4
REMOTE INTERFACES
Syntax Overview
4-6 TP04300 Series Interface & Applications Manual
Section C:
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Syntax
Syntax Overview
In Version 3, for both GPIB (IEEE-488.2) and Serial (RS-232C):
• All message strings to and from the TP04300A consist of ASCII characters.
• Numerical arguments are always sent/received in decimal format as a string of ASCII
characters.
• Some numerical arguments consist of a series of binary flags. They are sent as a decimal
number equal to the sum of the binary weights of each flag bit that is a “one.”
• Commands with arguments must have a space between the command and the argument.
• Serial (RS-232C) program messages (strings) must be terminated with a line feed. GPIB
program messages (strings) may be terminated with a line feed, by setting the EOI line, or
both.
• In GPIB mode, response messages from the TP04300A are terminated with a line feed
character with the EOI line set. In Serial mode, response messages are terminated with a
carriage return followed by a line feed.
• Program message unit separators “;” (semicolons) are required to delimit multiple com-
mands or queries in a single program message (string).
• In serial mode, the ! (exclamation point) character acts as the device clear command. It is
sent as a single character (no terminator) and should never otherwise appear in a message.
• The System parses commands as explained in Command Processing (page 4-7)
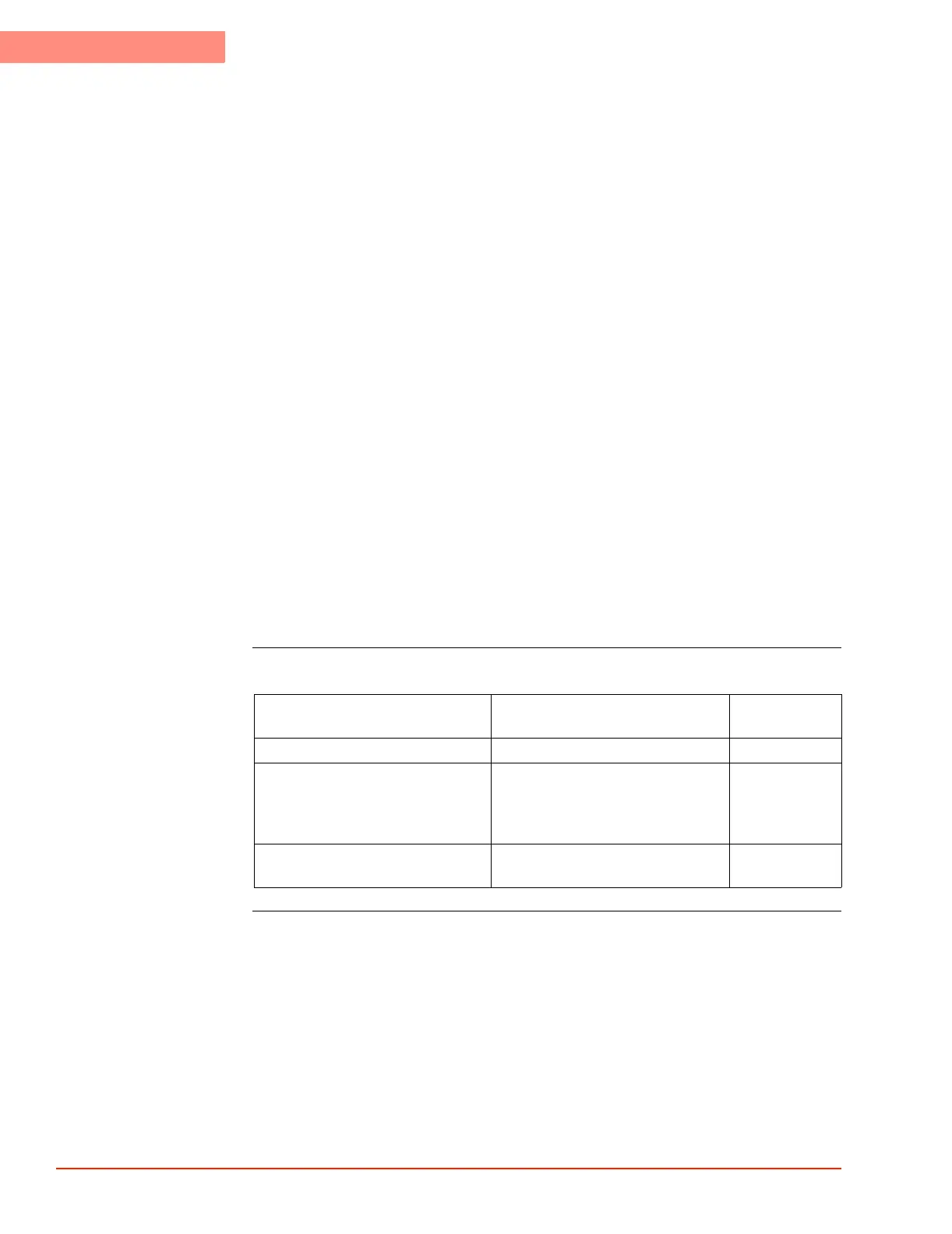
Command Examples
Description From Host to System System
Returns
Read the current temperature. TEMP?<LF> 25<LF>
Set the temperature setpoint to
25 °C, the “at temperature” window
to 3 °C, and the soak time to 15
seconds.
SETP 25;WNDW 3;SOAK 15<LF>
Read the setpoint and the current
temperature.
SETP?;TEMP?<LF> 25;24.9<LF>
 Loading...
Loading...