TURBOCHARGER SYSTEM - Description TC-3
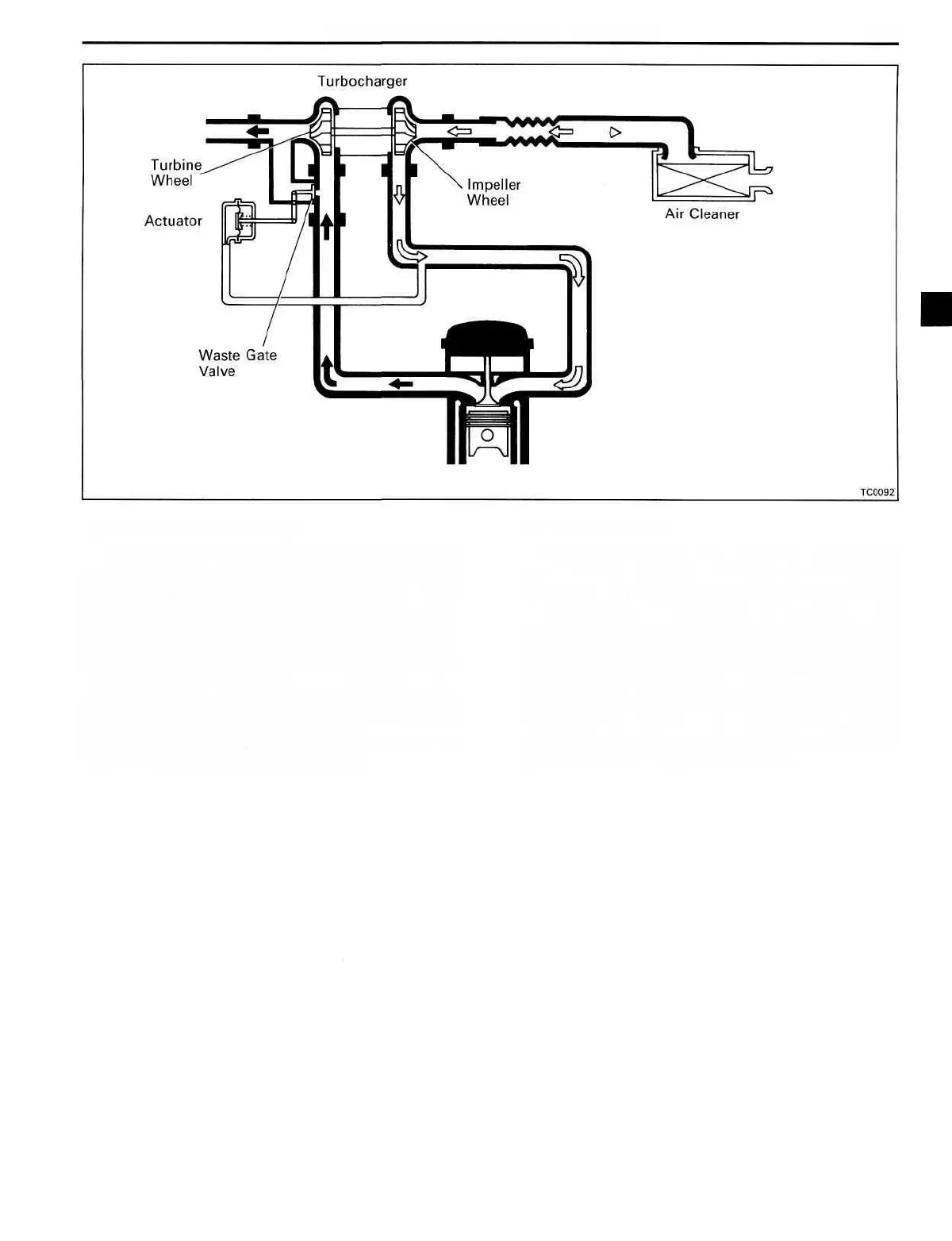
Operation of Turbocharger
Exhaust gas acts on the turbine wheel inside the
turbine housing, causing it to revolve. When the
turbine wheel revolves, the impeller wheel which
is located on the same shaft also revolves, com-
pressing the intake air which has passed through
the air cleaner. When expelled from the compres-
sor housing the compressed air is supplied to the
cylinders. When the engine speed increases, the
exhaust gas volume increases and the turbine wheel
revolutions increasa (approx. 20,000 — 11 5,000
rpm), thus the turbocharged air pressure grows
greater and engine output increases.
Waste Gate Valve
If the turbocharged air pressure exceeds the
prescribed air pressure, the flow of exhaust gas
by-passes the turbine, controlling turbine wheel
revolutions and turbocharged air pressure. This
by-pass valve which controls the quantity of ex-
haust gas flowing to the turbine is called the waste
gate valve. When the charged air pressure exceeds
the prescribed pressure, the actuator operates, the
waste gate valve opens and part of the exhaust gas
by-passes the turbine. This causes a drop in the
turbine revolution rate and controls the charged air
pressure within the prescribed limits.
 Loading...
Loading...