Engineering Information 06.2005
6SE7087-6QX70 (Version AE) Siemens AG
11-34 Compendium Motion Control SIMOVERT MASTERDRIVES
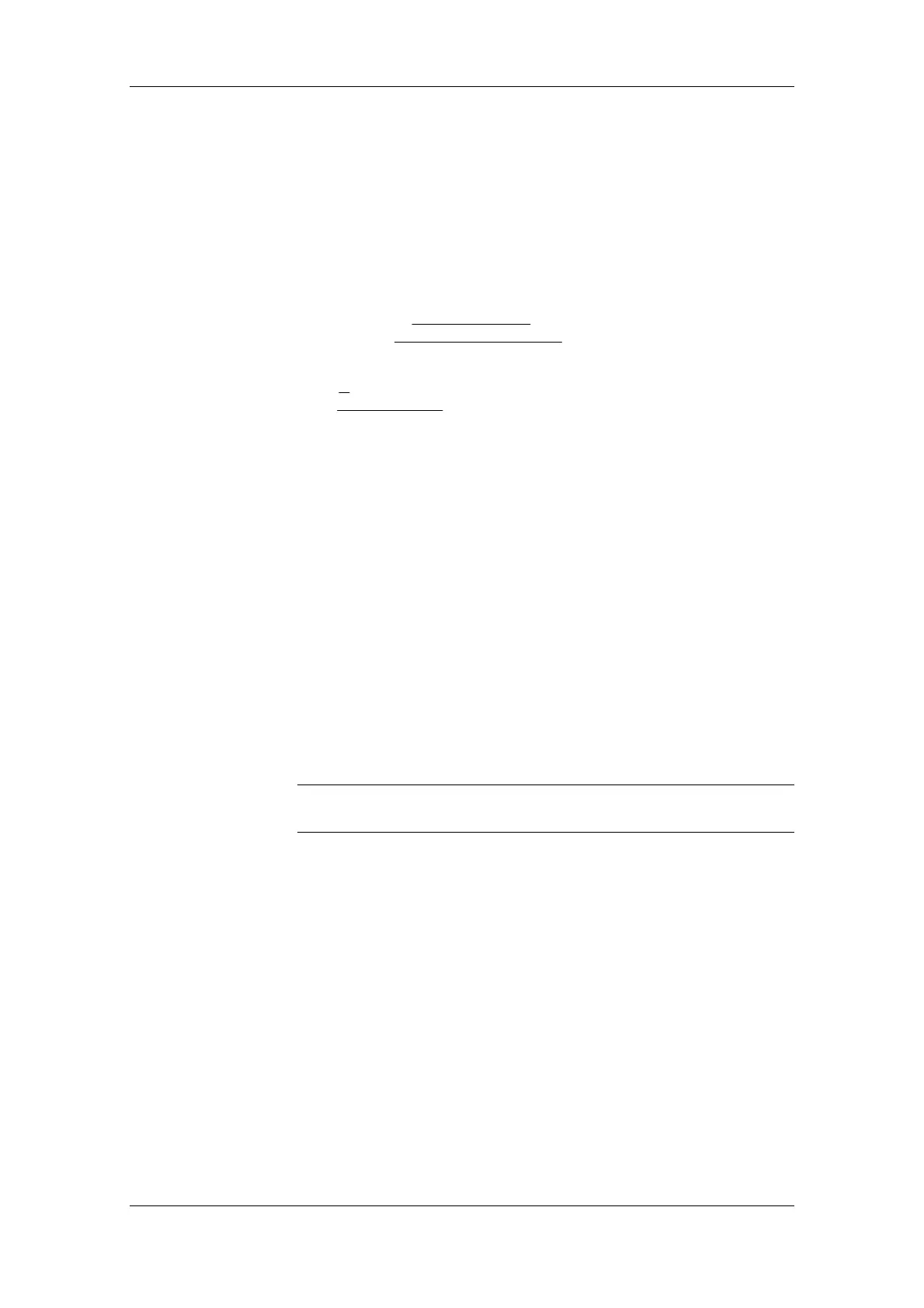
The maximum braking power and the mean braking power have to be
calculated for later rating of the braking resistors. The maximum power
output of the motor during braking has already been calculated (see 6.).
♦ The maximum braking power is therefore:
PP kW
br Mot v Mot Invmax max
... .=⋅⋅=−⋅⋅=−
4 53 0 92 0 98 4 08
♦ The mean braking power is obtained from the negative
characteristic of the motor power output as follows:
P
PP
t
T
br mean
Mot v A Mot v E
i
Mot Inv
=
+
⋅
′
⋅⋅
∑
2
∆
ηη
=
⋅− ⋅
⋅⋅=−
1
2
453 025
35
092 098 0146
(.).
.
.. .kW
11.9.2 Calculating the y-axis as the travel gear
♦ Mass to be transported m= 100 kg
♦ Diameter of drive wheel D= 0.1 m
♦ Max. speed v
max
= 1 m/s
♦ Max. acceleration and deceleration a
max
= 2.5 m/s
2
♦ Distance travelled s= 0.5 m
♦ Cycle time T= 7 s
♦ Mech. efficiency η
mech
= 0.9
♦ Specific travelling resistance w
f
= 0.1
♦ Mech. accuracy ∆s
mech
= ±0.1 mm
♦ Overall accuracy required ∆s
tot
= ±0.2 mm
The same calculating procedures apply to the y-axis as the propelling
drive as to the x-axis. This calculation is therefore dispensed with.
With i=10, the motor selected is a 1FT6041-4AF7 motor with a SPG75-
M1 gear unit and the smallest 6SE7012-0TP50 Compact PLUS inverter
with I
Un
=2 A. Because the drive of the y-axis always runs alone and,
with regard to its power, is small in comparison to the drives of the x-
axis and the z-axis, it is not taken into account in the rating of the
rectifier unit and the braking resistor.
7. Determinination
of braking power
1. Data of the drive
NOTE
 Loading...
Loading...











