
 Loading...
Loading...
Do you have a question about the Fuji Electric frenic mini series and is the answer not in the manual?
| Output Frequency | 0.1 to 400 Hz |
|---|---|
| Control Method | V/F control, Sensorless vector control |
| Cooling Method | Fan cooling |
| Model | Frenic Mini series |
| Overload Capacity | 150% for 60 seconds |
| Protection | Overcurrent, Overvoltage, Undervoltage, Overheating, Short circuit |
| Communication | RS-485 (Modbus RTU) |
| Ambient Temperature | -10°C to +50°C (non-freezing) |
| Humidity | 95% (non-condensing) |
| Altitude | Up to 1000 m above sea level |
| Input Voltage | 200 to 240 VAC, 380 to 480 VAC |
| Braking Unit | Built-in (optional external for higher power models) |
Details key inverter features like optimum performance, braking resistor, and stable operation.
Details how to run/stop the motor, set frequency, and monitor running status.
Covers setting function codes, checking data, monitoring status, and maintenance info.
Explains how the inverter enters Alarm mode and handles alarm conditions.
Guides on selecting motors and inverters considering load and operational requirements.
Provides a procedure for selecting appropriate braking resistors based on requirements.
Explains various protective functions, their LED displays, and related function codes.
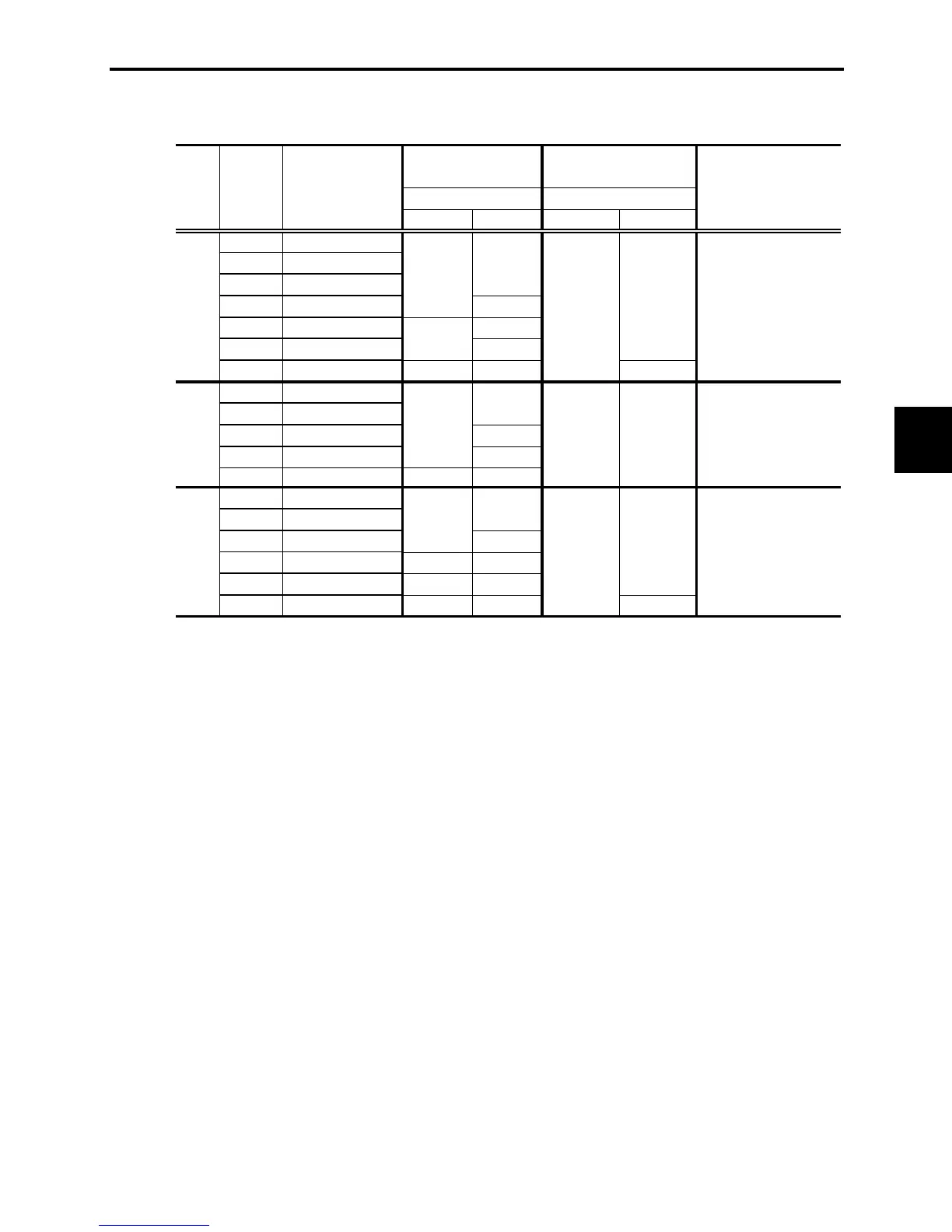
Provides tables summarizing function codes, their data ranges, and settings.
Offers detailed explanations for each function code group (F, E, C, P, H, J, y).











