7 IPMC
7.1 IP Multicast (IPMC)
IP communication, just as Ethernet communication, allows the devices in a network
to send packets to a single host or to all hosts, in unicast or broadcast transmission,
respectively. There are several applications that have a logical architecture of one
sender to a set of receivers, such as PMU applications. To fill that kind of applications,
the IP Multicast (IPMC) transmission is used
Be aware when using distinct layer protocols with the Multicast transmission mechanism. There are layer 2 and layer 3
multicast possibilities when it comes to power system basic communication.
Phasor Measurement Units use UDP protocol to send data throughout the network. Thus, in this context, multicast messages
are messages sent to an IP address inside a range of IP addresses defined as multicast addresses.
GOOSE, Sampled Values and PTP messages are mapped directly at the Ethernet frame, and the Multicast mechanism is assured
by its MAC address destination. This means these messages cannot be directly routed (e. g., they cannot be transmitted in their
original form over WANs), and they are sent to a MAC address, which is not the end node MAC address, but the multicast MAC
address.
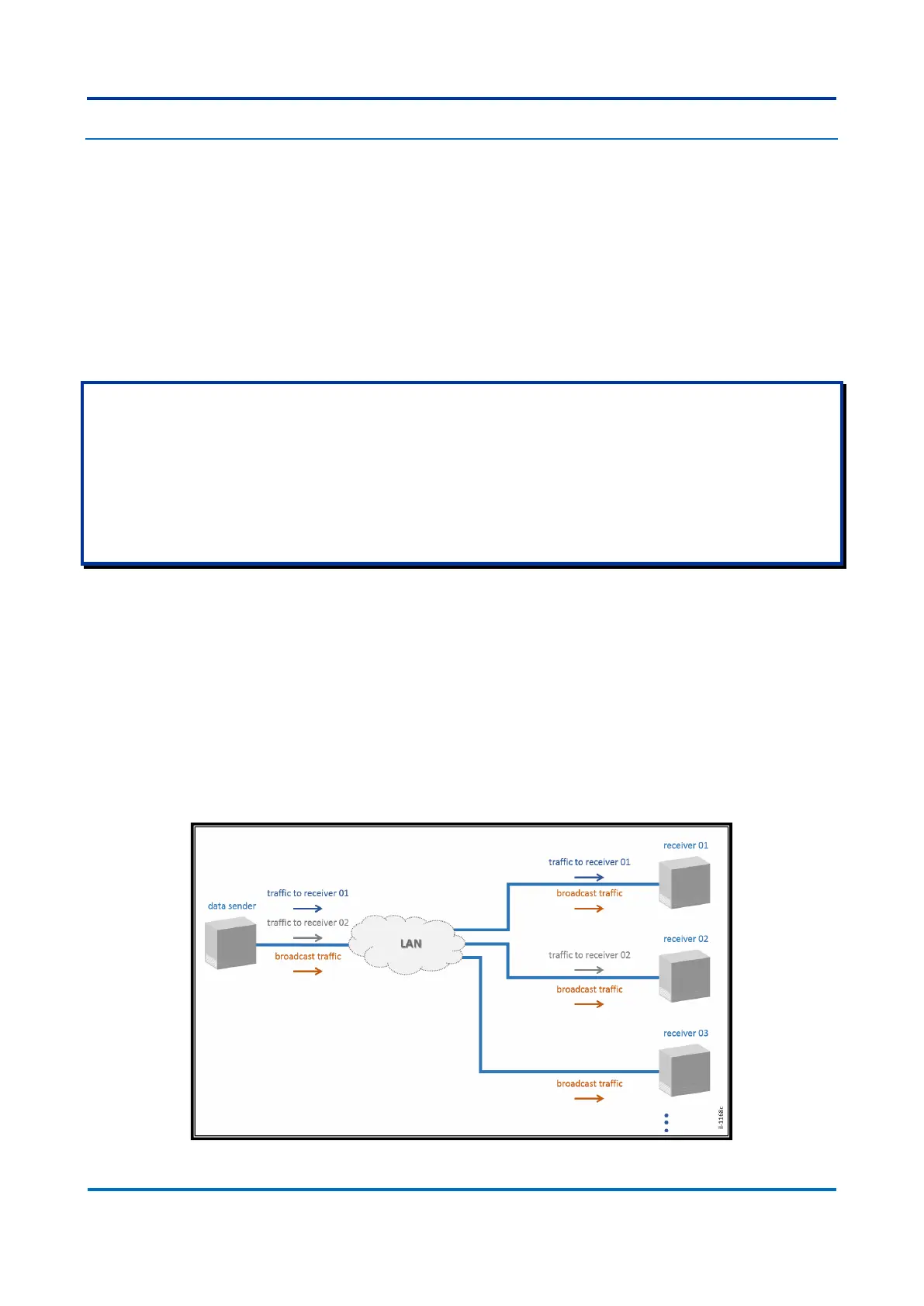
The figures below illustrate unicast, broadcast and multicast communication. Both
figures show a set of users expecting messages from one sender. As expected,
unicast transmission is from one sender to a specific receiver. In broadcast, the
message is sent to all receivers in the subnet.
Using mullticast filters, the equipment that is not expecting these messages don't
receive it, different from the broadcast transmission, where broadcast messages are
forwarded to all nodes in a given LAN. Without multicast filtering, multicast messages
are sent just as broadcast messages, but the nodes that don't expect multicast
messages don't process it. On the other hand, broadcast messages are always
processed by the nodes.
Figure 33: Unicast and Broadcast communication
 Loading...
Loading...