Planning wireless systems
105542_en_05 PHOENIX CONTACT 133 / 198
8.7 Selecting antenna cables and antennas
When installing a wireless system, it is very important that you use low-loss coaxial cables.
Using an unsuitable cable may lead to considerable loss in performance which cannot be
compensated by high antenna gain or by high transmission power. For every 3 dB of coaxial
cable loss, half the transmission power will be lost before reaching the antenna. The re-
ceived signal will also be reduced.
Consider the following factors when selecting the cable:
– Cable length to the antenna
– Acceptable signal loss
– Options for routing the cables
Antennas
• Select the antenna according to the wireless system and the required range.
In addition, the different antenna types are suitable for the following areas of application:
Omnidirectional antenna
– Numerous devices in different directions, e.g., in mesh networks or networks with
repeaters
– Freely mobile applications
– Applications without a line of sight
In reflective environments the signal can be received via an indirect route.
Directional antenna
– Large distances
– Point-to-point connections
– Stationary or linear mobile applications
– Multiple point-to-point paths, decoupling due to directivity and different polarization
levels (see Figure 8-7)
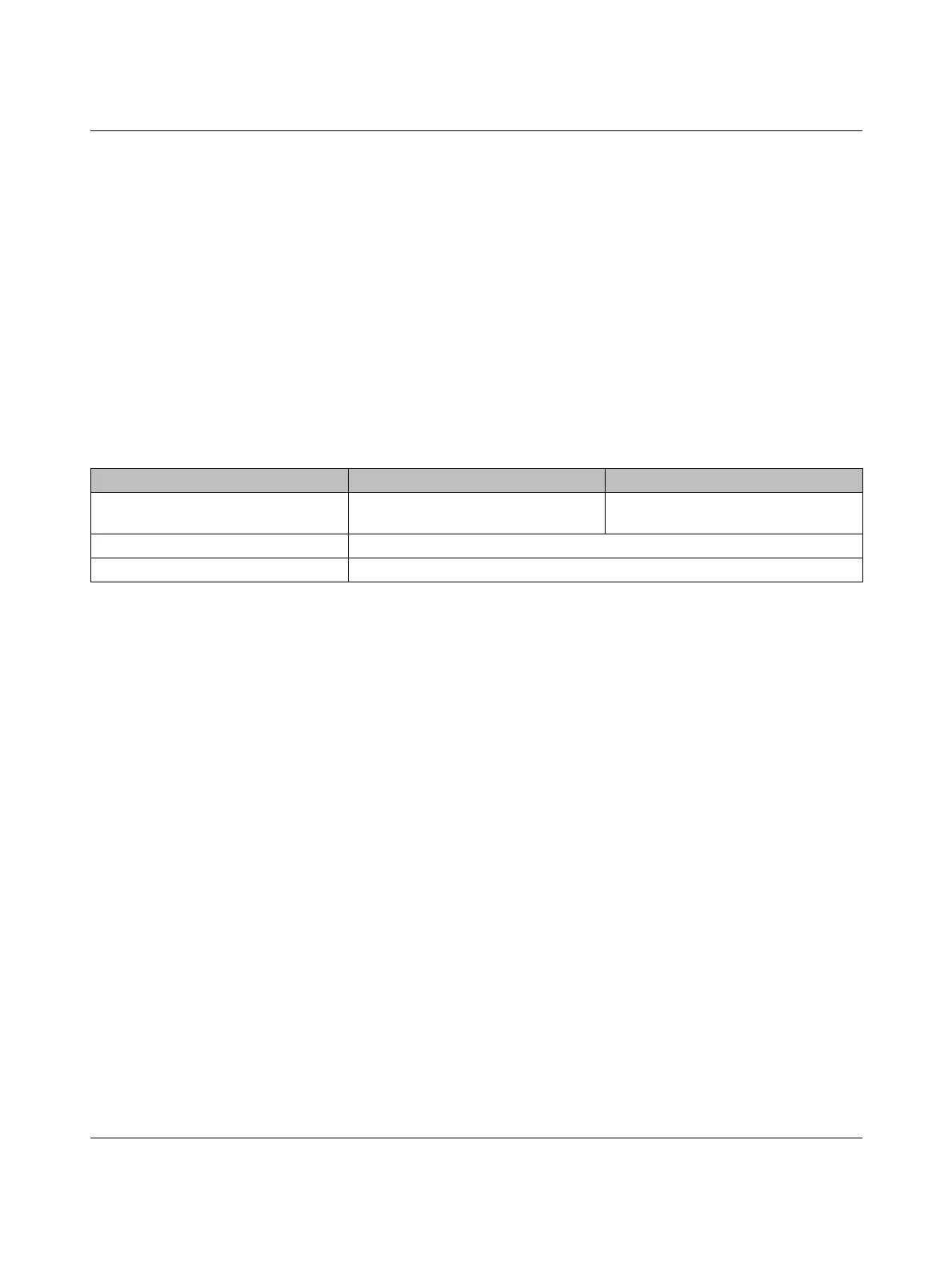
Table 8-2 Application of antennas
Range Antenna, 2.4 GHz Antenna, 868 MHz
Short range and direct line of sight
without any obstacles
Small omnidirectional antenna -
Medium range Large omnidirectional antenna (note the vertical opening angle)
Long range Directional antenna (note the small horizontal opening angle)

 Loading...
Loading...