Full Command and Function Reference 3-43
Specifying 0 for x
key
clears all user key assignments and restores the standard key assignments.
Specifying S as the argument for DELKEYS suppresses all standard key assignments on the user
keyboard. This makes keys without user key assignments inactive on the user keyboard. (You can
make exceptions using ASN, or restore them all using STOKEYS.) If you are stuck in User
mode – probably with a “locked” keyboard – because you have reassigned or suppressed the
keys necessary to cancel User mode, do a system halt (“warm start”): press and hold ‡ and
C simultaneously, releasing C first. This cancels User mode. Deleted user key assignments
still take up from 2.5 to 62.5 bytes of memory each. You can free this memory by packing your
user key assignments by executing RCLKEYS 0 DELKEYS STOKEYS.
Access: !&H
KEYS DELKEYS
!°L MODES KEYS DELKEYS ( °is the left-shift of the Nkey).
Flags: User-Mode Lock (–61) and User Mode (–62) affect the status of the user keyboard.
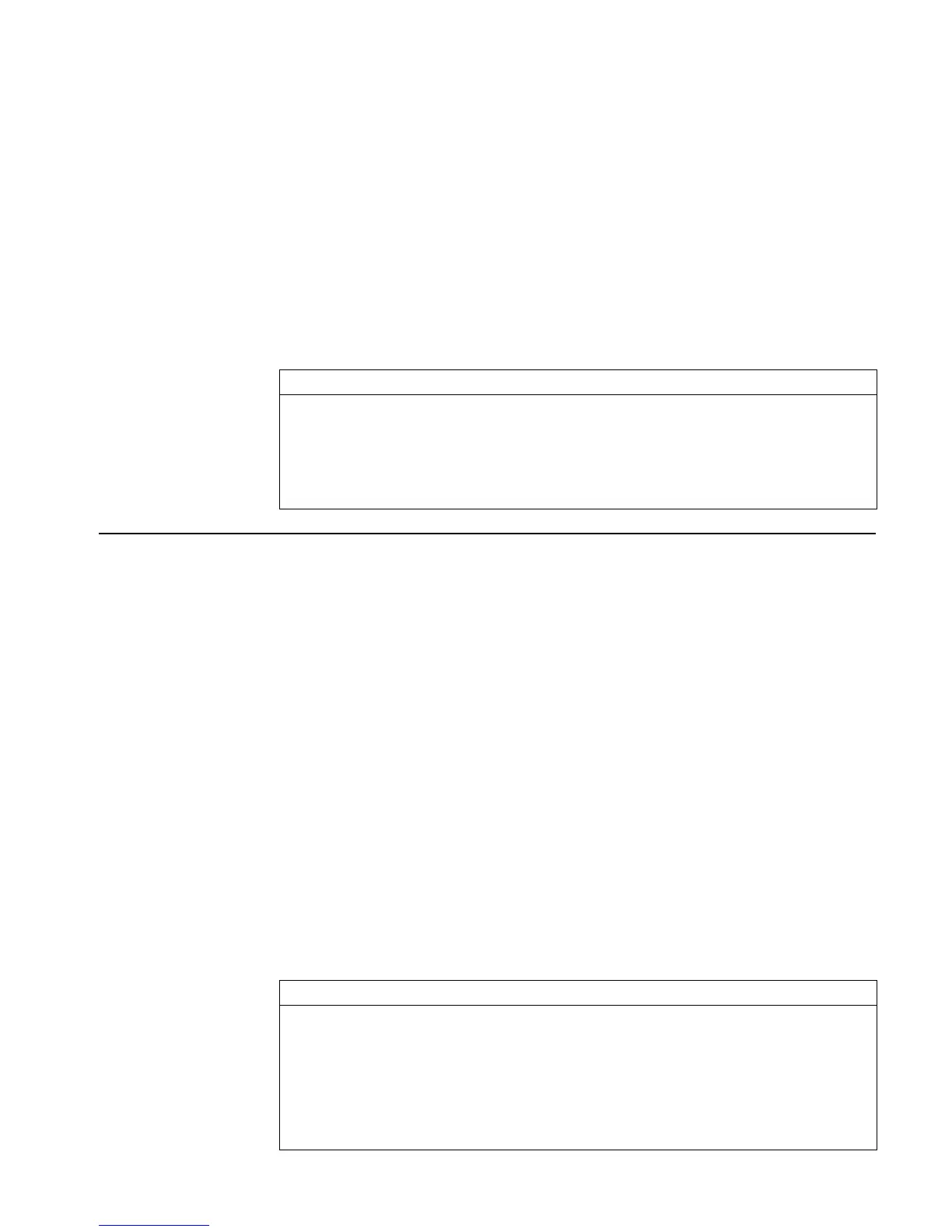
Input/Output:
Level 1/Argument 1 Level 1/Item 1
x
key
→
{ x
key1
, ... ,x
key n
}
→
0
→
'S'
→
See also: ASN, RCLKEYS, STOKEYS
DEPND
Type: Command
Description: Dependent Variable Command: Specifies the dependent variable (and its plotting range for
TRUTH plots).
The specification for the dependent variable name and its plotting range is stored in the reserved
variable PPAR as follows:
• If the argument is a global variable name, that name replaces the dependent variable entry in
PPAR.
• If the argument is a list containing a global name, that name replaces the dependent variable
name but leaves unchanged any existing plotting range.
• If the argument is a list containing a global name and two real numbers, or a list containing a
name, array, and real number, that list replaces the dependent variable entry.
• If the argument is a list containing two real numbers, or two real numbers from levels 1 and 2,
those two numbers specify a new plotting range, leaving the dependent variable name
unchanged. (LASTARG returns a list, even if the two numbers were entered separately.)
The default entry is Y.
The plotting range for the dependent variable is meaningful only for plot type TRUTH, where it
restricts the region for which the equation is tested, and for plot type DIFFEQ, where it specifies
the initial solution value and absolute error tolerance.
Access: …µ
DEPND
Input/Output:
Level 2/Argument 1 Level 1/Argument 2 Level 1/Item 1
'global'
→
{ global }
→
{ global, y
start
, y
end
}
→
{y
start
, y
end
}
→
y
start
y
end
→
 Loading...
Loading...