Coulombs Measurements 5-7
Zero check hop and auto discharge hop
Using the zero check feature (going from the enabled state to the disabled state) causes a sud-
den change in the charge reading and is known as zero check hop. This sudden change in charge
also occurs when the auto discharge feature resets the charge reading to zero. This hop in charge
can be eliminated by taking a reading the instant zero check is disabled or when an auto dis-
charge occurs, and subtracting it from all subsequent readings. A better way to deal with this hop
in charge is to enable Rel immediately after zero check is disabled or when auto discharge resets
the charge reading. This action nulls out the charge reading caused by the hop.
Application
Capacitance measurements
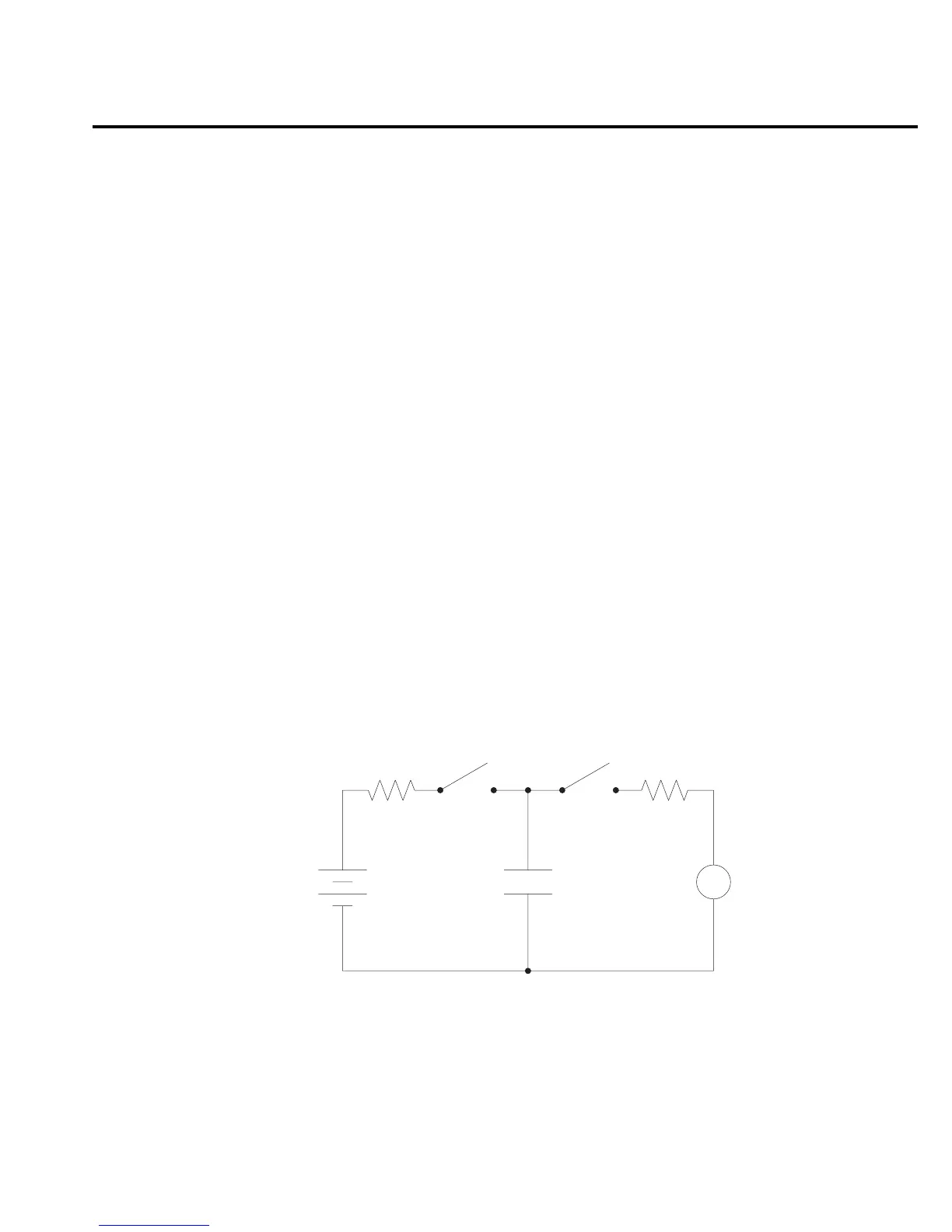
Figure 5-2 shows a general test circuit to measure a capacitor (C). Resistors R1 and R2 are
used to limit current. Select a value for R1 that will limit current to ≤100mA, and select a value
for R2 that will limit current to ≤20mA.
When switch S1 is closed, the Keithley Model 230 voltage source charges the capacitor. After
waiting sufficient time for the capacitor to fully charge, open switch S1 and close switch S2 to
measure the charge. The capacitance can now be calculated as follows:
C = Q/V
where; C is the capacitance (in farads)
Q is the measured charge (in coulombs)
V is the voltage used to charge the capacitor
230
V-Source
R1 R2
S1 S2
Q
6514
C
C = Q/V
Figure 5-2
Measuring
capacitors

 Loading...
Loading...











