11.2 CPU Module Operating Modes
11.2.1 Operating Modes
There are two operating modes. They can be used to control a user program and all tasks.
STOP mode: A program is not executed in this mode. Users can download a module table, initialize CPU
configuration and other setting, download a program, check a program, and force a bit ON/OFF.
RUN mode: A program is executed in this mode. Users can NOT download a module table, and initialize CPU
configuration and other setting.
11.2.2 Status and Operation under Different Operating Modes
The following table lists the status and operation states for RUN and STOP modes.
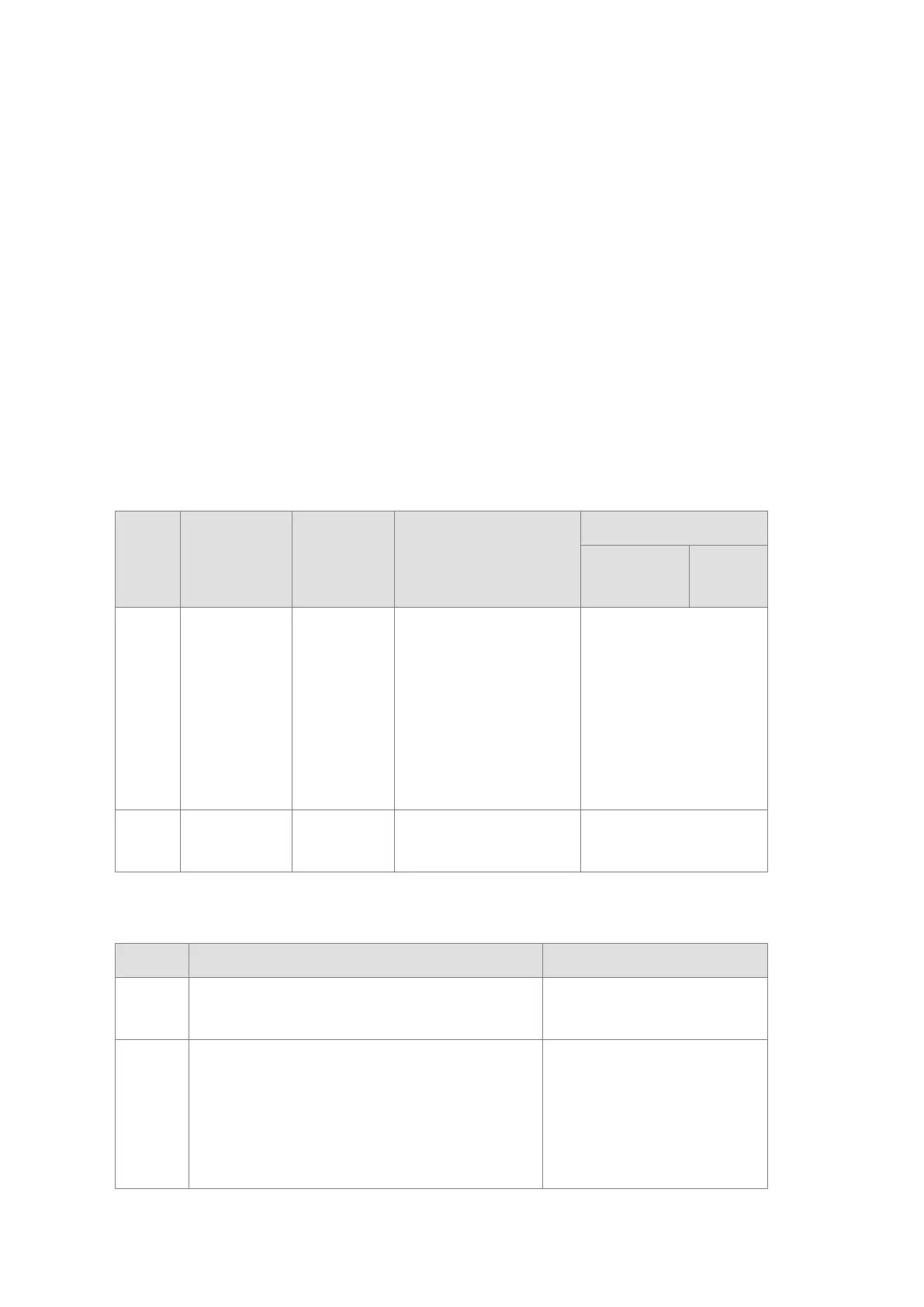
Basic operation
CPU
mode
Program
I/O
refreshing
External output
Program memory
Non-latched
area
Latched
area
STOP
The execution
of the program
stops.
I/O refreshing
executes.
OFF. If you set the I/O
module so that the final
state of the external output
on the I/O module is
retained, the final state of
the external output on the
I/O module is retained.
The data in the program
memories is retained.
RUN
The program
executes.
executes.
The program controls the
external output.
The program controls the
program memories.
Relationship between the operating modes and tasks
Mode Loop task Interrupt task
STOP Execution of a loop tasks stops.
Execution of an interrupt task
stops.
RUN
The tasks that have not been executed are in the
HALT state.
If a task is active, or the instruction TKON is
executed, the task executes.
If a task is not active, or the instruction TKOFF
If the condition of the interrupt is
met, the interrupt task executes.
Send Quote Requests to info@automatedpt.com
Call +1(800)985-6929 To Order or Order Online At Deltaacdrives.com
Send Quote Requests to info@automatedpt.com
Call +1(800)985-6929 To Order or Order Online At Deltaacdrives.com

 Loading...
Loading...