12-8
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers SIP and SPA Software Configuration Guide
OL-14127-08
Chapter 12 Overview of the POS SPAs
SPA Architecture
Path of a Packet in the Egress Direction
The following steps describe the path of an egress packet through the 2-Port OC-48c/STM-16 POS SPA:
1. The host sends packets to the SPA using the SPI4.2 bus.
2. The SPA stores the data in the appropriate SPI4 channel’s first-in first-out (FIFO) queue.
3. The SPA passes the packet from the SPI4 interface to the POS processor where it is encapsulated in
a POS frame and FCS is added.
4. The POS frame is sent to the SONET/SDH framer where it is placed into the SONET payload.
5. The framer adds the FCS and SONET/SDH overhead.
6. The framer sends the data to the SFP optics for transmission onto the network.
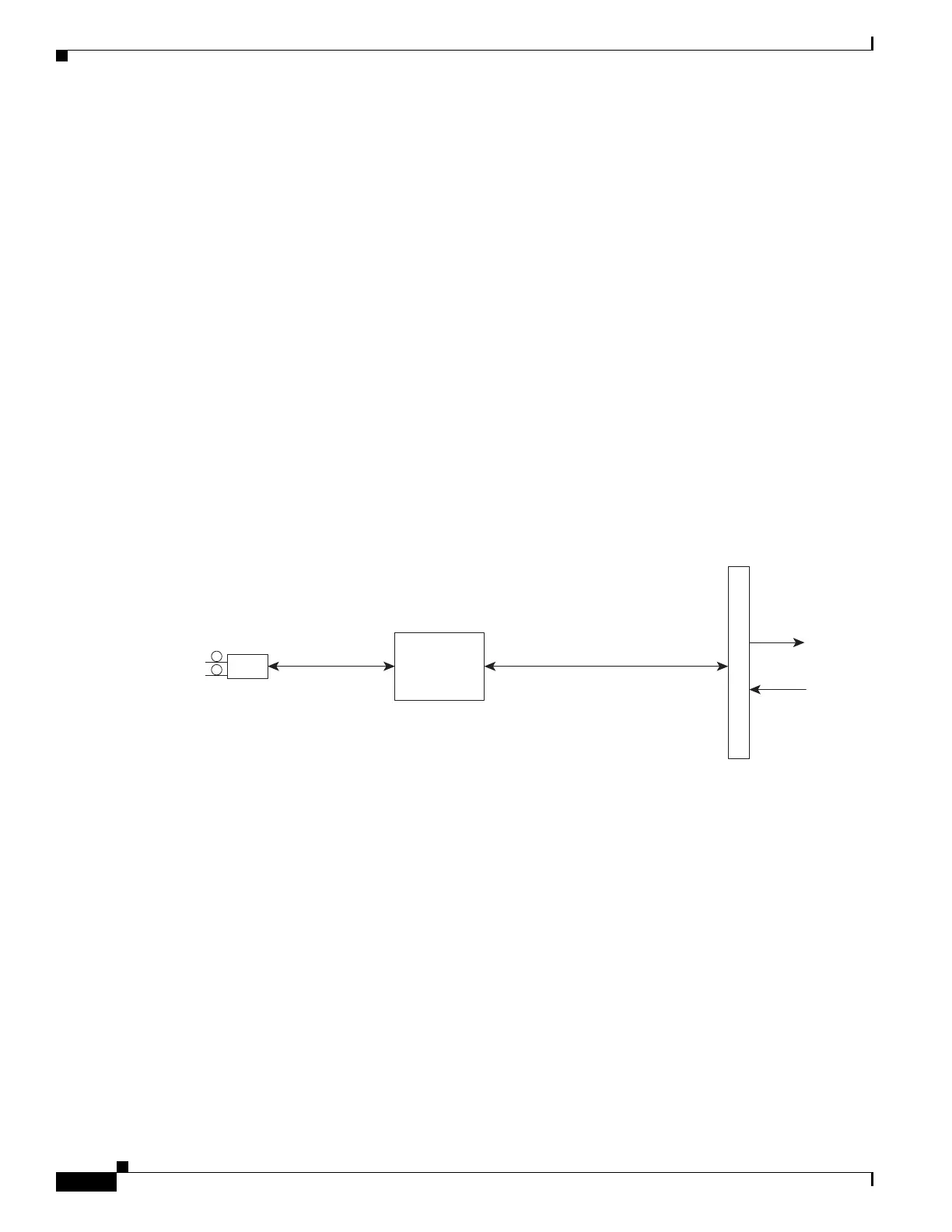
1-Port OC-192c/STM-64 POS XFP SPA Architecture
Figure 3 identifies the primary hardware devices that are part of the POS SPA architecture. The figure
shows a single optics transceiver. The 1-Port OC-192c/STM-64 POS XFP SPA supports XFP optics.
Figure 3 1-Port OC-192c/STM-64 POS XFP SPA Architecture
In POS mode, every incoming and outgoing packet on the OC-192 POS SPAs goes through the
SONET/SDH framer and SPI4.2 interface.
Path of a Packet in the Ingress Direction
The following steps describe the path of an ingress packet through the 1-Port OC-192c/STM-64 POS
XFP SPA:
1. The framer receives SONET/SDH streams from the XFP optics, extracts clocking and data, and
processes the section, line, and path overhead.
2. The framer extracts the POS frame payload and verifies the frame size and frame check sequence
(FCS).
3. The framer passes valid frames to the System Packet Level Interface 4.2 (SPI4.2) interface on the
SPA.
4. The SPI4.2 interface transfers frames to the host through the SPI4.2 bus for further processing and
switching.
SONET/SDH
Streams
Optics
Transceiver
SPI4.2 Bus
Packets
SONET/SDH
Framer
SPA
Connector
To
Host
From
129796

 Loading...
Loading...











