Model 6220/6221 Reference Manual Delta, Pulse Delta, and Differential Conductance 5-51
Return to Section 5 topics
Differential Conductance
Differential measurements can be used to study the individual slopes of an I-V (or
V-I) curve. By applying a known differential current (dI) to a device, differential volt-
age (dV) measurements can be performed. With dI and dV known, differential
conductance (dG) (and differential resistance dR) can be calculated.
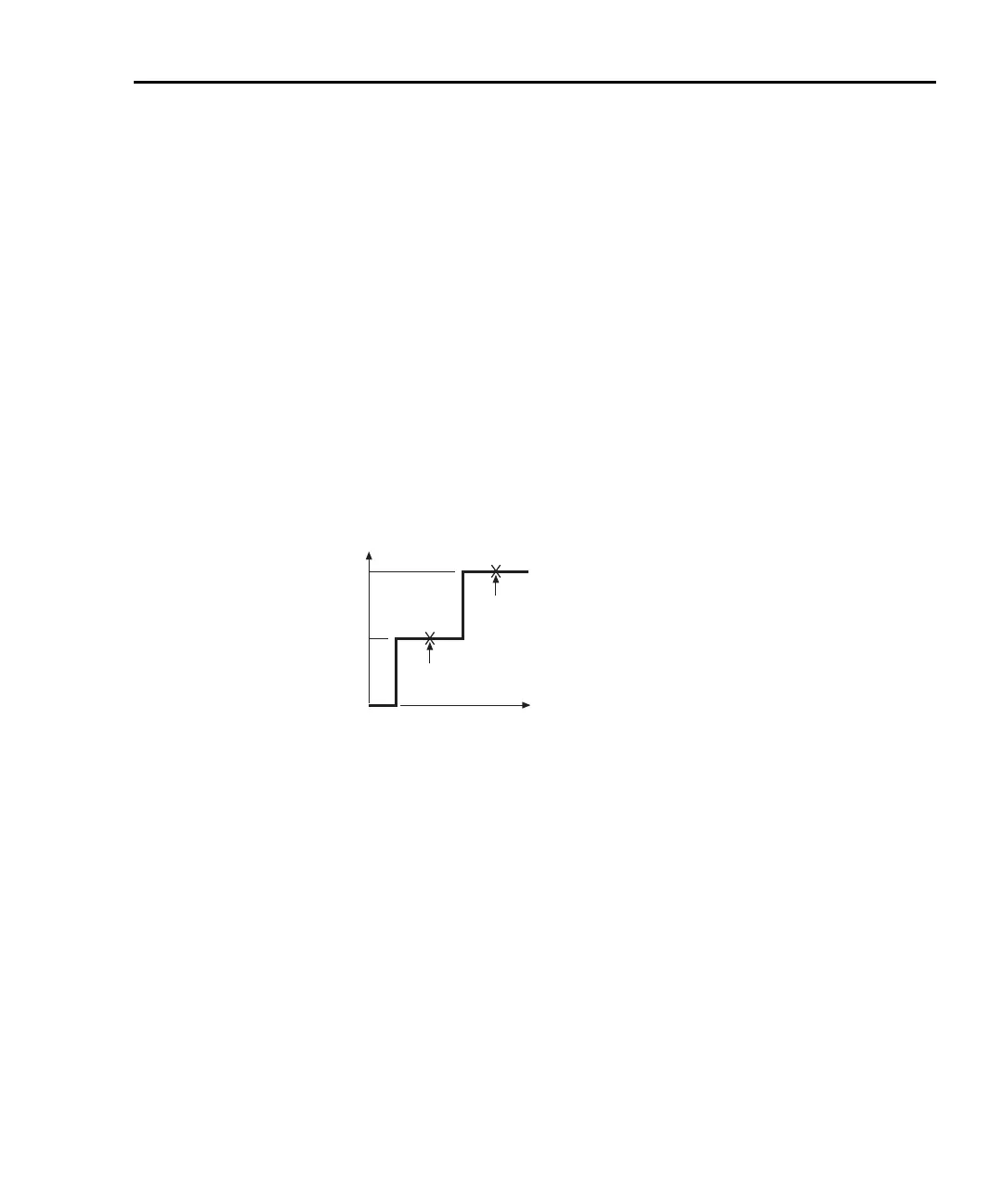
Basic measurement process
The basic process for differential voltage measurements is shown by the example
in Figure 5-13. As shown, two current steps are applied to a device and voltage is
measured at each step. From these two source-measure points (A and B), differ-
ential current (dI), differential voltage (dV), differential conductance (dG), and dif-
ferential resistance (dR) can be calculated as shown in the illustration. These
measurements examine the straight-line slope between points A and B.
Figure 5-13
Basic differential measurements
Model 622x measurement process
When using the Model 2182/2182A with the Model 622x, a more sophisticated
process is used to perform differential measurements. The delta measurement
process is used to eliminate the effects of thermal EMFs, and a 3-point moving
average calculation algorithm is used to provide more accurate readings.
This differential measurement process is shown in Figure 5-14. The Model 622x is
configured to output a stepped sweep with a specified Delta, which is the differen-
tial current (dI). As shown in the illustration, Delta is added to and subtracted from
each subsequent step in the sweep. The solid line in Figure 5-14 is the actual out-
put of the Model 622x.
As shown, each differential voltage calculation (dV Calc) uses the three previous
Model 2182/2182A A/D measurement conversions. Keep in mind that dI (Delta) is
the same for all calc points. With dI known and dV calculated, the Model 622x can
also calculate, display, and store the differential conductance (dG) or differential
resistance (dR) for each calc point.
0µA
20µA
40µA
VMEAS
(20µV)
ISOURCE
time
dI = I
B
I
A
= 40µA 20µA
= 20µA
dV = V
B
V
A
= 60µV 20µV
= 40µV
A
V
MEAS
(60µV)
B
dG = dI/dV
= 20µA / 40µV
= 0.5S
dR = dV/dI
= 40µV / 20µA
= 2W
Test Equipment Depot - 800.517.8431 - 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176 - TestEquipmentDepot.com

 Loading...
Loading...