13 / 100
Siemens Commissioning Guide CM1G5192en
Building Technologies 4 EMC-compatible installation of SED2 29.07.2010
4.4 EMC-compatible wiring
• Use only shielded cables for the motor. The shielding should have the lowest possible HF impedance and must
be continuous
• Use only shielded cables for the signal, control and data lines (shielded twisted pair)
• The HF transfer resistance at the connecting points between shielding and housing should be kept as low as
possible
• Connect the shielding of motor and control cables to ground at both ends. For that purpose, use EMC cable
fittings (EMC fittings, EMC cable clamps, EMC terminals and similar that ensure 360° contact of shielding)
• Avoid high equalization currents on the shielding by ensuring a low-resistance (min. 16 mm
2
copper) and low-
impedance connection between VSD housing and ground (potential equalization rail)
• Connect the neutral conductor of the motor controlled by the VSD directly to the earth connection (PE) of the
associated VSD
• Avoid cable loops
• Supply power to all devices in a starlike pattern
4.4.1 Potential equalization and earthing
• Connect all electrical components separately (starlike) to potential equalization
• VSDs using filters produce discharge currents which, in the event of fault (e.g. mains failure), can significantly
exceed rated currents. To avoid dangerous voltages, all VSDs of protection class IP54 or IP20 must therefore
be earthed via the metal frame or the earth terminal
. In the case of discharge currents exceeding 3.5 mA,
one of the 3 following criteria must be satisfied to ensure compliance with EN 50178 and EN 60335: Either
− the potential equalization line must have a cross-sectional area of at least 10 mm
2
, or
− the potential equalization line must be monitored for disruptions, or
− a second potential equalization line must be installed
Since discharge currents represent high-frequency disturbance variables, earthing must always be of low
resistance using large surfaces and the shortest path from the VSD to earthing or the potential equalization
line.
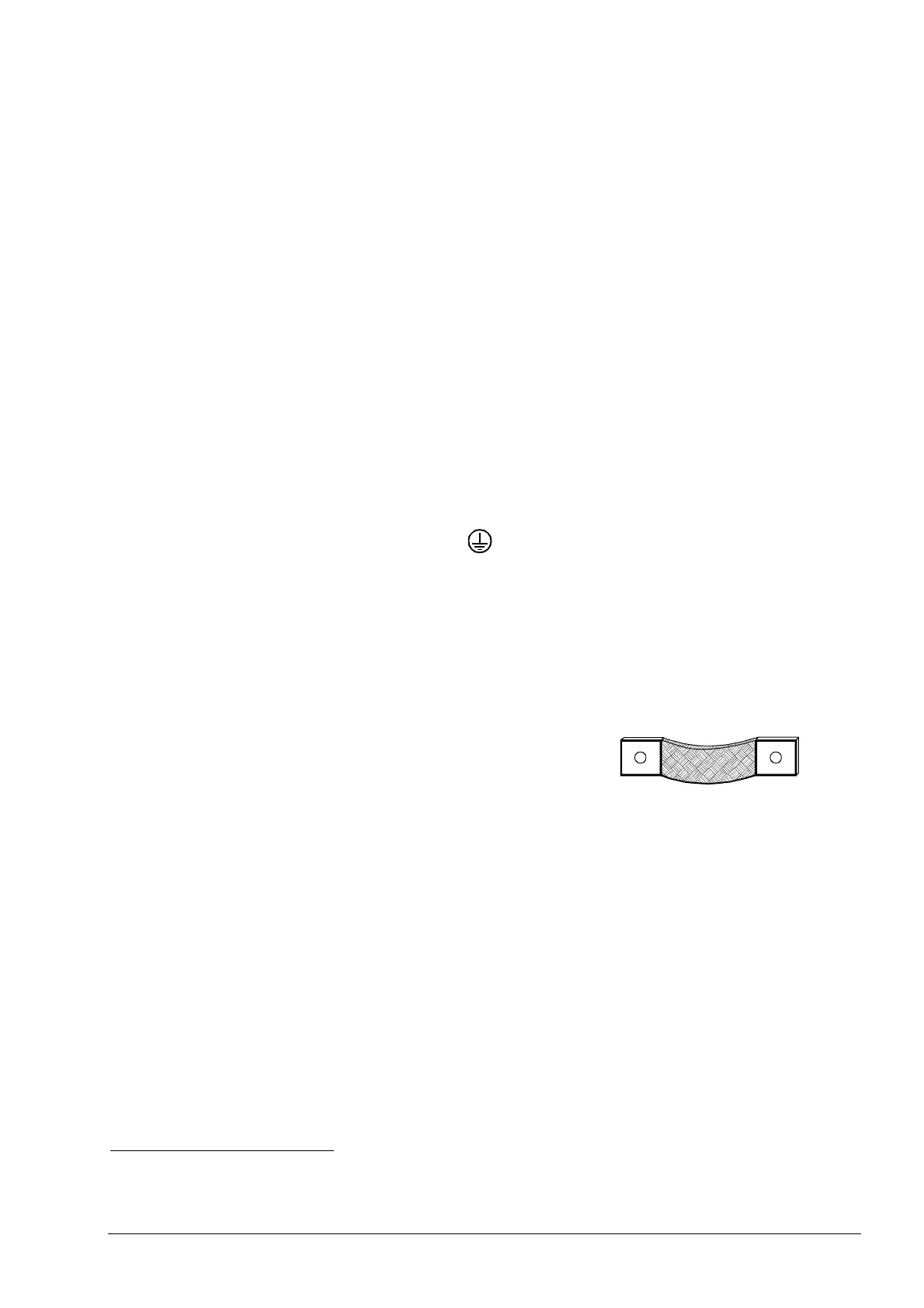
• For potential equalization lines, use flat, ribbon type conductors,
tin-plated copper mesh or similar (cross-sectional area at least
16 mm
2
) as they have a lower impedance at high frequencies
• Connect each motor controlled by the VSD to the ground or earthing point of the monoblock, also using a
potential equalization line having a large cross-sectional area (refer to illustrations on pages 15 and 16)
• Ensure that e
ach piece of control equipment (e.g. a PLC or a BACS
1
) connected to the VSD is connected to the
same ground or same earthing point as the VSD using a short potential equalization line (potential equalization
rail)
1
PLC: Programmable Logic Controller
BACS: Building Automation and Control System
 Loading...
Loading...
















