You can use unique rate settings for each function when using the front panel or the remote interface.
Rate cannot be set for continuity. The continuity rate is fixed at 0.006 PLC.
The Series 3700A uses internal references to calculate an accurate and stable reading. When the
NPLC setting is changed, each reference is automatically updated to the new NPLC setting before a
reading is generated. Therefore, frequent NPLC setting changes can result in slower measurement
speed.
Setting Rate from the front panel
The RATE key sets measurement speed from the front panel. Press the RATE key until the speed
message is displayed. The second line of the display contains the NPLC setting.
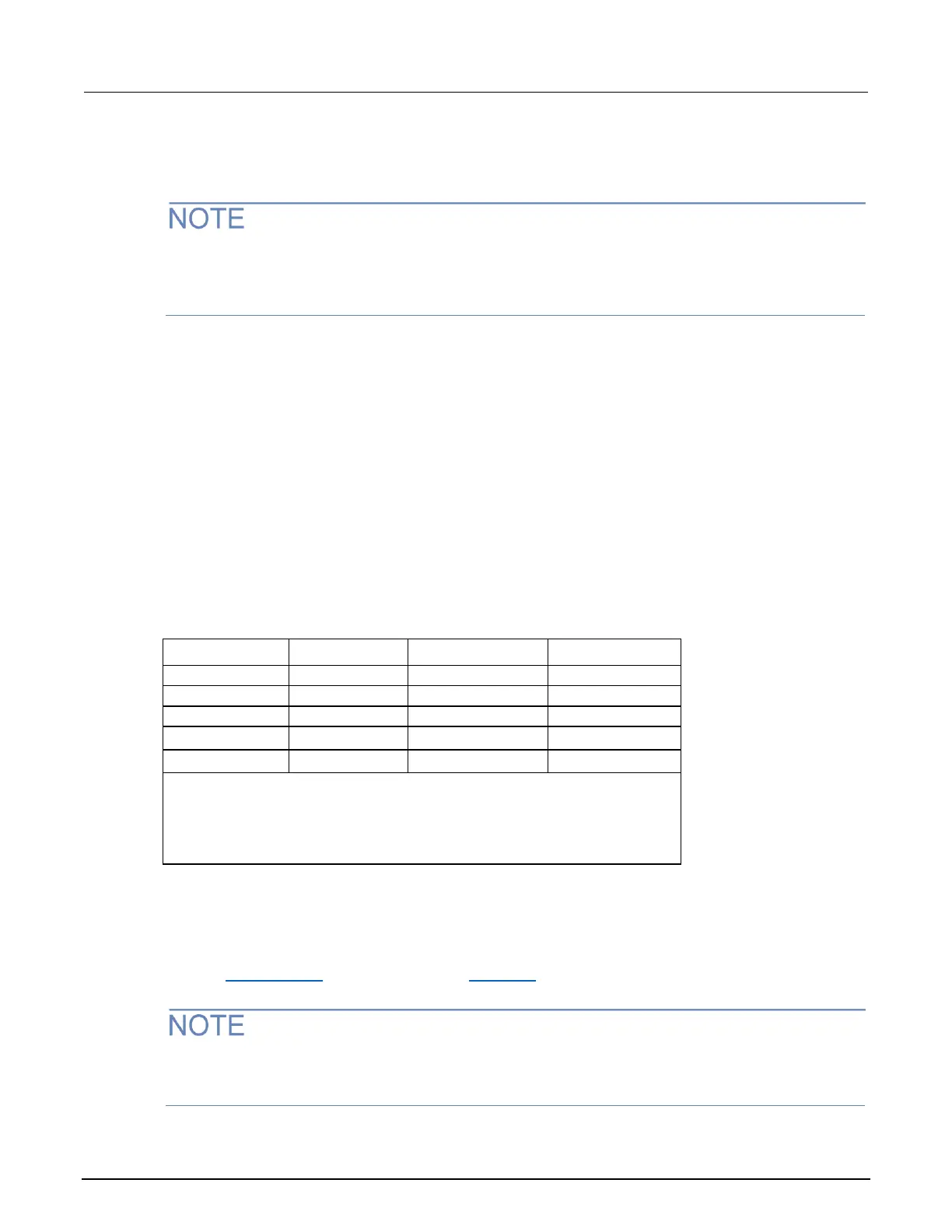
The front panel rate settings for all but the AC functions are as follows:
• FAST sets integration time to 0.1 PLC. Use FAST if speed is of primary importance (at the
expense of increased reading noise and fewer usable digits).
• MED sets integration time to a medium rate of 1 PLC. Use MED when a compromise between
noise performance and speed is acceptable.
• SLOW sets integration time to 5 PLC. SLOW provides better noise performance at the expense
of speed.
For the AC functions (ACV, ACV dB, and ACI), the RATE key sets integration time and bandwidth.
FAST sets NPLC to 1, while the MED and SLOW NPLC settings are ignored.
A summary of the rate settings are shown in the following table.
NOTES:
NPLC = Number of power line cycles.
BW = Bandwidth (in Hz).
APER = Aperture in seconds.
X = Setting ignored (fixed NPLC).
You can also set the rate using the NPLC option in the function attribute menu. Press CONFIG, then
DMM to display the function attribute menu. From the function attribute menu, select NPLC to select
a specific value for NPLC.
Setting measurement speed from a remote interface
Use the dmm.aperture (on page 11-145) or dmm.nplc (on page 11-209) command to set the
measurement speed (integration time) through the remote interface.
For dmm.nplc settings that are less than 0.2 power line cycles, sending dmm.AUTOZERO_ONCE
results in significant delays. For example, the delay time at a NPLC of 0.0005 is 2.75 s. The delay
time at 0.199 is 5.45 s.

 Loading...
Loading...