HEIDENHAIN TNC 426, TNC 430 165
6.6 Path Contours—FK Free Contour Programming
Example NC blocks
Relative data
Data whose values are based on another contour element are called
relative data. The soft keys and program words for entries begin with
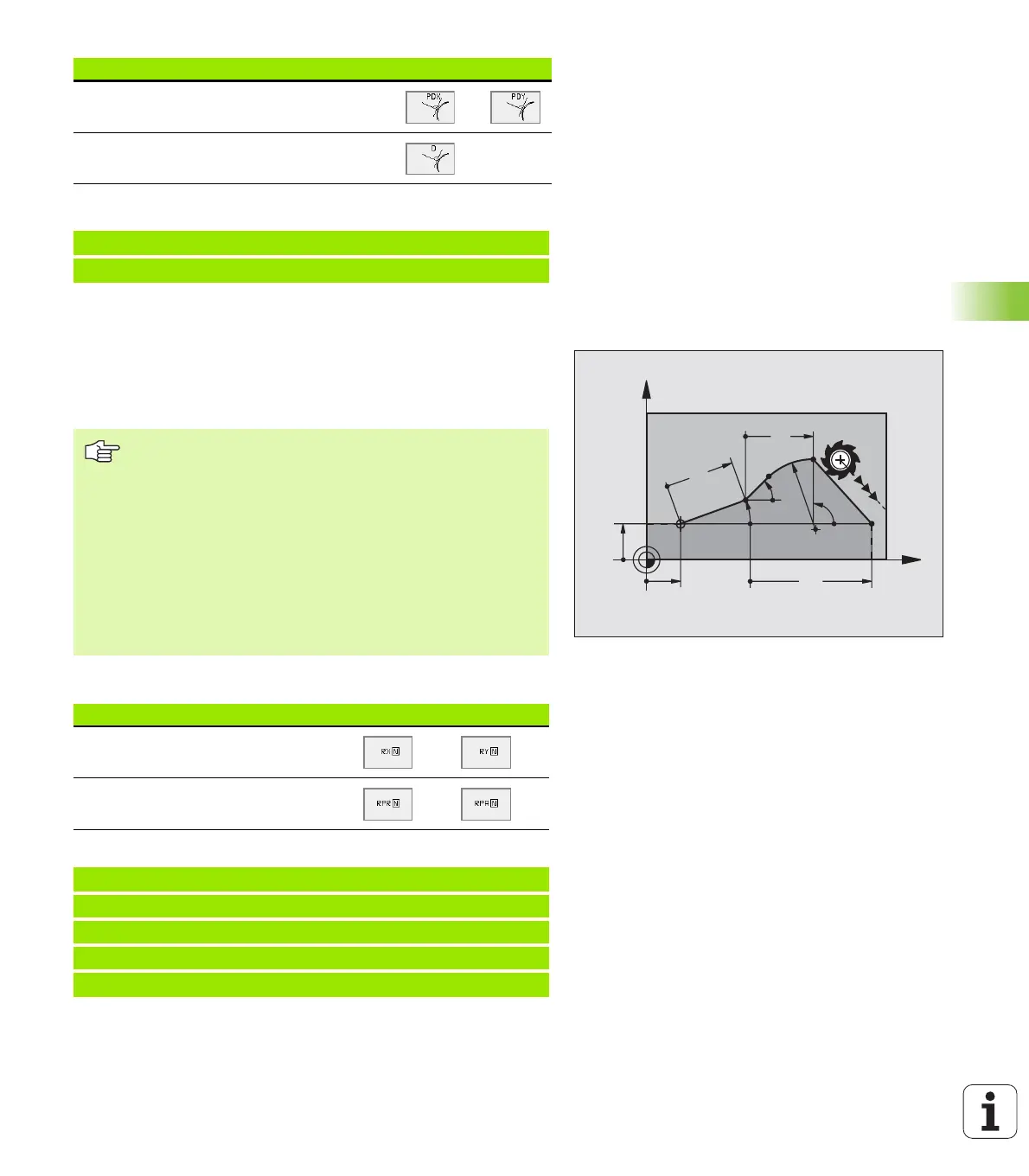
the letter “R” for Relative. The figure at right shows the entries that
should be programmed as relative data.
Data relative to block N: End point coordinates
Example NC blocks
X and Y coordinates of an auxiliary pointnear
a circular arc
Distance auxiliary point/circular arc
13 FC DR- R10 P1X+42.929 P1Y+60.071
14 FLT AN-70 PDX+50 PDY+53 D10
Known data Soft keys
The coordinates and angles for relative data are always
programmed in incremental dimensions. You must also
enter the block number of the contour element on which
the data are based.
The block number of the contour element on which the
relative data are based can only be located up to 64
positioning blocks before the block in which you program
the reference.
If you delete a block on which relative data are based, the
TNC will display an error message. Change the program
first before you delete the block.
Known data Soft keys
Cartesian coordinates
relative to block N
Polar coordinates relative to block N
12 FPOL X+10 Y+10
13 FL PR+20 PA+20
14 FL AN+45
15 FCT IX+20 DR– R20 CCA+90 RX 13
16 FL IPR+35 PA+0 RPR 13
X
Y
35
10
10
20°
R20
20
45°
20
FPOL
90°

 Loading...
Loading...