■ local-distance—Administrative distance for local routes in the range 1–255.
The default is 200.
■ The default value is 20 for external routes, 200 for internal route, and 200 for
local routes.
■ The new distance is applied to all routes that are subsequently placed in the IP
routing table. To apply the new distance to routes that are already present in the
IP routing table, you must use the clear ip routes * command to reinstall BGP
routes in the IP routing table.
■ Use the no version to return the distances to their default values, 20, 200, and
200.
■ See distance bgp.
Example 1 Routes learned from other sources can be preferred to routes learned by means of
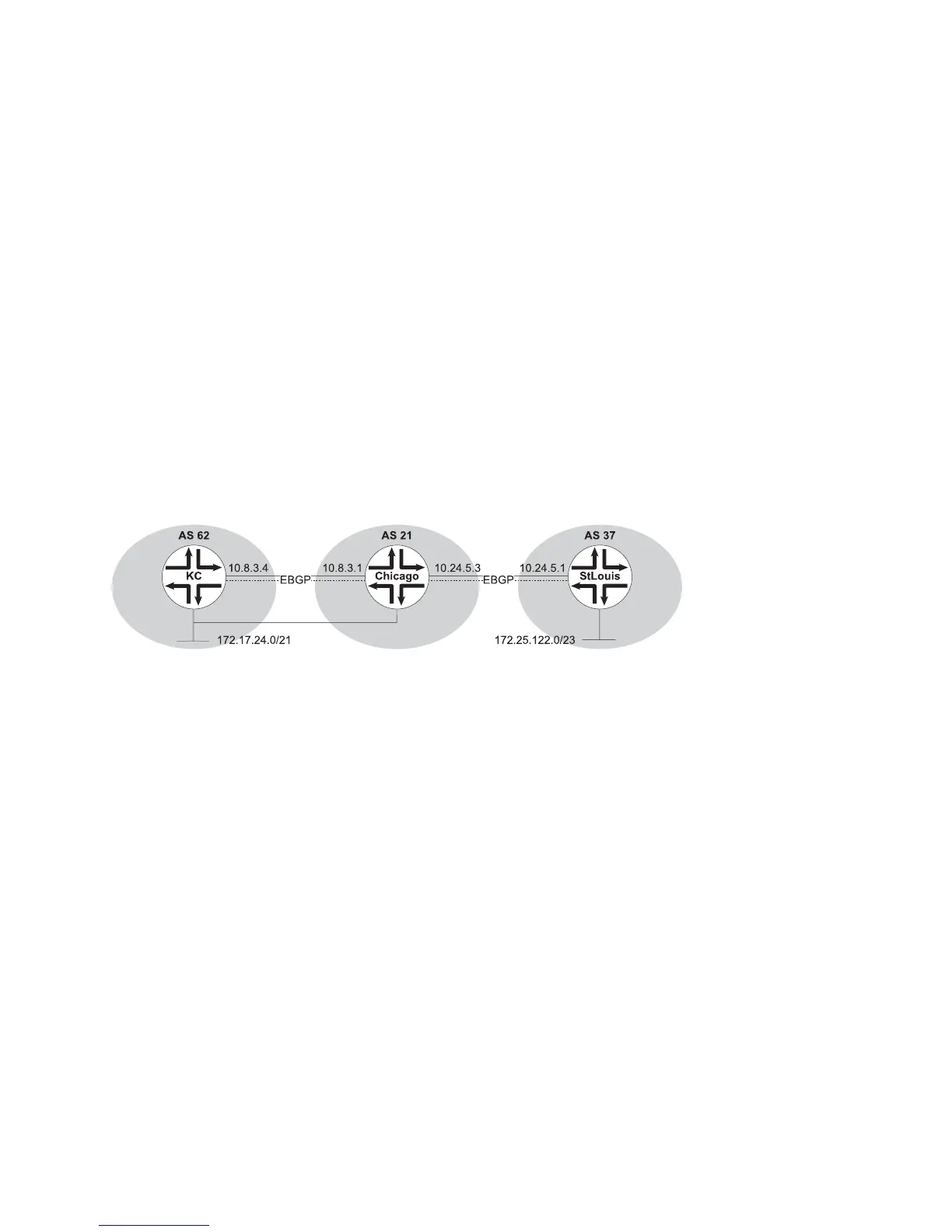
BGP. Consider the network structure shown in Figure 38 on page 138.
Figure 38: Administrative Distances
Suppose router KC originates 172.17.24.0/21 and advertises the route to router
Chicago by means of EBGP. Both router KC and router Chicago are directly connected
to the network represented by 172.17.24.0/21. If you issue the show ip route
command on router Chicago, the BGP route does not appear. Instead, only the
connected route is displayed.
Both routes are in the IP routing table, but the show ip route command displays
only the best route. (Use the show ip route all command to display all best routes;
in this case the BGP route and the connected route.) Connected routes have a default
distance of 0. Routes learned by means of EBGP have a default value of 20. The
connected route is a better route than the EBGP route and appears in the command
display.
In practice, if two BGP peers are connected to the same network, both peers should
originate the route.
Example 2 Consider the network structure shown in Figure 39 on page 139. Router Chicago
originates prefix 192.168.11.0/24 and advertises it by means of EBGP to router
Albany. Router Albany advertises the route to router Boston by means of IBGP.
Router Albany also redistributes the route into the interior gateway protocol RIP,
which informs router NY of the route. Router NY propagates the route to router
Boston by means of RIP, from which it is injected into BGP.
138 ■ Interactions Between BGP and IGPs
JUNOSe 11.1.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...