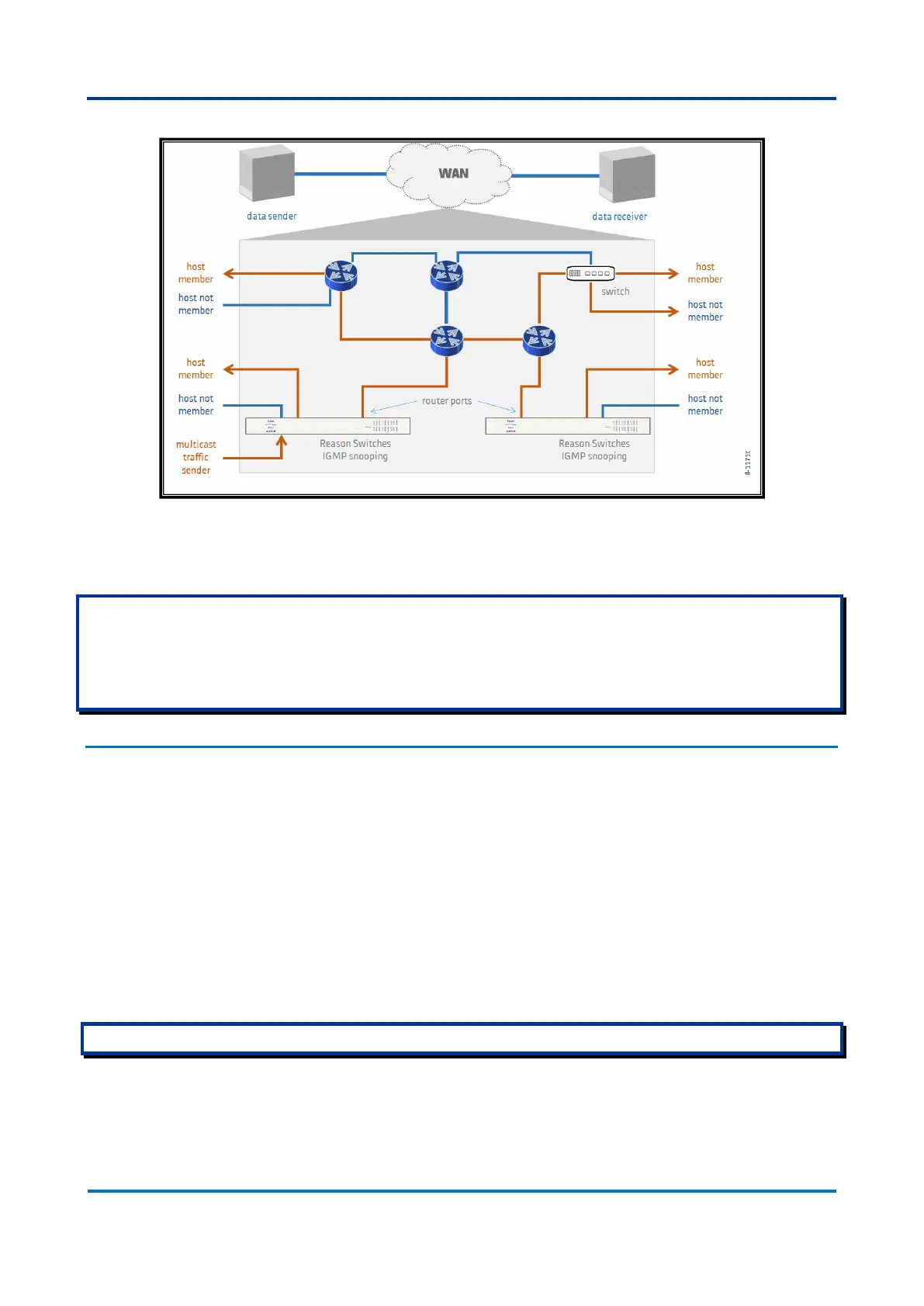
Figure 36: IGMP Snooping at a given LAN
IGMP snooping function is associated to the VLAN at Reason Switches. If there is no VLAN usage at the network, the IGMP
Snooping VLAN must be configured to operate at VLAN ID (VID) “1”.
If IGMP multicast protocol is used, be sure that all equipment at the Local or Wide Area Network have support to IGMP protocol,
and be sure that they have support to the same version of IGMP. Reason Switches have support to IGMPv1, IGMPv2 and IGMPv3
protocols.
7.3 MLD Snooping
Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) is a part of ICMPv6 protocol. It was defined at the
RFC 2710 (version 1) and then upgraded to version 2 through RFC 3810. Its usage is
much like IGMP, but instead of multicast transmission over IPv4 networks, MLD works
over IPv6 networks.
Protocol mechanism is very similar to IGMP. To be part of a group that is receiving a
multicast data from a sender, the MLD receiver must send a “join group” message,
which must be understood by MLD-aware layer 2 switches, such as Reason Switches,
and routers at the network. If it wants to stop receiving data, then a “leave group”
message must be sent.
MLD snooping can be understood, from an application point of view, as IGMP snooping for IPv6 networks.
When using this feature as multicast transmission function, all equipment at the
network (routers, switches) must be capable to read the IP packet headers and
inspect its multicast group. In case of layer 2 switches, multicast transmission
benefits can only be obtained if the switch can handle MLD snooping function. If not,
 Loading...
Loading...