control 11-25
11.9 Calculating example
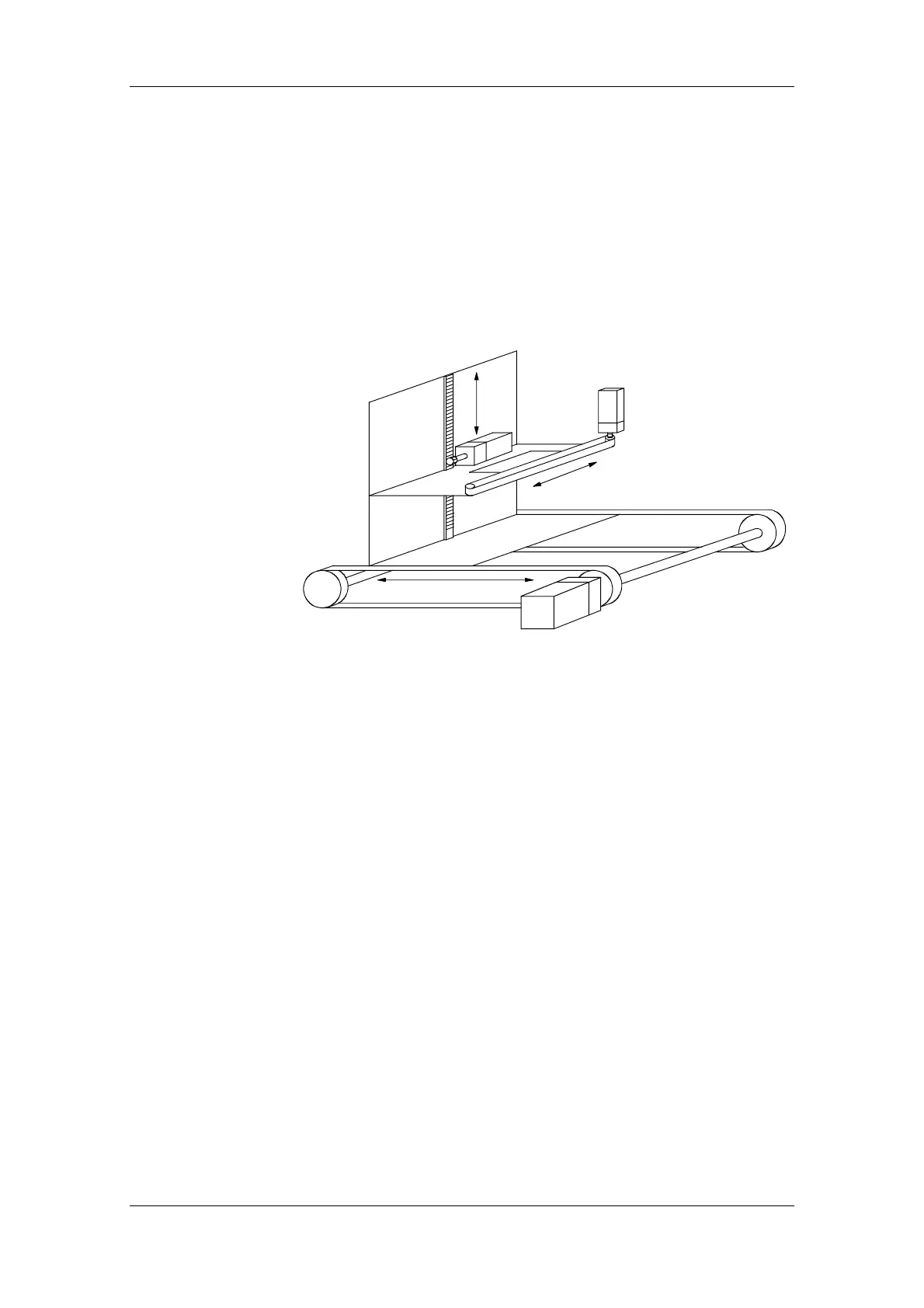
A three-axis conveyor vehicle is to be designed. The x-axis is the main
propelling drive, the y-axis is the fork drive and the z-axis is the lifting
drive. The propelling drive and the lifting drive can be operated
simultaneously whereas the fork drive only operates alone. The x-axis
and the y-axis are driven via toothed belts. The z-axis is driven via a
gear rack. Three inverters are to be used on one rectifier unit.
Positioning is to be carried out non-centrally in the inverter. The
Profibus is to be used for connection to a PLC.
Y
X
Z
Fig. 11-12 Line drawing of a three-axis conveyor vehicle
11.9.1 Calculation of the x-axis as the travel gear
♦ Mass to be transported m= 400 kg
♦ Diameter of drive wheel D= 0.14 m
♦ Max. speed v
max
= 1.6 m/s
♦ Max. acceleration and deceleration a
max
= 6.4 m/s2
♦ Distance travelled s= 2 m
♦ Cycle time T= 7 s
♦ Mech. efficiency η
mech
= 0.9
♦ Specific travelling resistance w
f
= 0.1
♦ Mech. accuracy ∆s
mech
= ±0.1 mm
♦ Overall accuracy required ∆s
tot
= ±0.2 mm
1. Data of the drive
 Loading...
Loading...











