6-4 ● Setting Communication Environment
6.2.2 Transmission Specifications
(1) Communication method: Half duplex
(2) Startup method: Started up by host
(3) Synchronization method: Asynchronous
(4) Transmission method: Bit serial transmission
(5) Baud rate: 150, 300, 600, 1,200, 2,400, 4,800, 9,600, 19,200, 38,400(bps)
(6) Codes transmitted: Alphanumerical characters, symbols, dedicated
characters, user pattern characters, and punctuation characters
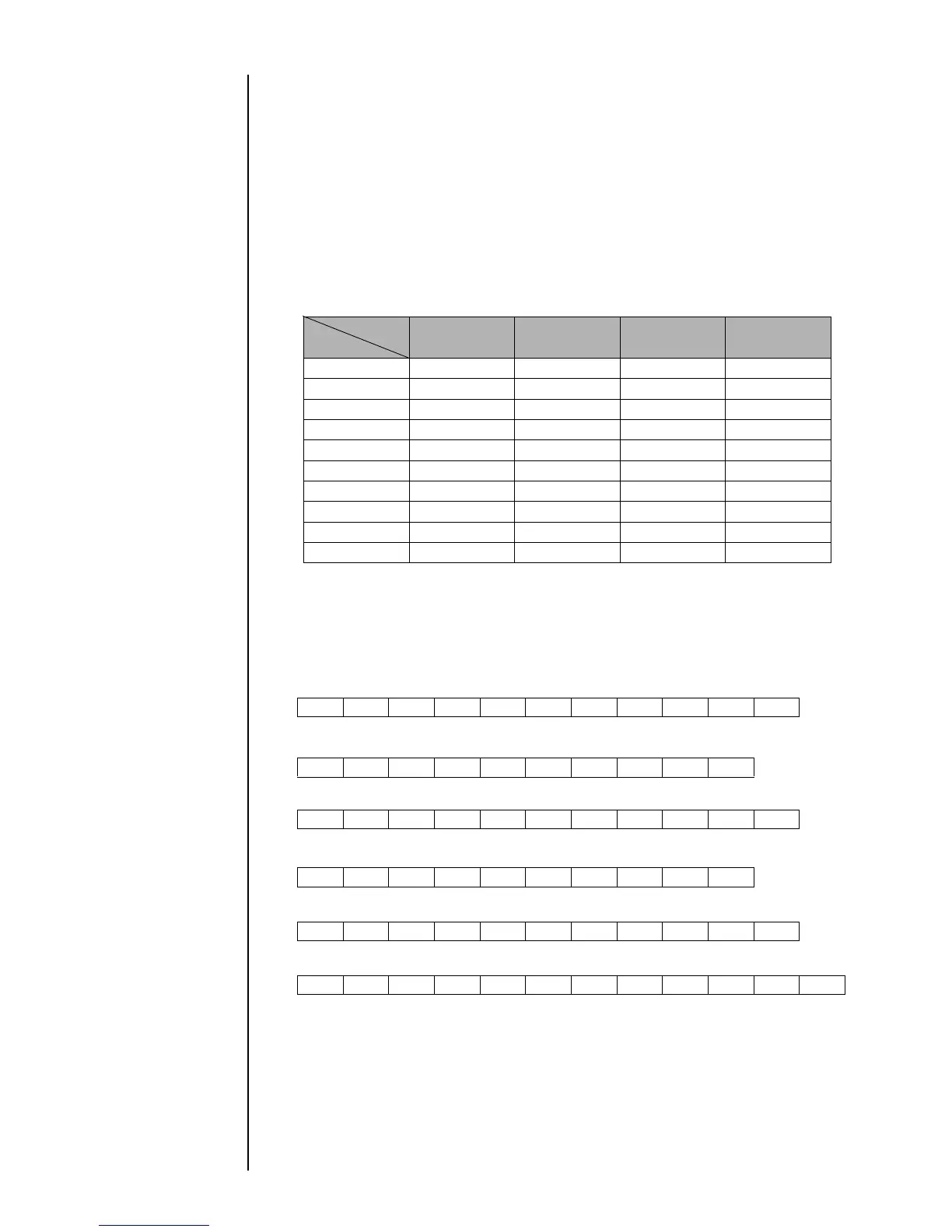
(7) Data format: Formats A through J are selectable (see the table below).
No other formats can be chosen.
Data format table
Item Start bit Data length Parity bit Stop bits
Format (bits) (bits) (bits) (bits)
A171 (even)2
B171 (odd)2
C171 (even)1
D171 (odd)1
E18None2
F (default) 1 8 None 1
G181 (even)1
H181 (odd)1
I181 (even)2
J181 (odd)2
Selecting a data length of 7 bits allows you to transmit alphanumerical characters and
symbols but inhibits you from transmitting punctuation characters and using 2-byte
codes to send dedicated characters and user pattern characters.
(8) Bit configuration
Formats A and B
Start b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 Parity Stop Stop
Formats C and D
Start b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 Parity Stop
Format E
Start b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 Stop Stop
Format F
Start b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 Stop
Formats G and H
Start b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 Parity Stop
Formats I and J
Start b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 b7 Parity Stop Stop
Order of code transmission: Transmission occurs beginning with the least significant
bit (b0).
(9) Error control
● Vertical parity error (detection on an individual character basis)
● Overrun error
● Framing error
 Loading...
Loading...