5 Loop Protection
5.1 Loop Fundamentals
In a network, a loop can be understood as more than one Layer 2 connection paths
between endpoints. Typical examples of loop is connecting two switches using more
than one port, as occurs in a ring topology, or connecting a port to another port of
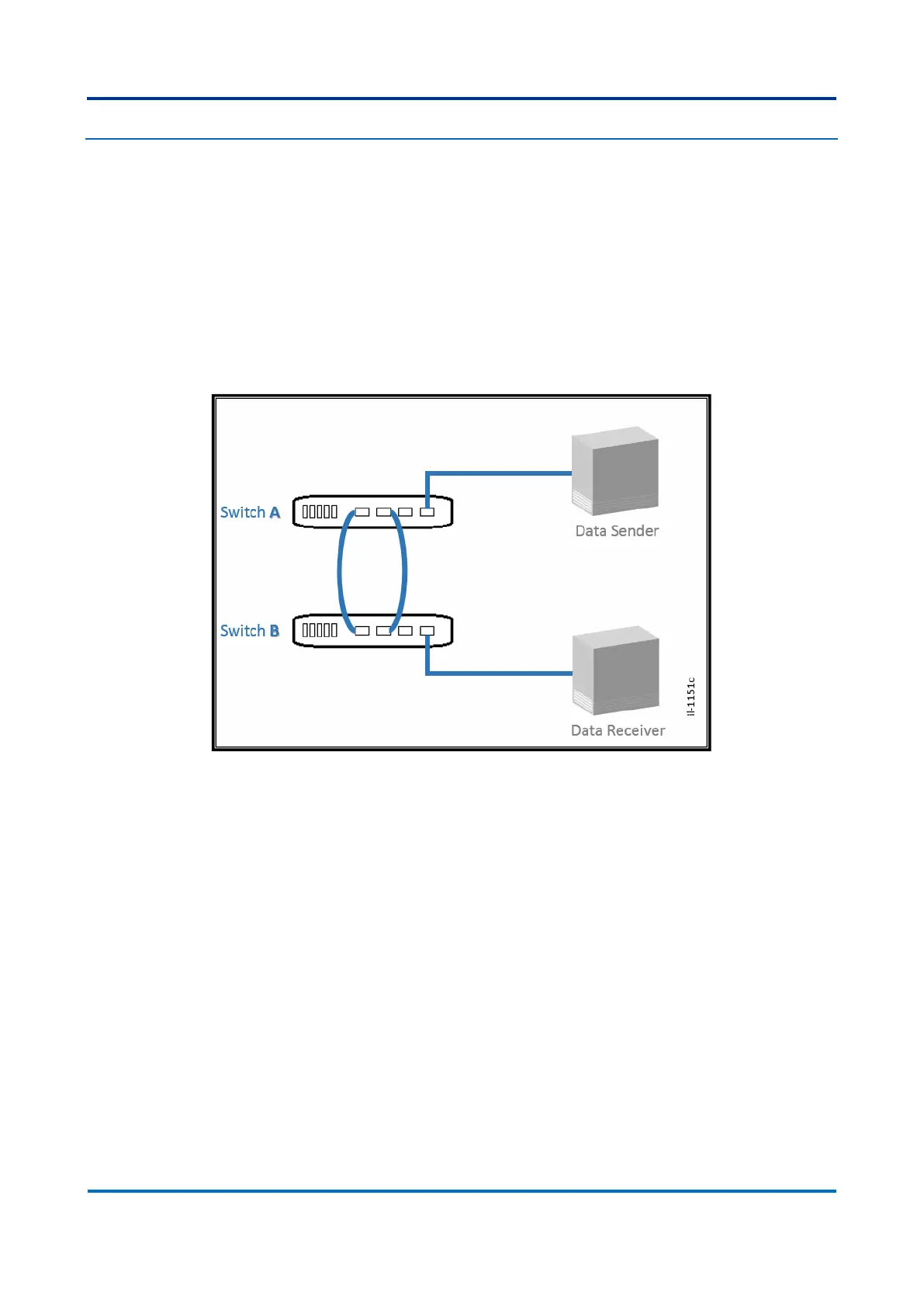
the same switch. The figure below exemplifies a loop topology.
Figure 13: Bridge Loop
In the bridge loop given, there are three main problems:
Unicast frame duplication;
Multicast frame flooding;
Address table non convergence.
If the Data Sender starts transmitting data to the Receiver, switch A will understand
that the Receiver is in two different ports, and thus will send data through both ports.
Switch B will map MAC address of the Receiver at two ports and thus will send it from
both. This behavior will insert duplicate frames for each data transmitted, which can
cause undesirable behavior of nodes, like an application crash.
If the Data Sender starts a multicast communication, the link between the switches
would become quickly saturated. As the switch operates as a transparent bridge,
 Loading...
Loading...