If redistribution is enabled globally, global configuration is given higher priority than interface configuration.Note
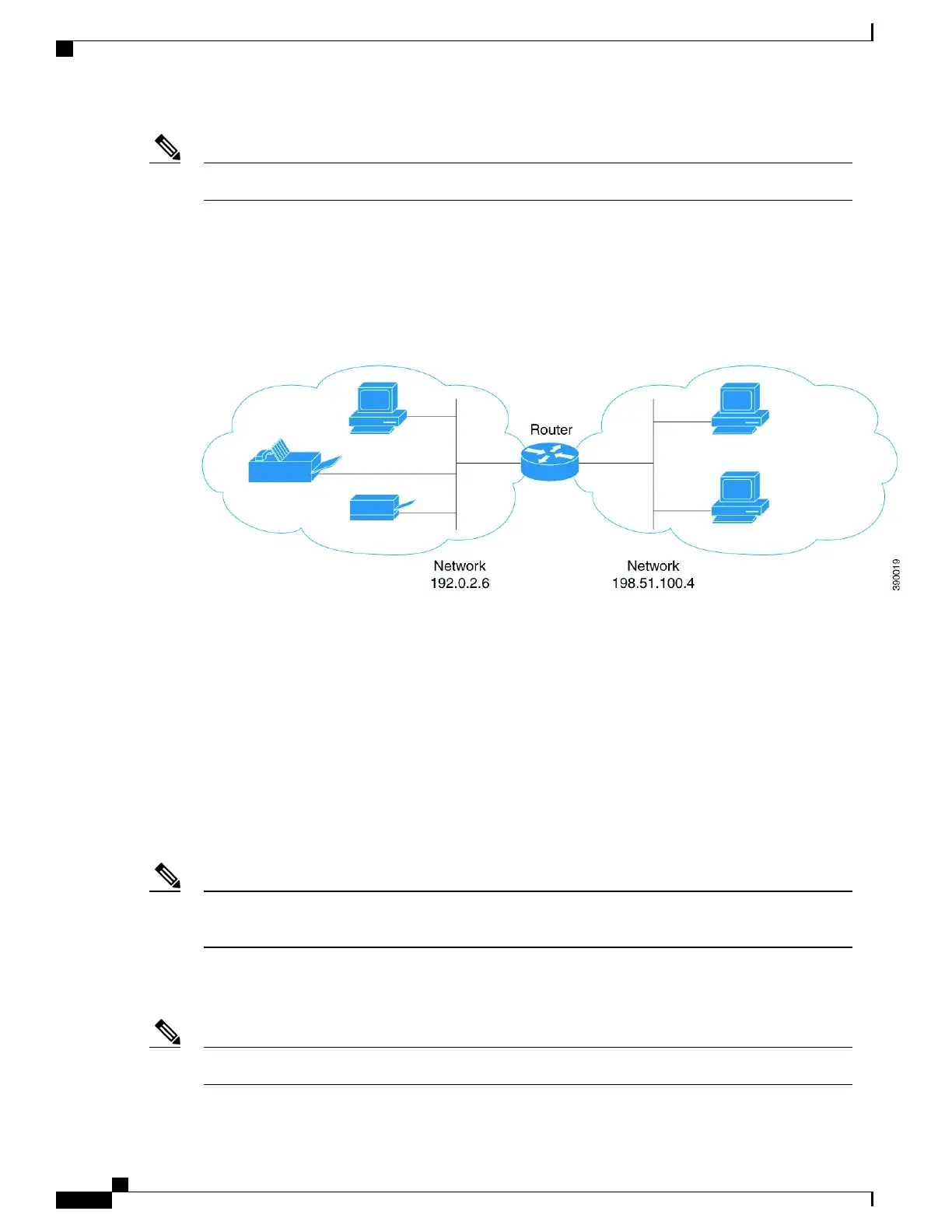
For example, if the mDNS gateway functionality is enabled on the router in this figure, then service information
can be sent from one subnet to another and vice-versa. For example, the printer and fax service information
being advertised in the network with IP address 192.0.2.6 are redistributed to the network with IP address
198.51.100.4. The printer and fax service information in the network with IP address 192.0.2.6 is learned by
mDNS-enabled hosts and devices in the other network.
Figure 15: Sample Networking Scenario
Filtering
After configuring the mDNS gateway and subnets, you can filter services that you want to redistribute. While
creating a service list, the permit or deny command options are used:
•
The permit command option allows you to permit or transport specific service list information.
•
The deny option allows you to deny service list information that is available to be transported to other
subnets.
You need to include a sequence number when using the permit or deny command option. The same service
list name can be associated with multiple sequence numbers and each sequence number will be mapped to a
rule.
If no filters are configured, then the default action is to deny service list information to be transported
through the device or interface.
Note
Query is another option provided when creating service lists. You can create queries using a service list. If
you want to browse for a service, then active queries can be used. This function is helpful to keep the records
refreshed in the cache.
Active queries can only be used globally and cannot be used at the interface level.Note
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
312 OL-32598-01
Configuring the Service Discovery Gateway
Service Discovery Gateway
 Loading...
Loading...











