User's Manual 11. Quality of Service
Version 4.4.3 131 MP-20x Multimedia Home Gateway
11.7 Configuring Basic VoIP QoS Example
The 'Traffic Shaping' feature only ensures priority to calls that originate from inside the
device. When giving VoIP priority over data, the bottleneck is effectively moved from the
Cable modem/fiber transceiver into the device. To give priority to calls from the LAN, you
must define a traffic priority rule (for SIP and RTP from the device on the LAN).
This section recommends a minimal QoS configuration that ensures sufficient QoS for
VoIP calls when the device is connected behind a broadband cable modem/fiber
transceiver with limited uplink bandwidth and the user runs bandwidth-consuming
applications on the PC.
Since most modems do not have any priority mechanisms, the Tx bandwidth of the device
should be limited according to the modem’s uplink bandwidth. Since the device
automatically gives higher priority to VoIP packets (in its internal queues), it is not
necessary to define traffic shaping classes.
To configure basic QoS for VoIP:
1. From the menu bar, click the QoS menu link, and then click the Traffic Shaping tab;
the ‘Traffic Shaping’ screen appears.
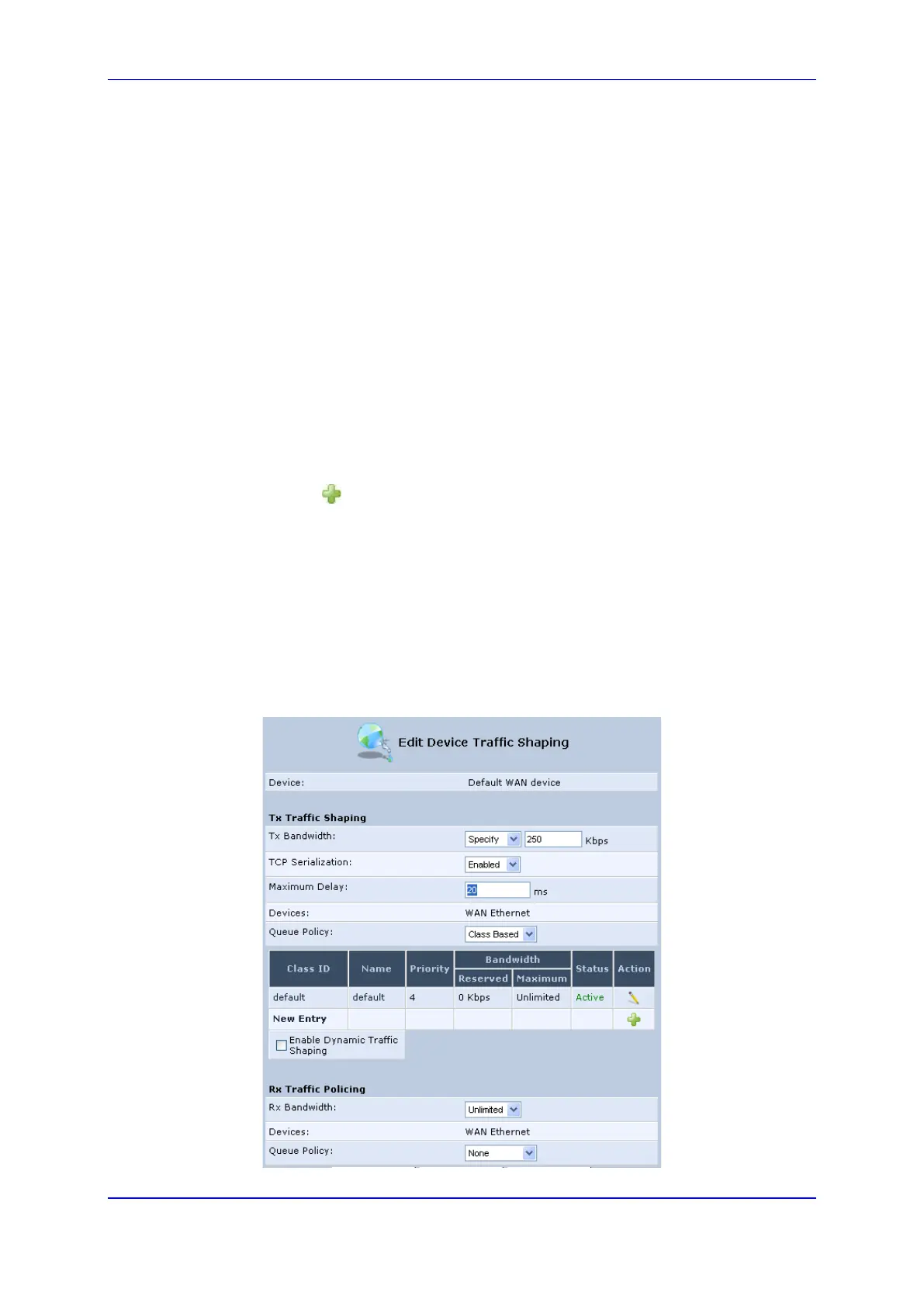
2. Click the New icon; the screen 'Add Device Traffic Shaping' appears.
3. From the 'Device' drop-down list, select 'Default WAN Device' (or your PPTP/L2TP
connection you have created), and then click OK; the 'Edit Device Traffic Shaping'
screen appears.
4. Limit the Tx bandwidth (in the 'Tx Bandwidth' field) according to your modem’s uplink
bandwidth.
5. To prevent jitter in outgoing RTP packets, from the 'TCP Serialization' drop-down list,
select 'Enabled', and then in the 'Maximum Delay' field, define the maximum allowed
delay (e.g. 20 milliseconds). This causes long TCP packets to be fragmented when
there is an active voice call.
Figure 11-13: Edit Device Traffic Shaping

 Loading...
Loading...