MPLS Label Stacking
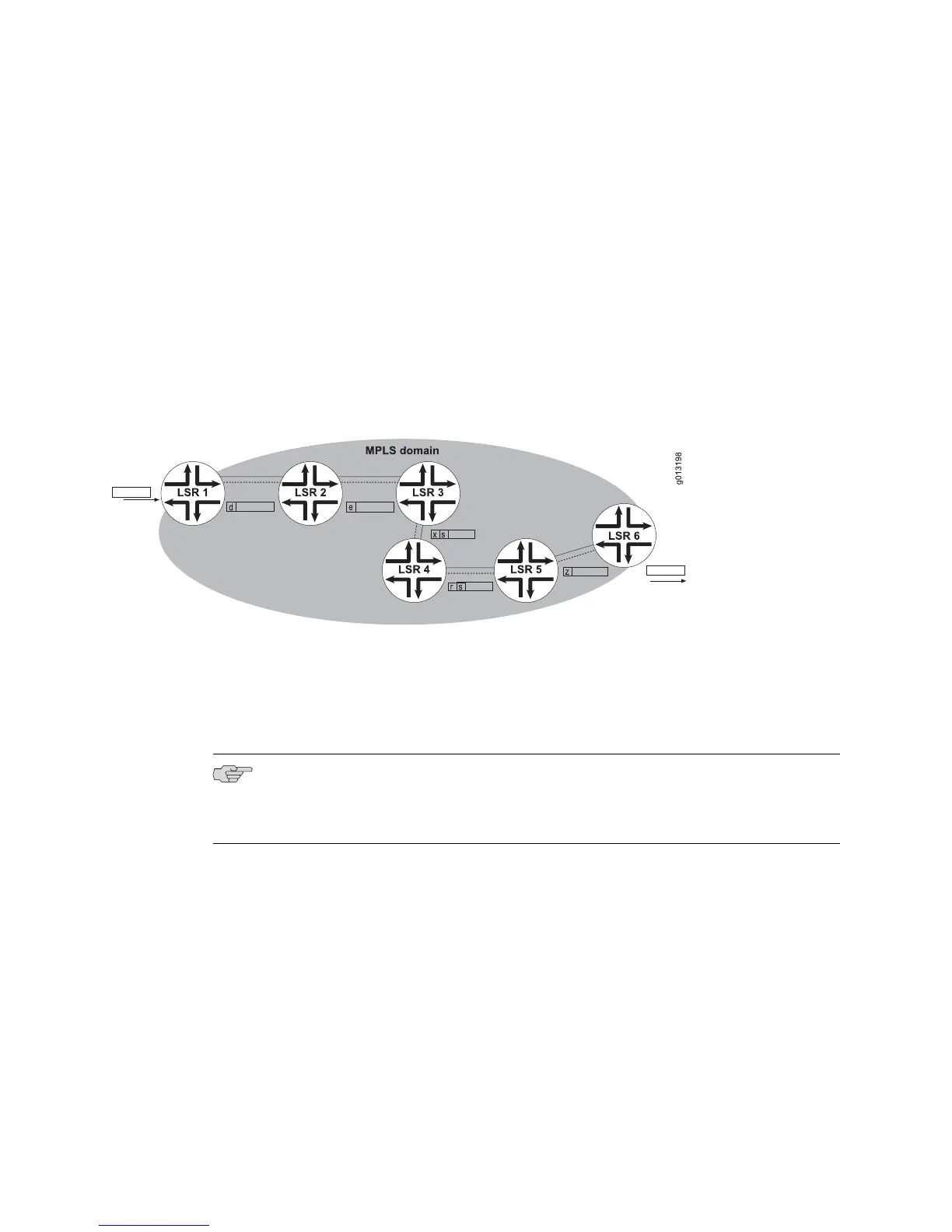
Figure 49 on page 212 shows an LSP that uses label stacking. The ingress node, LSR
1, receives an unlabeled data packet and prepends label d to the packet. LSR 2
receives the packet, removes label d and uses it as an index in its forwarding table
to find the next label, prepending label e to the packet. LSR 3 removes label e and
prepends label s (negotiated with LSR 5) to the packet. LSR 3 pushes label x on top
of label s. LSR 4 pops the top (outermost) label, x, and pushes label r on top of label
s. LSR 5 pops label r, determines that it must pop label s, and pushes label z on the
empty stack. Finally, the egress node, LSR 6, removes label z and determines where
to forward the packet outside the MPLS domain.
Figure 49: Label Stacking
The configuration shown in Figure 49 on page 212 is an example of an LSP within an
LSP (a tunnel within a tunnel). The first LSP consists of LSR 1, LSR 2, LSR 3, LSR 5,
and LSR 6. The second LSP consists of LSR 3, LSR 4, and LSR 5. The two LSPs have
different ingress and egress points. LSR 1 and LSR 6 are LERs. Less obviously, LSR
3 and LSR 5 are also LERs, but for the internal LSP.
NOTE: Label stacking is typically employed for LSR peers that are not directly
connected. Figure 49 on page 212 is a simplified example to illustrate the concept of
label stacking.
MPLS Labels and Label Spaces
MPLS uses labels from either the platform label space or the interface label space. ATM
AAL5 interfaces always use labels from only the interface label space. For every
interface using the interface label space, you must define the range available to the
router for labels in the interface label space. All other interface types always use
labels from only the platform label space. You cannot configure the range for the
platform label space.
The platform label space is a large, single, unconfigurable pool of labels that can be
shared by the platform—all MPLS interfaces on a given virtual router. By contrast,
interface labels enable you to effectively create multiple smaller pools of labels, each
used only by a particular interface. When you configure interface labels, you restrict
only a given interface to a particular range of labels. Other interfaces in that VR can
212 ■ MPLS Label Switching and Packet Forwarding
JUNOSe 11.1.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...