GV 640 Service Manual 35
For internal use only
6.1.3 Zeolite properties
Zeolite is the term for a group of minerals with a crystalline structure able to absorb (gather and retain
on the surface) and to desorb (release) molecules.
The name zeolite is from the Greek zeein for “boil” and lithos for “stone”.
The material heats up when it absorbs hydrogen molecules. This is why it bears the byname “boiling
stone”. Zeolites are crystalline silicate minerals which occur naturally in numerous compositions, but
which can also be produced synthetically. They comprise a microporous solid structure. Depending on
the type of structure, a structure made up of pores and/or channels of the same shape in which the
materials are absorbed. The pores can only absorb materials with molecules whose dynamic diameter
is smaller than that of the pore openings of the zeolite structure. The arrangement of cavities and chan-
nels in the material results in an extremely large internal surface. This may cover > 1000 m² for each
gramme of zeolite.
Zeolite minerals can store an amount of water of up to around 40% of their dry weight, depending on
the type of mineral. Heating releases the absorbed water again.
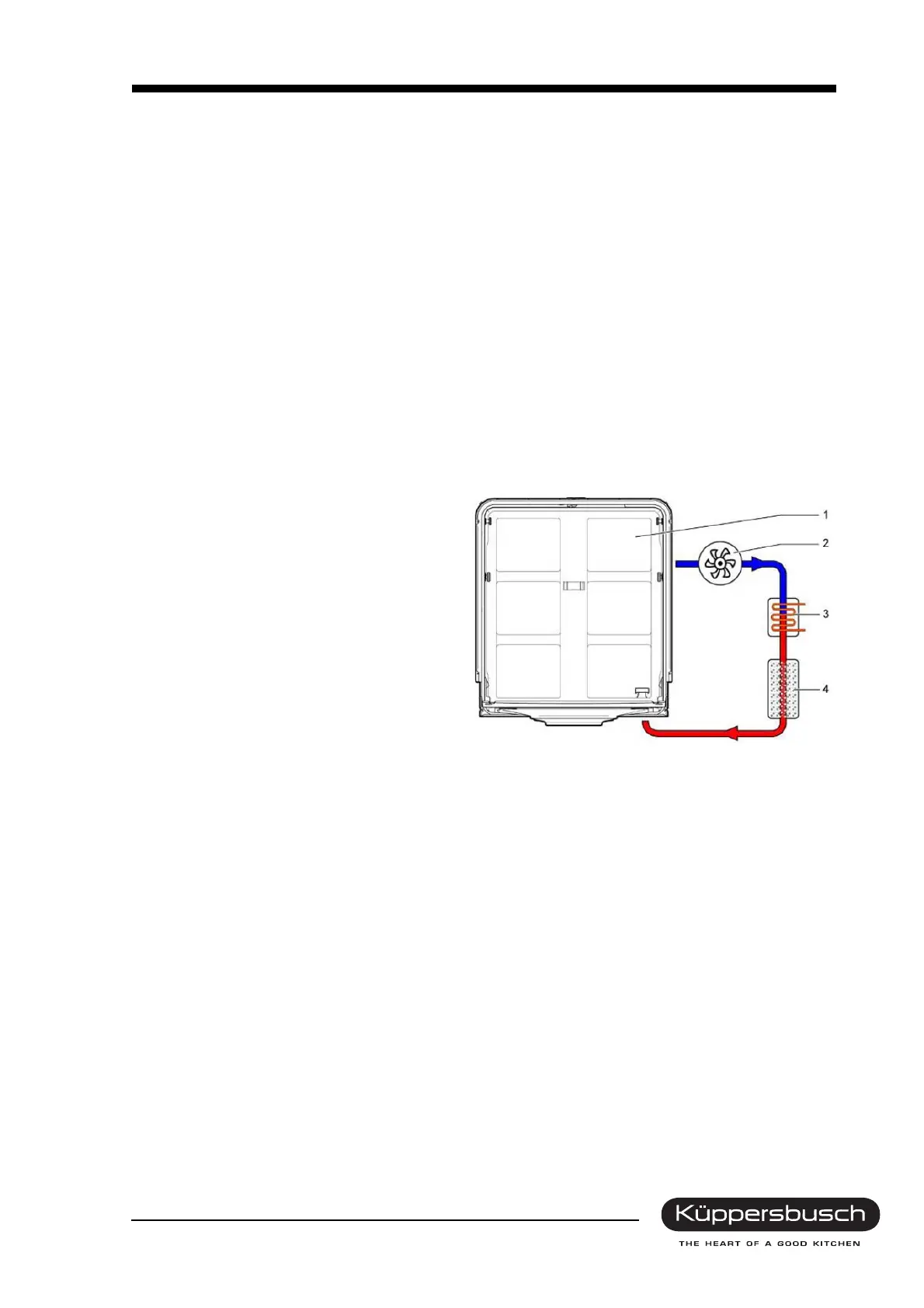
6.1.4 Cleaning phase and desorption
Zeolite needs to be heated up in order to ena-
ble the system to absorb moisture. This is car-
ried out during the cleaning phase. With the
help of the fan, air is lead out of the interior of
the container, heated up by a heating element
and lead through the container filled with zeo-
lite granulate material.
The zeolite releases the stored moisture and is
then in a position to absorb moisture again in
the next drying phase. This process is called
desorption (releasing the stored material).
Warm, humid air is lead back into the interior
and supports the heating up of the dishes.
The desorption process will have been com-
pleted when a temperature of 40°C has been
reached in the rinsing cavity. Since the circula-
tion pump is activated, identification can be
carried out by the heater NTCs. This process is
repeated in each rinsing cycle in which the ze-
olite heater is activated.
1 Rinsing cavity
2Fan
3 Hot-air heating system
4 Zeolite container

 Loading...
Loading...