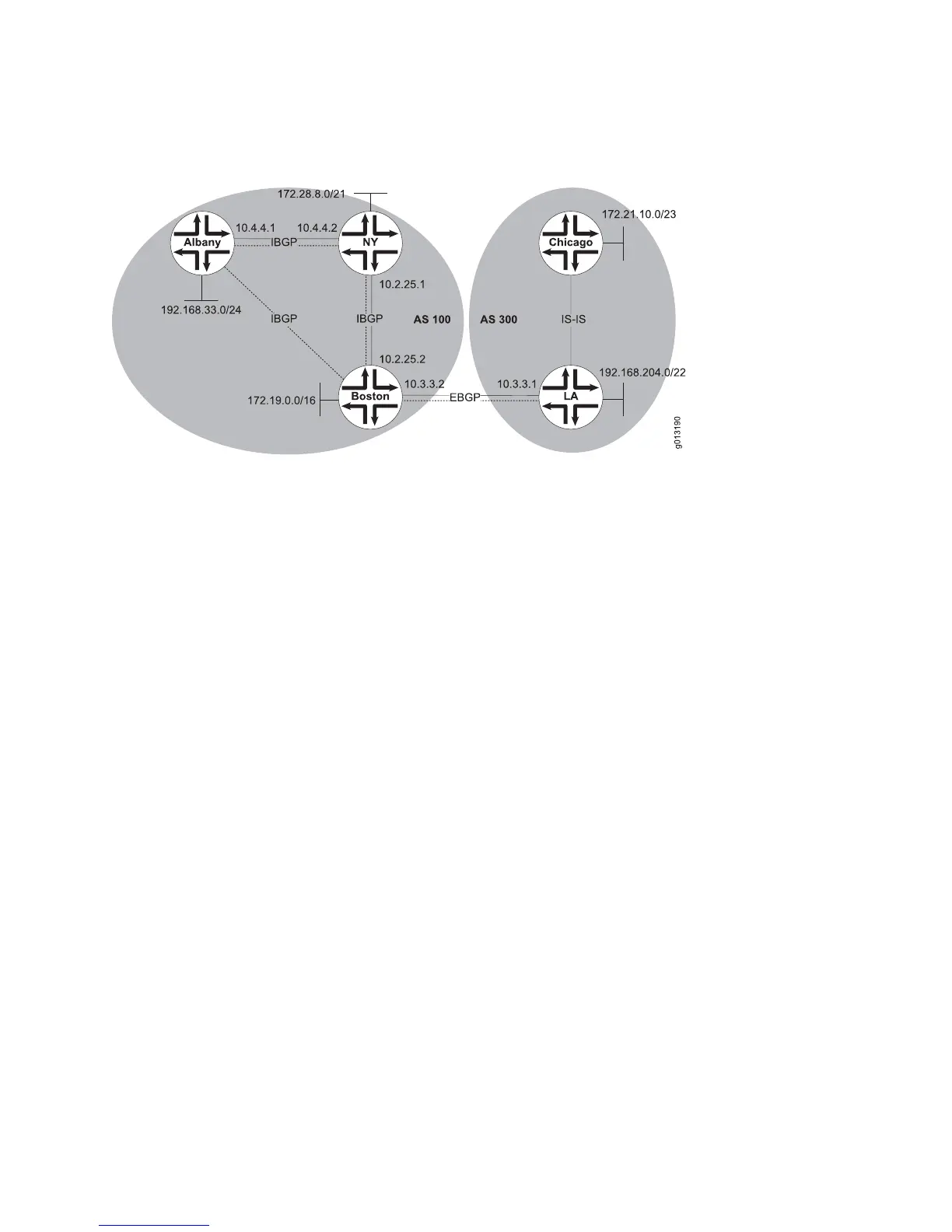
Figure 33: The Origin Attribute
Consider the sample topology shown in Figure 33 on page 118. Because routers Albany
and Boston are not directly connected, they learn the path to each other by means
of an IGP (not illustrated).
The following commands configure router Boston:
host1(config)#ip route 172.31.125.100 255.255.255.252
host1(config)#router bgp 100
host1(config-router)#neighbor 10.2.25.1 remote-as 100
host1(config-router)#neighbor 10.4.4.1 remote-as 100
host1(config-router)#neighbor 10.3.3.1 remote-as 300
host1(config-router)#network 172.19.0.0
host1(config-router)#redistribute static
The following commands configure router NY:
host2(config)#router bgp 100
host2(config-router)#neighbor 10.4.4.1 remote-as 100
host2(config-router)#neighbor 10.2.25.2 remote-as 100
host2(config-router)#network 172.28.8.0 mask 255.255.248.0
The following commands configure router Albany:
host3(config)#router bgp 100
host3(config-router)#neighbor 10.4.4.2 remote-as 100
host3(config-router)#neighbor 10.2.25.2 remote-as 100
host3(config-router)#network 192.168.33.0 mask 255.255.255.0
The following commands configure router LA:
host4(config)#router bgp 300
host4(config-router)#neighbor 10.3.3.2 remote-as 100
host4(config-router)#network 192.168.204.0 mask 255.255.252.0
host4(config-router)#redistribute isis
118 ■ Selecting the Best Path
JUNOSe 11.1.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide

 Loading...
Loading...