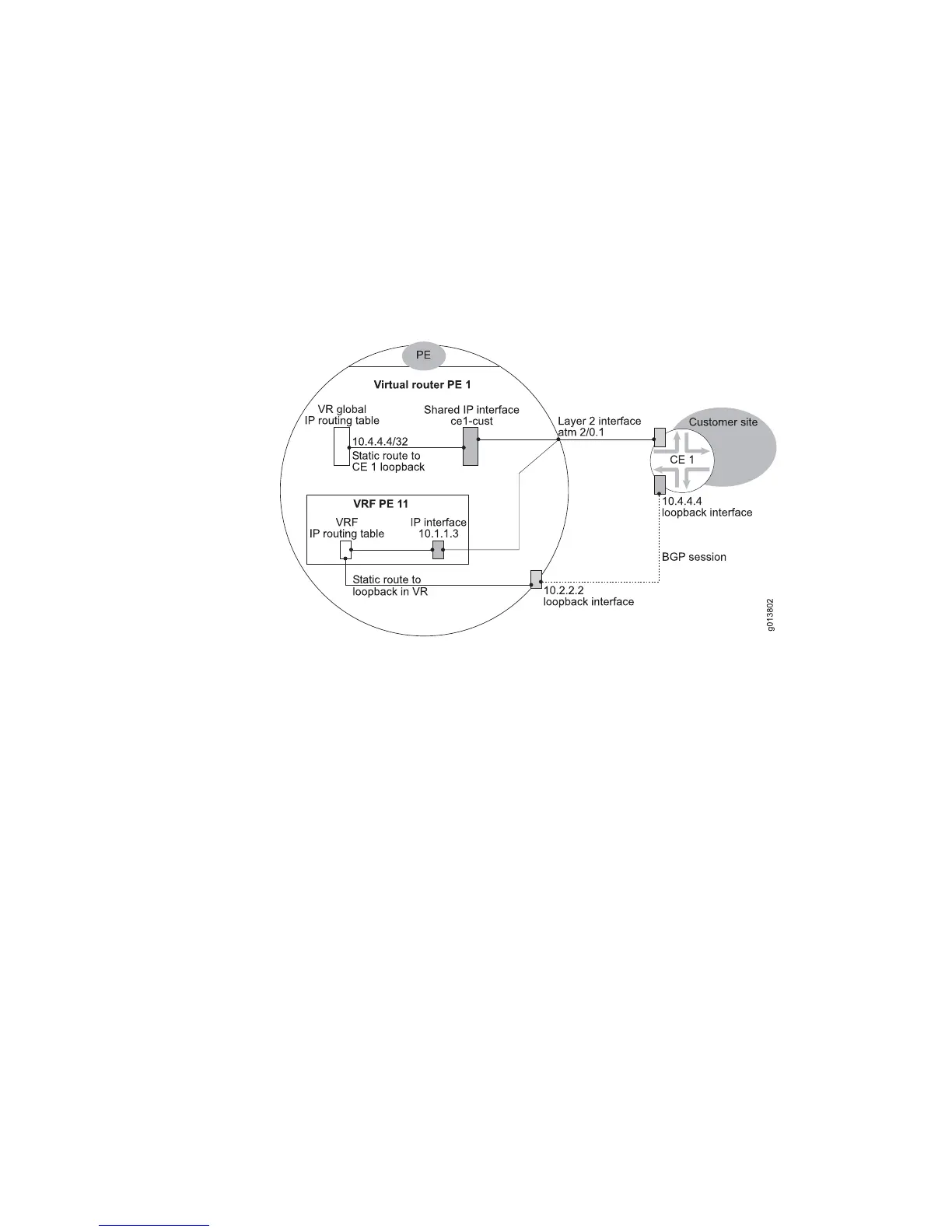
interface in the parent VR that is used for BGP peering with the CE router. To achieve
this configuration, you must do both of the following:
1. In the parent VR, create a shared IP interface for the PE-CE interface and point
a static route to the loopback of the CE router to the shared interface.
2. Use a global import map in the VRF to import into the VRF the route to the
loopback interface in the parent VR.
Figure 104: BGP Session Between CE Router and Parent VR
The following commands configure a shared IP interface in the parent VR and point
a static route for the loopback in the CE router to it:
host1(config)#virtual-router pe1
host1:pe1(config)#interface ip ce1-cust
host1:pe1(config-if)#ip share-interface atm2/0.1
host1:pe1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.3 255.255.255.255
host1:pe1(config-if)#exit
host1:pe1(config)#ip route 10.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 ip ce1-cust
The following commands make the loopback in the parent VR reachable from the
VRF by means of a global import map:
host1(config)#virtual-router pe1
host1:pe1(config)#prefix-list VRloop permit 10.2.2.2/32
host1:pe1(config)#route-map globimaploop
host1:pe1(config-route-map)#match ip address prefix-list VRloop
host1:pe1(config-route-map)#exit
host1:pe1(config)#ip vrf pe11
host1:pe1(config-vrf)#rd 100:1
host1:pe1(config-vrf)#route-target both 100:1
host1:pe1(config-vrf)#global import map globimaploop
The following commands create a BGP session between the CE router and the parent
VR.
466 ■ Providing Internet Access to and from VPNs
JUNOSe 11.1.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide

 Loading...
Loading...