D - 8 Reserved Variables
The $RESET$ operation („&ôL %RESET% ) resets the PPAR parameters ( except ptype ) to their default
values, and erases PICT. (Note: the & means to press and hold the „key while pressing ô).
Note that res behaves differently for the statistical plot types BAR, HISTOGRAM, and SCATTER than for
other plot types. For BAR, res specifies bar width; for HISTOGRAM, res specifies bin width; res does not affect
SCATTER.
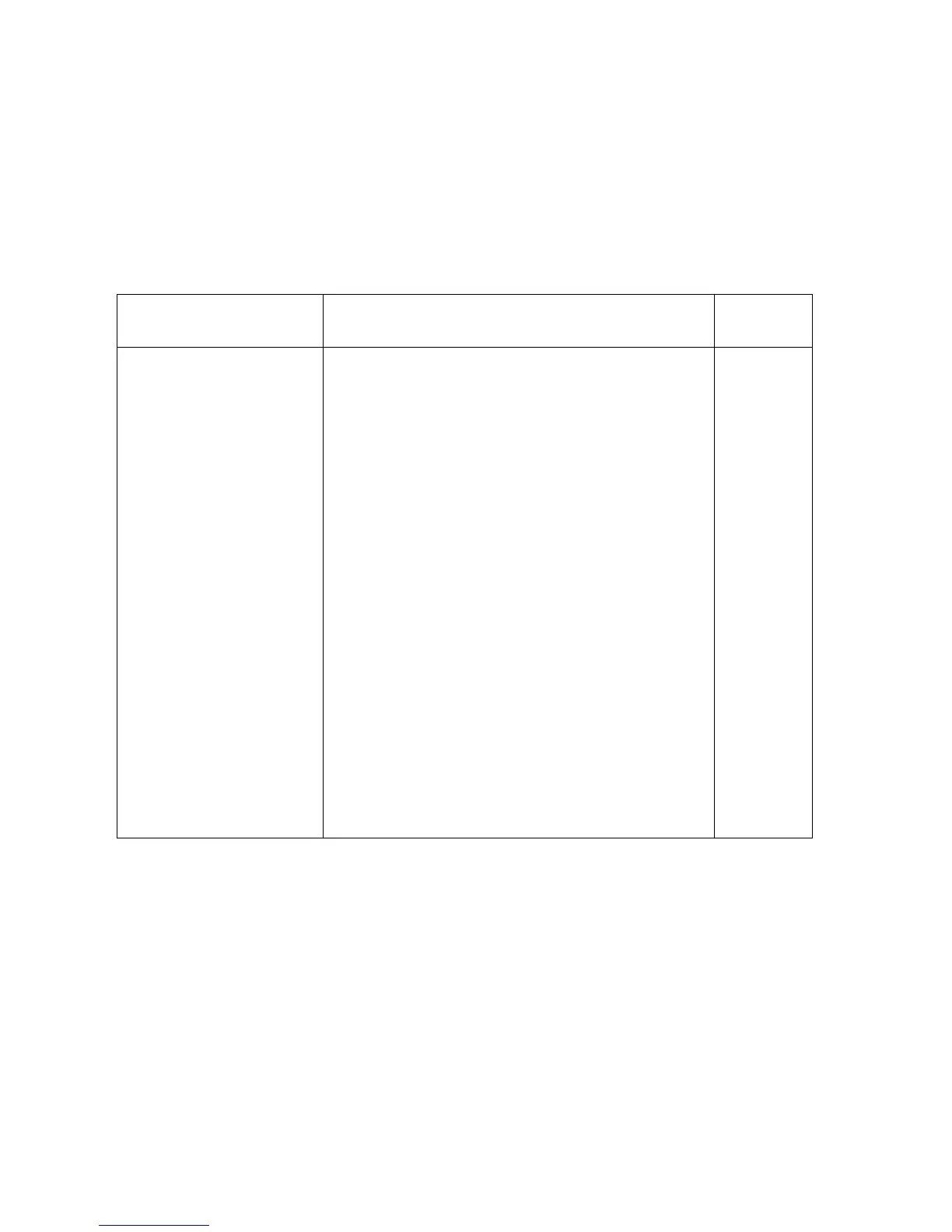
PRTPAR
PRTPAR is a variable in the HOME directory that contains a list of printing parameters. It is created
automatically the first time you use a printing command.
Parameter (Command) Description
Default
Value
delay time (DELAY)
A real number, in the range 0 to 6.9, specifying the
number of seconds the HP 49 waits between sending
lines. This should be at least as long as the time
required to print the longest line. If the delay is too
short for the printer, you will lose data. The delay
setting also affects serial printing if transmit-pacing
( in IOPAR ) is not being used.
1.8
remap (OLDPRT stores
the character-remapping
string for the HP 82240A
Infrared Printer)
A string defining the current remapping of the
extended character set for printing. The string can
contain as many characters as you want to remap, with
the first character being the new character 128, the
second being the new character 129, etc. ( Any
character number that exceeds the string length will
not be remapped. ) See the example below.
Empty
string.
line length
A real number specifying the number of characters in a
line for serial printing. This does not affect infrared
printing.
80
line termination
A string specifying the line-termination method for
serial printing. This does not affect infrared printing.
Note that control character 13 is the carriage return and
10 is the line feed.
Control
characters
13 and 10.
Parameters without modified commands can be modified with a program by storing new values in the list
contained in PRTPAR ( use the PUT command ).
Example: If the remapping string were “ABCDEFGH” and the character to be printed had value 131, then the
character actually printed would be “D”, since 131
–128=3 and “A” has the value zero. A character code of 136
or greater would not be remapped since 136
–128=8, which exceeds the length of the string.
REALASSUME
The variable REALASSUME contains a list of variables which the CAS assumes are real values.
STARTED
If it exists, the STARTED variable is evaluated when the command-line editor is evaluated.
 Loading...
Loading...